Imaging Sci Dent.
2019 Sep;49(3):241-249. 10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.241.
Maxillary ameloblastoma in an 8-year-old child: A case report with a review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Department of Diagnostic Sciences, Rutgers School of Dental Medicine, NJ, USA. sangeetha7455@gmail.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rutgers School of Dental Medicine, NJ, USA.
- 3Department of Pathology, Immunology and Laboratory Medicine, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, NJ, USA.
- KMID: 2458374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.241
Abstract
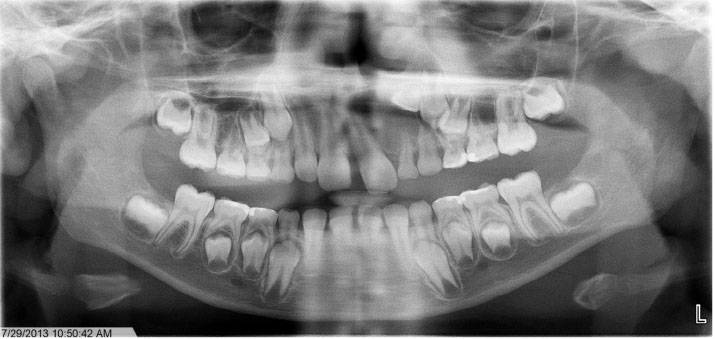
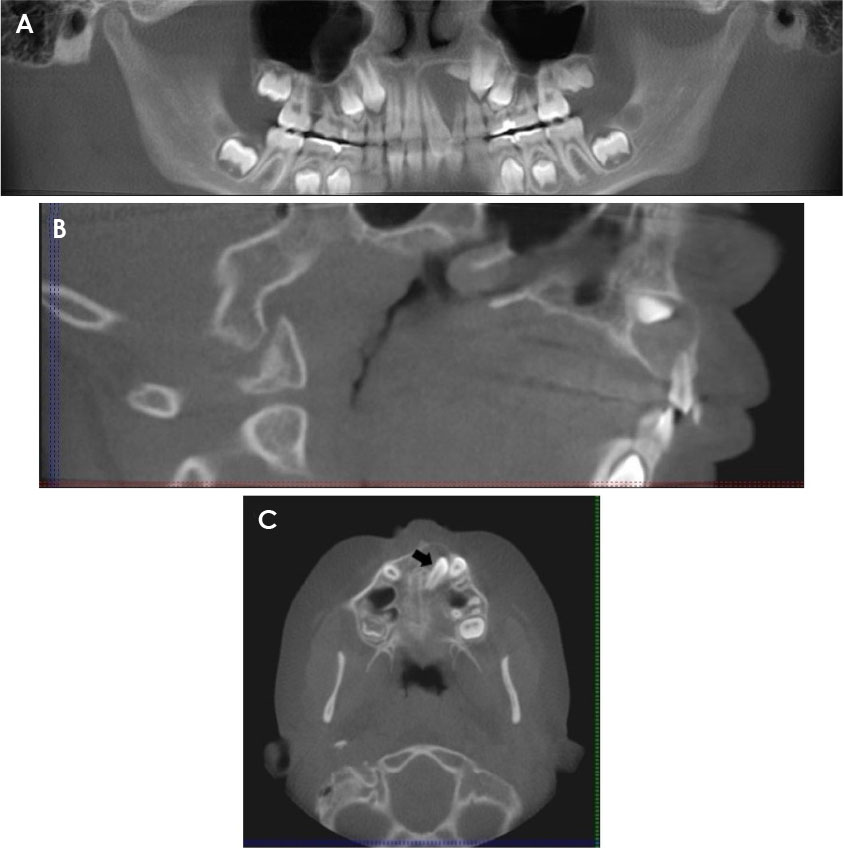
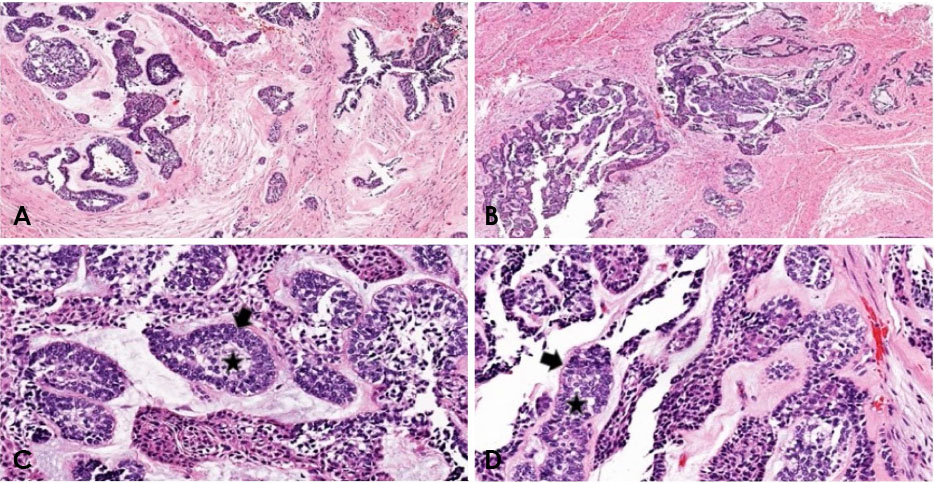
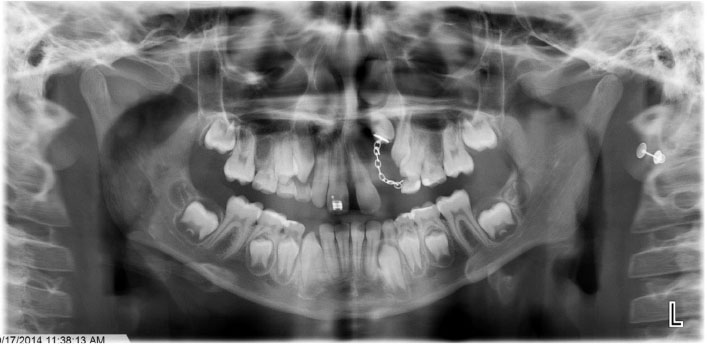
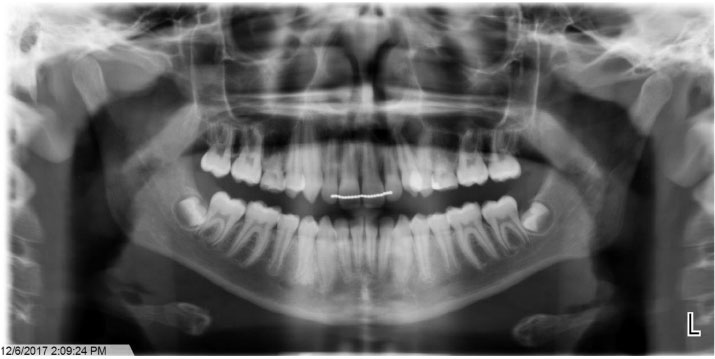
- Ameloblastoma is a benign locally invasive tumor with a high tendency to recur. It is considered rare in the pediatric population, with most cases diagnosed in the third to fifth decades of life. Approximately 80% of ameloblastomas occur in the molar and ramus region of the mandible, while 20% of cases occur in the maxillary posterior region. This report presents a case of plexiform ameloblastoma in an uncommon location in an 8-year-old child. The lesion was initially thought to be a dentigerous cyst, based on its location and radiographic appearance. The clinical and radiographic features, histopathology, and treatment of solid, plexiform, maxillary ameloblastoma are reviewed, with an added emphasis on a literature review of ameloblastoma in children. This report emphasize the importance of long-term follow-up, since recurrence may occur many years after initial tumor removal.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders/Elsevier;2009.2. Zhang J, Gu Z, Jiang L, Zhao J, Tian M, Zhou J, et al. Ameloblastoma in children and adolescents. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 48:549–554.
Article3. Kreppel M, Zöller J. Ameloblastoma - clinical, radiological, and therapeutic findings. Oral Dis. 2018; 24:63–66.4. Bansal S, Desai RS, Shirsat P, Prasad P, Karjodkar F, Andrade N. The occurrence and pattern of ameloblastoma in children and adolescents: an Indian institutional study of 41 years and review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 44:725–731.
Article5. Arotiba GT, Ladeinde AL, Arotiba JT, Ajike SO, Ugboko VI, Ajayi O. Ameloblastoma in Nigerian children and adolescents: a review of 79 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:747–751.
Article6. Butt FM, Guthua SW, Awange DA, Dimba EA, Macigo FG. The pattern and occurrence of ameloblastoma in adolescents treated at a university teaching hospital, in Kenya: a 13-year study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012; 40:e39–e45.
Article7. Giraddi GB, Arora K, Saifi AM. Ameloblastoma: a retrospective analysis of 31 cases. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2017; 7:206–211.
Article8. Kashyap B, Reddy PS, Desai RS. Plexiform ameloblastoma mimicking a periapical lesion: a diagnostic dilemma. J Conserv Dent. 2012; 15:84–86.
Article9. Singer SR, Mupparapu M, Philipone E. Cone beam computed tomography findings in a case of plexiform ameloblastoma. Quintessence Int. 2009; 40:627–630.10. Castro-Silva II, Israel MS, Lima GS, de Queiroz Chaves Lourenço S. Difficulties in the diagnosis of plexiform ameloblastoma. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 16:115–118.
Article11. Payne SJ, Albert T, Lighthall JG. Management of ameloblastoma in the pediatric population. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 26:168–174.
Article12. Takahashi K, Miyauchi K, Sato K. Treatment of ameloblastoma in children. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998; 36:453–456.
Article13. Al-Khateeb T, Ababneh KT. Ameloblastoma in young Jordanians: a review of the clinicopathologic features and treatment of 10 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:13–18.
Article14. Chukwuneke FN, Anyanechi CE, Akpeh JO, Chukwuka A, Ekwueme OC. Clinical characteristics and presentation of ameloblastomas: an 8-year retrospective study of 240 cases in Eastern Nigeria. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 54:384–387.
Article15. Huang IY, Lai ST, Chen CH, Chen CM, Wu CW, Shen YH. Surgical management of ameloblastoma in children. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 104:478–485.
Article16. Pogrel MA, Montes DM. Is there a role for enucleation in the management of ameloblastoma? Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38:807–812.
Article17. Iordanidis S, Makos C, Dimitrakopoulos J, Kariki H. Ameloblastoma of the maxilla. Case report. Aust Dent J. 1999; 44:51–55.
Article18. McClary AC, West RB, McClary AC, Pollack JR, Fischbein NJ, Holsinger CF, et al. Ameloblastoma: a clinical review and trends in management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; 273:1649–1661.
Article