Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2019 Aug;23(3):291-294. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.3.291.
Laparoscopic pancreatic neck transection and double pancreatico-jejunostomy, an alternative surgical approach to chronic pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Makati City Hospital, Makati City, Philippines.
- 2Division of HBP Surgery, Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cmkang@yuhs.ac
- 3Pancreatobiliary Cancer Center, Yonsei Cancer Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2456030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.3.291
Abstract
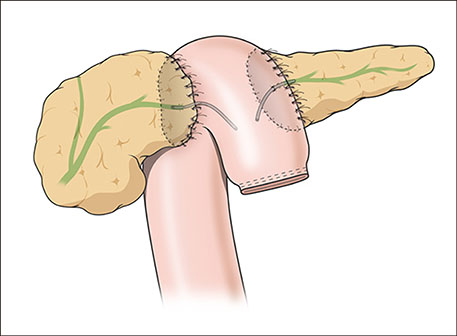
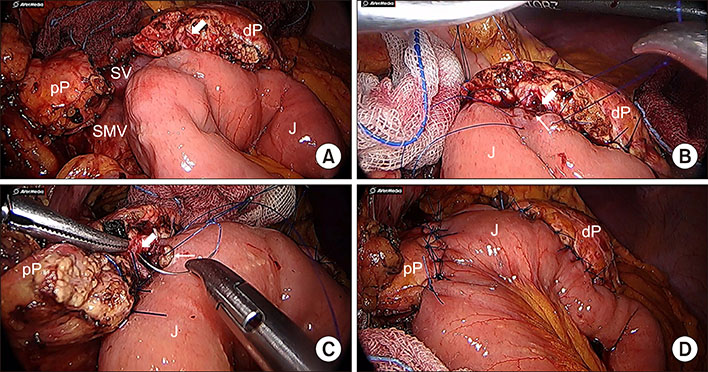
- Chronic pancreatitis is a benign inflammatory process that results symptoms pertaining to loss of endocrine and exocrine function. Pain poses a great challenge in the management of CP and intractable pain represents the main indication for surgical intervention. Surgical options for CP ranges from pancreatic resection to pure drainage procedures. Herein, we present the case of 68 year-old female with recurrent abdominal pain due to chronic pancreatitis, who underwent successful laparoscopic pancreatic neck transection and double pancreatico-jejunostomy (duct-to-mucosa). Pre-operative imaging revealed a uniformly dilated pancreatic duct with encrusted pancreatic stone in the pancreatic head near the ampulla of Vater, with no inflammatory mass. Pre-operative laboratory work-ups were all normal. Pancreas texture was noted to be intermediate to soft. During pancreatic neck transection, there was spontaneous deviation of distal stump laterally leaving an ample space to accommodate jejunal loop. PD measured 8 mm. The standard duct to mucosa double layer simple interrupted suture was used for PJ anastomosis. There were no significant intra-operative events. No transfusion was required. Total operation time was 297 minutes, and it took 129 minutes for laparoscopic PJ completion. Immediate post-operative course was unremarkable. This case suggests laparoscopic double PJ can be an alternative surgical approach to reduce the pancreatic duct pressure in chronic pancreatitis. Based on accumulating experiences, long-term outcome also needs to be investigated to address potential role of this technique.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strobel O, Büchler MW, Werner J. Surgical therapy of chronic pancreatitis: indications, techniques and results. Int J Surg. 2009; 7:305–312.
Article2. Perwaiz A, Singh A, Chaudhary A. Surgery for chronic pancreatitis. Indian J Surg. 2012; 74:47–54.
Article3. Plagemann S, Welte M, Izbicki JR, Bachmann K. Surgical treatment for chronic pancreatitis: past, present, and future. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017; 2017:8418372.
Article4. Lin JW, Cameron JL, Yeo CJ, Riall TS, Lillemoe KD. Risk factors and outcomes in postpancreaticoduodenectomy pancreaticocutaneous fistula. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004; 8:951–959.
Article5. Wellner UF, Kayser G, Lapshyn H, Sick O, Makowiec F, Höppner J, et al. A simple scoring system based on clinical factors related to pancreatic texture predicts postoperative pancreatic fistula preoperatively. HPB (Oxford). 2010; 12:696–702.
Article6. Lew D, Afghani E, Pandol S. Chronic pancreatitis: current status and challenges for prevention and treatment. Dig Dis Sci. 2017; 62:1702–1712.
Article7. D'Haese JG, Ceyhan GO, Demir IE, Tieftrunk E, Friess H. Treatment options in painful chronic pancreatitis: a systematic review. HPB (Oxford). 2014; 16:512–521.8. Jarnagin WR. Blumgart's surgery of the liver, biliary tract and pancreas. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2017. p. 2120.9. Ahmed Ali U, Pahlplatz JM, Nealon WH, van Goor H, Gooszen HG, Boermeester MA. Endoscopic or surgical intervention for painful obstructive chronic pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 1:CD007884.
Article10. Cahen DL, Gouma DJ, Laramée P, Nio Y, Rauws EA, Boermeester MA, et al. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic vs surgical drainage of the pancreatic duct in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:1690–1695.
Article11. Fragulidis GP, Vezakis A, Dellaportas D, Sotirova I, Koutoulidis V, Kontis E, et al. “Puestow modified procedure in the era of advanced endoscopic interventions for the management of chronic lithiasic pancreatitis. A two cases report”. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 15:85–88.
Article12. Warshaw AL, Popp JW Jr, Schapiro RH. Long-term patency, pancreatic function, and pain relief after lateral pancreaticojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1980; 79:289–293.
Article13. Nealon WH, Thompson JC. Progressive loss of pancreatic function in chronic pancreatitis is delayed by main pancreatic duct decompression. A longitudinal prospective analysis of the modified puestow procedure. Ann Surg. 1993; 217:458–466. discussion 466–468.
Article14. Ahmed Ali U, Nieuwenhuijs VB, van Eijck CH, Gooszen HG, van Dam RM, Busch OR, et al. ; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. Clinical outcome in relation to timing of surgery in chronic pancreatitis: a nomogram to predict pain relief. Arch Surg. 2012; 147:925–932.
Article15. Partington PF, Rochelle RE. Modified Puestow procedure for retrograde drainage of the pancreatic duct. Ann Surg. 1960; 152:1037–1043.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fish-Mouth Closure of the Pancreatic Stump and Parachuting of the Pancreatic End with Double U Trans-Pancreatic Sutures for Pancreatico-Jejunostomy
- A Case of a Pancreaticogastric Fistula Following Acute Pancreatitis
- A Case of Pancreatico-gastric Fistulaafter Chronic Relapsing Pancreatitis
- Modified Puestow Procedure for Chronic Pancreatitis in a Child Due to Annular Pancreas and Duodenal Duplication: A Case Report
- Surgical Treatment of Pancreatitis