Yonsei Med J.
2019 Jan;60(1):10-21. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.1.10.
Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis in Korea: A Narrative Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, and Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sangwonlee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2428273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.1.10
Abstract
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a group of systemic necrotising vasculitides, which often involve small vessels, and which lead to few or no immune deposits in affected organs. According to clinical manifestations and pathological features, AAV is classified into three variants: microscopic polyangiitis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), and eosinophilic GPA. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria contributed to the classification of AAV, although currently the algorithm suggested by the European Medicines Agency in 2007 and the Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides proposed in 2012 have encouraged physicians to classify AAV patients properly. So far, there have been noticeable advancements in studies on the pathophysiology of AAV and the classification criteria for AAV in Western countries. However, studies analysing clinical features of Korean patients with AAV have only been conducted and reported since 2000. One year-, 5 year-, and 10 year-cumulative patient survival rates are reported as 96.1, 94.8, and 92.8%. Furthermore, initial vasculitis activity, prognostic factor score, age and specific organ-involvement have been found to be associated with either all-cause mortality or poor disease course. The rate of serious infection is 28.6%, and 1 year-, 5 year- and 10 year-cumulative hospitalised infection free survival rates range from 85.1% to 72.7%. The overall standardised incidence ratio of cancer in AAV patients was deemed 1.43 compared to the general Korean population.
MeSH Terms
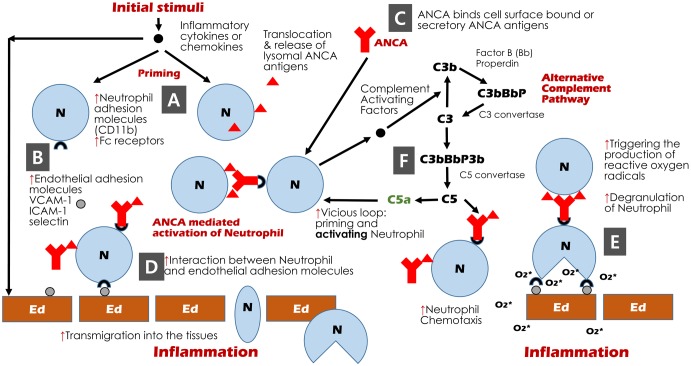
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Modified Body Mass Index at Diagnosis is a Useful Predictor of Mortality in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis
Jung Yoon Pyo, Sung Soo Ahn, Jason Jungsik Song, Yong-Beom Park, Sang-Won Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2022;29(3):154-161. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.3.154.
Reference
-
1. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1–11. PMID: 23045170.
Article2. Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:222–227. PMID: 16901958.
Article3. Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Hunder GG, Arend WP, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1101–1107. PMID: 2202308.
Article4. Masi AT, Hunder GG, Lie JT, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Arend WP, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1094–1100. PMID: 2202307.
Article5. Park YB, Kim JY, Linton JA, Jung HJ, Lee SK, Shin DH. Clinicopathologic study of Wegener's granulomatosis with special emphasis on early lesions in 10 Korean patients. Yonsei Med J. 2001; 42:46–54. PMID: 11293501.
Article6. Kim HW, Song YW. ANCA-associated vasculitis: report from Korea. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013; 17:708–711. PMID: 23292177.
Article7. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Hu P, Xiao H. Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013; 8:139–160. PMID: 23347350.
Article8. Xu PC, Cui Z, Chen M, Hellmark T, Zhao MH. Comparison of characteristics of natural autoantibodies against myeloperoxidase and anti-myeloperoxidase autoantibodies from patients with microscopic polyangiitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50:1236–1243. PMID: 21372002.
Article9. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-mediated disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10:463–473. PMID: 25003769.
Article10. Free ME, Bunch DO, McGregor JA, Jones BE, Berg EA, Hogan SL, et al. Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis have defective Treg cell function exacerbated by the presence of a suppression-resistant effector cell population. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1922–1933. PMID: 23553415.
Article11. von Borstel A, Sanders JS, Rutgers A, Stegeman CA, Heeringa P, Abdulahad WH. Cellular immune regulation in the pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitides. Autoimmun Rev. 2018; 17:413–421. PMID: 29428808.
Article12. Unizony S, Lim N, Phippard DJ, Carey VJ, Miloslavsky EM, Tchao NK, et al. Peripheral CD5+ B cells in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67:535–544. PMID: 25332071.
Article13. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. B cell-mediated pathogenesis of ANCA-mediated vasculitis. Semin Immunopathol. 2014; 36:327–338. PMID: 24777746.
Article14. Nagai M, Hirayama K, Ebihara I, Shimohata H, Kobayashi M, Koyama A. Serum levels of BAFF and APRIL in myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated renal vasculitis: association with disease activity. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011; 118:c339–c345. PMID: 21293157.
Article15. Chen M, Kallenberg CG. ANCA-associated vasculitides--advances in pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6:653–664. PMID: 20924413.
Article16. Kallenberg CG, Heeringa P, Stegeman CA. Mechanisms of Disease: pathogenesis and treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitides. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006; 2:661–670. PMID: 17133251.
Article17. Kallenberg CG, Stegeman CA, Abdulahad WH, Heeringa P. Pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitis: new possibilities for intervention. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013; 62:1176–1187. PMID: 23810690.
Article18. Nakazawa D, Shida H, Tomaru U, Yoshida M, Nishio S, Atsumi T, et al. Enhanced formation and disordered regulation of NETs in myeloperoxidase-ANCA-associated microscopic polyangiitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 25:990–997. PMID: 24385592.
Article19. Lee KH, Kronbichler A, Park DD, Park Y, Moon H, Kim H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. 2017; 16:1160–1173. PMID: 28899799.
Article20. Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Zvaifler NJ, McShane DJ, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1088–1093. PMID: 1975174.
Article21. Park ES, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Reclassification of polyarteritis nodosa based on the 1990 ACR criteria using the 2007 EMA algorithm modified by the 2012 CHCC definitions. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 36(Suppl 111):165–166.22. Cornec D, Cornec-Le Gall E, Fervenza FC, Specks U. ANCA-associated vasculitis - clinical utility of using ANCA specificity to classify patients. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016; 12:570–579. PMID: 27464484.
Article23. Millet A, Pederzoli-Ribeil M, Guillevin L, Witko-Sarsat V, Mouthon L. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: is it time to split up the group? Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72:1273–1279. PMID: 23606701.
Article24. Sokolowska BM, Szczeklik WK, Wludarczyk AA, Kuczia PP, Jakiela BA, Gasior JA, et al. ANCA-positive and ANCA-negative phenotypes of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA): outcome and long-term follow-up of 50 patients from a single Polish center. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014; 32(3 Suppl 82):S41–S47. PMID: 24854371.25. Kallenberg CG. Pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitis, an update. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011; 41:224–231. PMID: 21336557.
Article26. Yoo J, Kim HJ, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, et al. Clinical and prognostic features of Korean patients with MPO-ANCA, PR3-ANCA and ANCA-negative vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017; 35(Suppl 103):111–118. PMID: 28339364.27. Yoo J, Kim HJ, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, et al. The utility of the ACR/EULAR 2017 provisional classification criteria for granulomatosis with polyangiitis in Korean patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 36(Suppl 111):85–87. PMID: 29185957.28. Mukhtyar C, Lee R, Brown D, Carruthers D, Dasgupta B, Dubey S, et al. Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:1827–1832. PMID: 19054820.
Article29. Stone JH, Hoffman GS, Merkel PA, Min YI, Uhlfelder ML, Hellmann DB, et al. A disease-specific activity index for Wegener's granulomatosis: modification of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score. International Network for the Study of the Systemic Vasculitides (INSSYS). Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:912–920. PMID: 11318006.30. Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Seror R, Mahr A, Mouthon L, Le Toumelin P. French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG). FVSG) The Five-Factor Score revisited: assessment of prognoses of systemic necrotizing vasculitides based on the French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG) cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011; 90:19–27. PMID: 21200183.31. Exley AR, Bacon PA, Luqmani RA, Kitas GD, Gordon C, Savage CO, et al. Development and initial validation of the Vasculitis Damage Index for the standardized clinical assessment of damage in the systemic vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:371–380. PMID: 9041949.
Article32. Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36) I Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992; 30:473–483. PMID: 1593914.33. Mukhtyar C, Hellmich B, Jayne D, Flossmann O, Luqmani R. Remission in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006; 24(6 Suppl 43):S-93–S-98.34. Oh JS, Lee CK, Kim YG, Nah SS, Moon HB, Yoo B. Clinical features and outcomes of microscopic polyangiitis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:269–274. PMID: 19399269.
Article35. Ahn JK, Hwang JW, Lee J, Jeon CH, Cha HS, Koh EM. Clinical features and outcome of microscopic polyangiitis under a new consensus algorithm of ANCA-associated vasculitides in Korea. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:2979–2986. PMID: 21898069.
Article36. Oh YJ, Ahn SS, Park ES, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, et al. Chest and renal involvements, Birmingham vascular activity score more than 13.5 and five factor score (1996) more than 1 at diagnosis are significant predictors of relapse of microscopic polyangiitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017; 35(Suppl 103):47–54.37. Flossmann O, Berden A, de Groot K, Hagen C, Harper L, Heijl C, et al. Long-term patient survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:488–494. PMID: 21109517.
Article38. Lionaki S, Blyth ER, Hogan SL, Hu Y, Senior BA, Jennette CE, et al. Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitides: the role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody specificity for myeloperoxidase or proteinase 3 in disease recognition and prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:3452–3462. PMID: 23023777.
Article39. Kim HW, Kim JW, Im CH, Shin KC, Lee EY, Lee EB, et al. The clinicopathologic characteristics of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's): a retrospective study of 45 patients in Korea. Mod Rheumatol. 2013; 23:864–871. PMID: 22983617.
Article40. Yoo J, Kim HJ, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Birmingham vasculitis activity score of more than 9.5 at diagnosis is an independent predictor of refractory disease in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017; 20:1593–1605. PMID: 28766857.
Article41. Kim MY, Sohn KH, Song WJ, Park HW, Cho SH, Min KU, et al. Clinical features and prognostic factors of Churg-Strauss syndrome. Korean J Intern Med. 2014; 29:85–95. PMID: 24574837.
Article42. Kim DS, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Five factor score of more than 1 is associated with relapse during the first 2 year-follow up in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017; 20:1261–1268. PMID: 28261989.
Article43. Tan JA, Dehghan N, Chen W, Xie H, Esdaile JM, Avina-Zubieta JA. Mortality in ANCA-associated vasculitis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76:1566–1574. PMID: 28468793.44. Yamagata K, Usui J, Saito C, Yamaguchi N, Hirayama K, Mase K, et al. ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis in Japan: clinical features and prognostic changes. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012; 16:580–588. PMID: 22350463.
Article45. Li ZY, Gou SJ, Chen M, Zhao MH. Predictors for outcomes in patients with severe ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis who were dialysis-dependent at presentation: a study of 89 cases in a single Chinese center. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 42:515–521. PMID: 23332902.
Article46. Lee SW, Yu MY, Baek SH, Ahn SY, Kim S, Na KY, et al. Long-term prognosis of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-negative renal vasculitis: cohort study in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:542–546. PMID: 27051237.
Article47. Mun CH, Yoo J, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. The initial predictors of death in 153 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis in a single Korean centre. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 36(Suppl 111):65–72. PMID: 29465370.48. Holle JU, Gross WL, Latza U, Nölle B, Ambrosch P, Heller M, et al. Improved outcome in 445 patients with Wegener's granulomatosis in a German vasculitis center over four decades. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:257–266. PMID: 20862686.
Article49. Cartin-Ceba R, Golbin JM, Keogh KA, Peikert T, Sánchez-Menéndez M, Ytterberg SR, et al. Rituximab for remission induction and maintenance in refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's): ten-year experience at a single center. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:3770–3778. PMID: 22730028.
Article50. Bligny D, Mahr A, Toumelin PL, Mouthon L, Guillevin L. Predicting mortality in systemic Wegener's granulomatosis: a survival analysis based on 93 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 51:83–91. PMID: 14872460.
Article51. Charlier C, Henegar C, Launay O, Pagnoux C, Berezné A, Bienvenu B, et al. Risk factors for major infections in Wegener granulomatosis: analysis of 113 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:658–663. PMID: 18504289.
Article52. Godeau B, Mainardi JL, Roudot-Thoraval F, Hachulla E, Guillevin L, Huong Du LT, et al. Factors associated with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in Wegener's granulomatosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995; 54:991–994. PMID: 8546533.
Article53. Charles P, Néel A, Tieulié N, Hot A, Pugnet G, Decaux O, et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitides: a multicentre retrospective study on 80 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53:532–539. PMID: 24282319.
Article54. Weidanz F, Day CJ, Hewins P, Savage CO, Harper L. Recurrences and infections during continuous immunosuppressive therapy after beginning dialysis in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 50:36–46. PMID: 17591523.
Article55. Palsson R, Choi HK, Niles JL. Opportunistic infections are preceded by a rapid fall in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) titer in patients with ANCA associated vasculitis. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:505–510. PMID: 11908563.56. Yoo J, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Birmingham vasculitis activity and chest manifestation at diagnosis can predict hospitalised infection in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018; 37:2133–2141. PMID: 29557539.
Article57. Ni J, Qiu LJ, Hu LF, Cen H, Zhang M, Wen PF, et al. Lung, liver, prostate, bladder malignancies risk in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence from a meta-analysis. Lupus. 2014; 23:284–292. PMID: 24429300.
Article58. Liang Y, Yang Z, Qin B, Zhong R. Primary Sjogren's syndrome and malignancy risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:1151–1156. PMID: 23687261.59. Onishi A, Sugiyama D, Kumagai S, Morinobu A. Cancer incidence in systemic sclerosis: meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1913–1921. PMID: 23576072.
Article60. Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Bettio S, Zen M, Gatto M, Punzi L, et al. The clinical features, diagnosis and classification of dermatomyositis. J Autoimmun. 2014; 48-49:122–127. PMID: 24467910.
Article61. Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin C, Flavell RA. Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013; 13:759–771. PMID: 24154716.
Article62. Mahr A, Heijl C, Le Guenno G, Faurschou M. ANCA-associated vasculitis and malignancy: current evidence for cause and consequence relationships. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013; 27:45–56. PMID: 23507056.
Article63. Hoffman GS, Kerr GS, Leavitt RY, Hallahan CW, Lebovics RS, Travis WD, et al. Wegener granulomatosis: an analysis of 158 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1992; 116:488–498. PMID: 1739240.
Article64. Knight A, Askling J, Ekbom A. Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Int J Cancer. 2002; 100:82–85. PMID: 12115591.
Article65. Heijl C, Harper L, Flossmann O, Stücker I, Scott DG, Watts RA, et al. Incidence of malignancy in patients treated for antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: follow-up data from European Vasculitis Study Group clinical trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:1415–1421. PMID: 21616914.
Article66. Faurschou M, Sorensen IJ, Mellemkjaer L, Loft AG, Thomsen BS, Tvede N, et al. Malignancies in Wegener's granulomatosis: incidence and relation to cyclophosphamide therapy in a cohort of 293 patients. J Rheumatol. 2008; 35:100–105. PMID: 17937462.67. Wester Trejo MAC, Bajema IM, van Daalen EE. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and malignancy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018; 30:44–49. PMID: 28957961.
Article68. Yoo J, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Cancer development in Korean patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: a single centre study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 36(Suppl 111):73–77.69. Honda T, Uehara T, Matsumoto G, Arai S, Sugano M. Neutrophil left shift and white blood cell count as markers of bacterial infection. Clin Chim Acta. 2016; 457:46–53. PMID: 27034055.
Article70. Nigro KG, O'Riordan M, Molloy EJ, Walsh MC, Sandhaus LM. Performance of an automated immature granulocyte count as a predictor of neonatal sepsis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 123:618–624. PMID: 15743752.
Article71. Nahm CH, Choi JW, Lee J. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2008; 38:241–246. PMID: 18715852.72. Yoo J, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Delta neutrophil index is associated with vasculitis activity and risk of relapse in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Yonsei Med J. 2018; 59:397–405. PMID: 29611402.
Article73. Evans TC, Jehle D. The red blood cell distribution width. J Emerg Med. 1991; 9(Suppl 1):71–74. PMID: 1955687.
Article74. Tecer D, Sezgin M, Kanık A, Çncel NA, Öimen ÖB, Biçer A, et al. Can mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width show disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis? Biomark Med. 2016; 10:967–974. PMID: 27564580.
Article75. Aksoy S¸N, Savas¸ E, Sucu M, Kisacik B, Kul S, Zengin O. Association between red blood cell distribution width and disease activity in patients with Behçet's disease. J Int Med Res. 2015; 43:765–773. PMID: 26359293.
Article76. Kim HJ, Yoo J, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Red blood cell distribution width can predict vasculitis activity and poor prognosis in ganulomatosis with polyangiitis. Yonsei Med J. 2018; 59:294–302. PMID: 29436199.77. Leader A, Pereg D, Lishner M. Are platelet volume indices of clinical use? A multidisciplinary review. Ann Med. 2012; 44:805–816. PMID: 22413913.
Article78. Kisacik B, Tufan A, Kalyoncu U, Karadag O, Akdogan A, Ozturk MA, et al. Mean platelet volume (MPV) as an inflammatory marker in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2008; 75:291–294. PMID: 18403245.
Article79. Kim HJ, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Mean platelet volume can estimate the current vasculitis activity of microscopic polyangiitis. Rheumatol Int. 2018; 38:1095–1101. PMID: 29556749.
Article80. Kim Y, Choi H, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Systemic immune-inflammation index could estimate the cross-sectional high activity and the poor outcomes in immunosuppressive drugnaïve patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018; 9. 11. [Epub]. Available at: . DOI: 10.1111/nep.13491.81. Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio at diagnosis can estimate vasculitis activity and poor prognosis in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: a retrospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2018; 19:187. PMID: 30064369.
Article82. Park HJ, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Platelet to lymphocyte ratio is associated with the current activity of ANCA-associated vasculitis at diagnosis: a retrospective monocentric study. Rheumatol Int. 2018; 38:1865–1871. PMID: 30088046.
Article83. Ahn SS, Yoo J, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Clinical role of albumin to globulin ratio in microscopic polyangiitis: a retrospective monocentric study. Clin Rheumatol. 2018; 9. 15. [Epub]. Available at: . DOI: 10.1007/s10067-018-4292-y.
Article84. Moon JS, Ahn SS, Park YB, Lee SK, Lee SW. C-reactive protein to serum albumin ratio is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Yonsei Med J. 2018; 59:865–871. PMID: 30091320.
Article85. Charles Jennette J, Xiao H, Hu P. Complement in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Semin Nephrol. 2013; 33:557–564. PMID: 24161040.
Article86. Choi H, Kim Y, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Low serum complement 3 level is associated with severe ANCA-associated vasculitis at diagnosis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018; 8. 23. [Epub]. Availabla at: . DOI: 10.1007/s10157-018-1634-7.
Article87. Koldingsnes W, Nossent JC. Baseline features and initial treatment as predictors of remission and relapse in Wegener's granulomatosis. J Rheumatol. 2003; 30:80–88. PMID: 12508394.88. Ahn SS, Park ES, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Echocardiographic features in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis within 3 months before and after diagnosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2017; 36:2751–2759. PMID: 28988280.89. Berden AE, Ferrario F, Hagen EC, Jayne DR, Jennette JC, Joh K, et al. Histopathologic classification of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 21:1628–1636. PMID: 20616173.
Article90. Geetha D, Seo P. Renal transplantation in the ANCA-associated vasculitides. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:2657–2662. PMID: 17908271.
Article91. Mukhtyar C, Flossmann O, Hellmich B, Bacon P, Cid M, Cohen-Tervaert JW, et al. Outcomes from studies of antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody associated vasculitis: a systematic review by the European League Against Rheumatism systemic vasculitis task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:1004–1010. PMID: 17911225.
Article92. Hruskova Z, Geetha D, Tesar V. Renal transplantation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015; 30(Suppl 1):i159–i163. PMID: 25324359.
Article93. Schmitt WH, van der Woude FJ. Organ transplantation in the vasculitides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003; 15:22–28. PMID: 12496506.
Article94. Chaigne B, Guillevin L. Unsolved questions and concerns about treatment of anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016; 34(3 Suppl 97):S121–S128.95. Park ES, Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Renal outcome of kidney-transplantation in Korean recipients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 36(Suppl 111):115–120.96. Sun J, Zhang Y, Liu L, Liu G. Diagnostic accuracy of combined tests of anti cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014; 32:11–21. PMID: 24050751.97. Mariette X. Lymphomas complicating Sjögren's syndrome and hepatitis C virus infection may share a common pathogenesis: chronic stimulation of rheumatoid factor B cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:1007–1010. PMID: 11602464.98. Moon JS, Lee DD, Park YB, Lee SW. Rheumatoid factor false positivity in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis not having medical conditions producing rheumatoid factor. Clin Rheumatol. 2018; 37:2771–2779. PMID: 29119480.
Article99. Reininger L, Berney T, Shibata T, Spertini F, Merino R, Izui S. Cryoglobulinemia induced by a murine IgG3 rheumatoid factor: skin vasculitis and glomerulonephritis arise from distinct pathogenic mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990; 87:10038–10042. PMID: 2263605.
Article100. Ullman S, Høier-Madsen M, Halberg P, Jans H, Sylvest J. Deposits of immunoglobulins and complement in skin of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Influence of anti-rheumatic treatment. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979; 8:119–123. PMID: 377474.
Article101. Julian BA, Czerkinsky C, Russell MW, Galla JH, Koopman WJ, Mestecky J, et al. Striking elevation of serum IgA, IgA-containing immune complexes, and IgA rheumatoid factor in clinically silent dermatitis herpetiformis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987; 10:378–384. PMID: 3674013.
Article102. Kudou M, Yasuba H, Kobayashi Y, Hamada K, Kita H. Correlation between rheumatoid factor and peripheral eosinophil count in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Respirology. 2006; 11:830–832. PMID: 17052317.
Article103. Yokomori H, Oda M, Kaneko F, Kawachi S, Tanabe M, Yoshimura K, et al. Lymphatic marker podoplanin/D2-40 in human advanced cirrhotic liver--re-evaluations of microlymphatic abnormalities. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010; 10:131. PMID: 21059220.
Article104. Jiao J, Friedman SL, Aloman C. Hepatic fibrosis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009; 25:223–229. PMID: 19396960.
Article105. De Santis M, Crotti C, Selmi C. Liver abnormalities in connective tissue diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013; 27:543–551. PMID: 24090941.
Article106. Adler M, Gulbis B, Moreno C, Evrard S, Verset G, Golstein P, et al. The predictive value of FIB-4 versus FibroTest, APRI, FibroIndex and Forns index to noninvasively estimate fibrosis in hepatitis C and nonhepatitis C liver diseases. Hepatology. 2008; 47:762–763. PMID: 18220307.
Article107. Lee SW, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Park YB, Han KH, Park JY. Subclinical but significant liver fibrosis in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018; 10. 11. [In press].
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ANCA : The Marker Antibody of Vasculitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting with Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitic Neuropathy with Concurrent Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A Case of Propylthiouracil-induced Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-positive Vasculitis
- Co-existing proteinase 3-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with immunoglobulin A nephropathy