Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 Jul;11(4):529-537. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.4.529.
Underuse of Epinephrine for Pediatric Anaphylaxis Victims in the Emergency Department: A Population-based Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. matewoos@gmail.com
- KMID: 2448755
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.4.529
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Epinephrine is a key drug for treating anaphylaxis; however, its underuse is still a significant issue worldwide. The objective of this study was to compare epinephrine use between pediatric and adult patients who were treated with anaphylaxis in the emergency department (ED).
METHODS
The data were retrieved from the National Sample Cohort of South Korea, which contains claim data from the National Health Insurance Service. We included patients who visited the ED with a discharge code of anaphylaxis between 2004 and 2013. We assessed prescription information of epinephrine, antihistamine and systemic steroid, previous medical history and discharge disposition from the ED. The study population was categorized based on age at the visit.
RESULTS
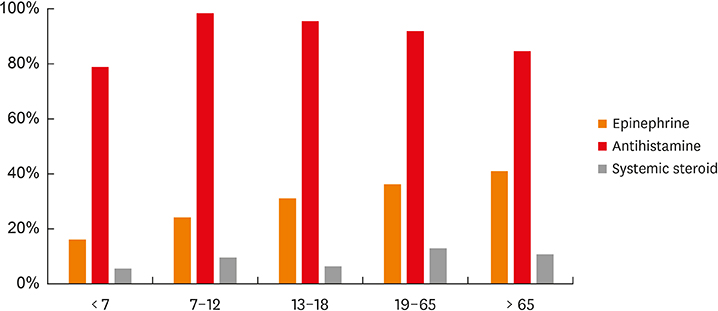
A total of 175 pediatric and 1,605 adult patients with anaphylaxis were identified. Only 42 (24%) of the pediatric patients were treated with epinephrine, while 592 (36.9%) of the adult patients were treated with epinephrine (P = 0.001). Furthermore, the pediatric patients were less likely to be treated with systemic steroid than the adult patients (6.9% vs. 12.3%, P = 0.047). The odds ratios for the administration of epinephrine relative to the baseline in the 19-65 age group were 0.34 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15-0.67), 0.56 (95% CI, 0.28-1.03) and 0.79 (95% CI, 0.45-1.33) in the < 7, 7-12 and 13-18 age groups, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The pediatric patients with anaphylaxis experienced a lower rate of epinephrine injection use than the adult patients and the injection use decreased as age decreased.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Vaccine-related Anaphylaxis Cases Confirmed by KCDC from 2001–2016
Eui jeong Roh, Mi-Hee Lee, Kun-Baek Song, Yeon Kyeong Lee, Min-Kyung Kim, Tae Eun Kim, Eun Hee Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(38):e337. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e337.
Reference
-
1. Lieberman P, Camargo CA Jr, Bohlke K, Jick H, Miller RL, Sheikh A, et al. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis: findings of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Epidemiology of Anaphylaxis Working Group. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006; 97:596–602.
Article2. Motosue MS, Bellolio MF, Van Houten HK, Shah ND, Campbell RL. National trends in emergency department visits and hospitalizations for food-induced anaphylaxis in US children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018; 29:538–544.
Article3. Turner PJ, Gowland MH, Sharma V, Ierodiakonou D, Harper N, Garcez T, et al. Increase in anaphylaxis-related hospitalizations but no increase in fatalities: an analysis of United Kingdom national anaphylaxis data, 1992–2012. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135:956–963.e1.
Article4. Hochstadter E, Clarke A, De Schryver S, LaVieille S, Alizadehfar R, Joseph L, et al. Increasing visits for anaphylaxis and the benefits of early epinephrine administration: a 4-year study at a pediatric emergency department in Montreal, Canada. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:1888–1890.e4.5. Peng MM, Jick H. A population-based study of the incidence, cause, and severity of anaphylaxis in the United Kingdom. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:317–319.
Article6. Bohlke K, Davis RL, DeStefano F, Marcy SM, Braun MM, Thompson RS. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis among children and adolescents enrolled in a health maintenance organization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:536–542.
Article7. Bellou A, Manel J, Samman-Kaakaji H, de Korwin JD, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Bollaert PE, et al. Spectrum of acute allergic diseases in an emergency department: an evaluation of one years' experience. Emerg Med (Fremantle). 2003; 15:341–347.
Article8. Moneret-Vautrin DA, Kanny G, Morisset M, Rancé F, Fardeau MF, Beaudouin E. Severe food anaphylaxis: 107 cases registered in 2002 by the Allergy Vigilance Network. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 36:46–51.9. Macdougall CF, Cant AJ, Colver AF. How dangerous is food allergy in childhood? The incidence of severe and fatal allergic reactions across the UK and Ireland. Arch Dis Child. 2002; 86:236–239.
Article10. Neugut AI, Ghatak AT, Miller RL. Anaphylaxis in the United States: an investigation into its epidemiology. Arch Intern Med. 2001; 161:15–21.11. Fleming JT, Clark S, Camargo CA Jr, Rudders SA. Early treatment of food-induced anaphylaxis with epinephrine is associated with a lower risk of hospitalization. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015; 3:57–62.
Article12. Bock SA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:191–193.
Article13. Sampson HA, Mendelson L, Rosen JP. Fatal and near-fatal anaphylactic reactions to food in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327:380–384.
Article14. Moneret-Vautrin DA, Morisset M, Flabbee J, Beaudouin E, Kanny G. Epidemiology of life-threatening and lethal anaphylaxis: a review. Allergy. 2005; 60:443–451.
Article15. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.
Article16. Lieberman P, Nicklas RA, Randolph C, Oppenheimer J, Bernstein D, Bernstein J, et al. Anaphylaxis--a practice parameter update 2015. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 115:341–384.
Article17. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, Cardona V, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal YM, et al. International consensus on (ICON) anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2014; 7:9.
Article18. Cohen MB, Saunders SS, Wise SK, Nassif S, Platt MP. Pitfalls in the use of epinephrine for anaphylaxis: patient and provider opportunities for improvement. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017; 7:276–286.
Article19. Wood JP, Traub SJ, Lipinski C. Safety of epinephrine for anaphylaxis in the emergency setting. World J Emerg Med. 2013; 4:245–251.
Article20. Liew PY, Craven JA. Adrenaline overdose in pediatric anaphylaxis: a case report. J Med Case Reports. 2017; 11:129.
Article21. Grossman SL, Baumann BM, Garcia Peña BM, Linares MY, Greenberg B, Hernandez-Trujillo VP. Anaphylaxis knowledge and practice preferences of pediatric emergency medicine physicians: a national survey. J Pediatr. 2013; 163:841–846.
Article22. Cho H, Kwon JW. Prevalence of anaphylaxis and prescription rates of epinephrine auto-injectors in urban and rural areas of Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 2018.
Article23. Jeong K, Lee JD, Kang DR, Lee S. A population-based epidemiological study of anaphylaxis using national big data in Korea: trends in age-specific prevalence and epinephrine use in 2010–2014. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018; 14:31.
Article24. Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, Shin SA, Kim K. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:e15.
Article25. Ninchoji T, Iwatani S, Nishiyama M, Kamiyoshi N, Taniguchi-Ikeda M, Morisada N, et al. Current situation of treatment for anaphylaxis in a Japanese pediatric emergency center. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018; 34:e64–e67.
Article26. Sidhu N, Jones S, Perry T, Thompson T, Storm E, Melguizo Castro MS, et al. Evaluation of anaphylaxis management in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016; 32:508–513.
Article27. Samady W, Trainor J, Smith B, Gupta R.. Food-induced anaphylaxis in infants and children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018; 121:360–365.
Article28. Simons FE. Anaphylaxis in infants: can recognition and management be improved? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:537–540.29. Thomson H, Seith R, Craig S. Downstream consequences of diagnostic error in pediatric anaphylaxis. BMC Pediatr. 2018; 18:40.
Article30. Braganza SC, Acworth JP, Mckinnon DR, Peake JE, Brown AF. Paediatric emergency department anaphylaxis: different patterns from adults. Arch Dis Child. 2006; 91:159–163.
Article31. Arroabarren E, Lasa EM, Olaciregui I, Sarasqueta C, Muñoz JA, Pérez-Yarza EG. Improving anaphylaxis management in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:708–714.
Article32. Rueter K, Ta B, Bear N, Lucas M, Borland ML, Prescott SL. Increased use of adrenaline in the management of childhood anaphylaxis over the last decade. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018; 6:1545–1552.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of clinical features of anaphylaxis patients according to epinephrine administration
- Accuracy for registration of disease codes in pediatric anaphylaxis
- Clinical Features and Treatment Patterns of Radiocontrast Mediainduced Anaphylaxis in the Emergency Department
- Comparison of Anaphylaxis and Angioedema with Oral Mucosal Involvement in a Single Pediatric Emergency Department
- Age group characteristics of clinical features and use of epinephrine in children with anaphylaxis who visited the emergency department