Ann Dermatol.
2019 Oct;31(5):591-593. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.5.591.
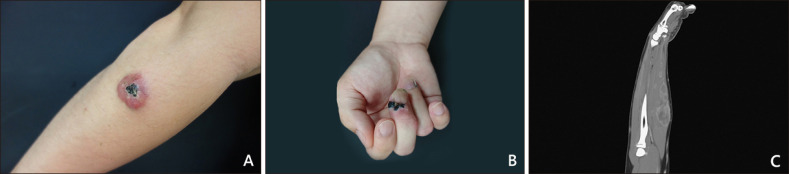
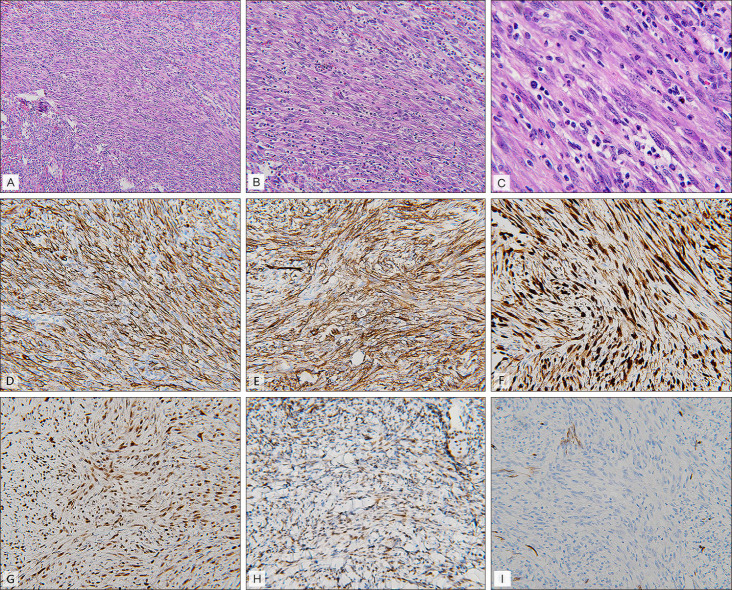
Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma in a 30-Year-Old Man: A Rare Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan. chevy0204@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 3Department of Pathology, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
- KMID: 2456242
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.5.591
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Raftopoulos E, Royer M, Warren M, Zhao J, Rush W. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018; 40:597–601. PMID: 29406432.
Article2. Horan NA, DiMaio DJ. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma. Cutis. 2017; 100:E13–E16.3. van IJzendoorn DGP, Sleijfer S, Gelderblom H, Eskens FALM, van Leenders GJLH, Szuhai K, et al. Telatinib is an effective targeted therapy for pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:2678–2687. PMID: 29511030.
Article4. Gabor KM, Sapi Z, Tiszlavicz LG, Fige A, Bereczki C, Bartyik K. Sirolimus therapy in the treatment of pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018; 65:e26781.
Article5. Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, Saus C, Kutzner H. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcomalike (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013; 149:459–465. PMID: 23715533.