Acute Crit Care.
2019 Feb;34(1):92-94. 10.4266/acc.2018.00073.
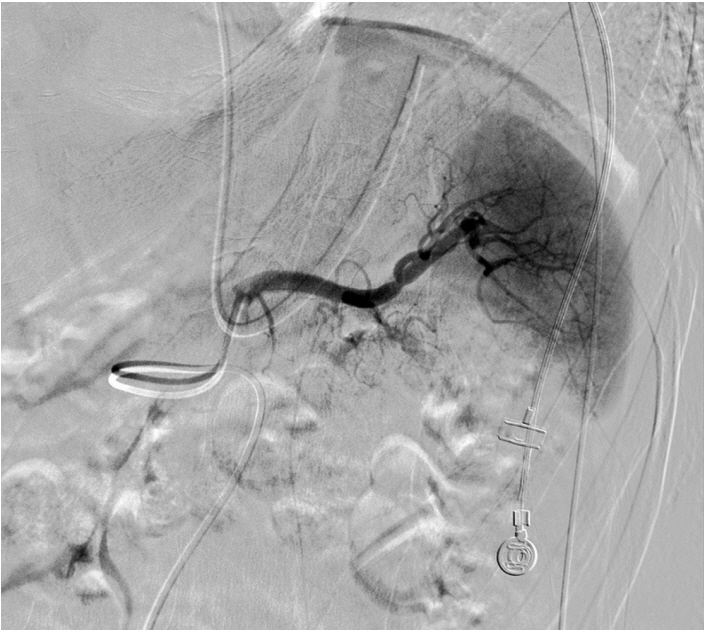
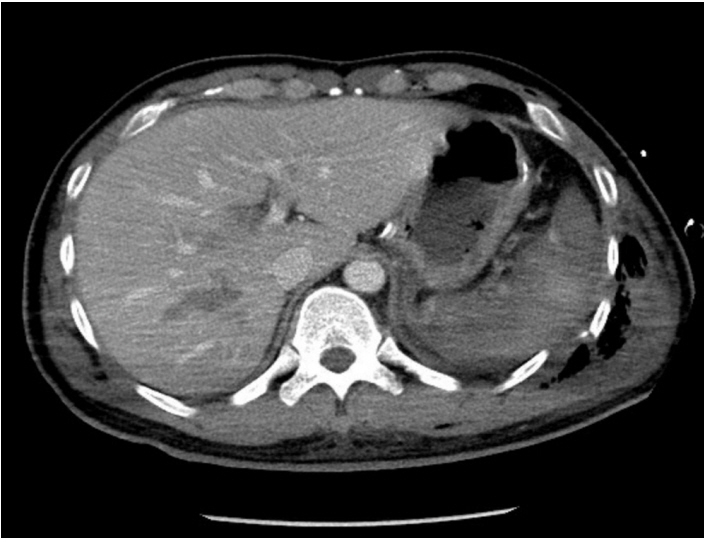
Splenic Liquefaction after Splenic Artery Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Trauma Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. kbhname@gmail.com
- KMID: 2449386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2018.00073
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crichton JC, Naidoo K, Yet B, Brundage SI, Perkins Z. The role of splenic angioembolization as an adjunct to nonoperative management of blunt splenic injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017; 83:934–43.
Article2. Li ES, Mu JX, Ji SM, Li XM, Xu LB, Chai TC, et al. Total splenic artery embolization for splenic artery aneurysms in patients with normal spleen. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:555–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Splenic artery embolization for trauma: a narrative review
- Splenic Arterial Embolization for Trauma and Beyond: A Case Series
- Spontaneous Splenic Rupture in a Vivax Malaria Case Treated with Transcatheter Coil Embolization of the Splenic Artery
- Successful Management of Splenic Artery Steal Syndrome after Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Splenic rupture following transcatheter arterial embolization of splenic artery pseudoaneurysm caused by acute pancreatitis