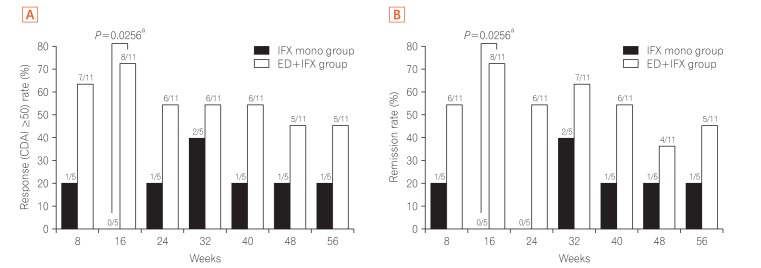
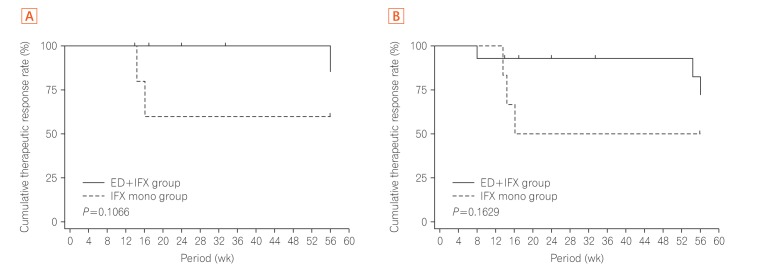
Effect of elemental diet combined with infliximab dose escalation in patients with Crohn's disease with loss of response to infliximab: CERISIER trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Third Department of Internal Medicine, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Mitaka, Japan. thisamatsu@ks.kyorin-u.ac.jp
- 2Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Yokohama, Japan.
- 3Department of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
- 4Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, National Hospital Organization, Higashi-Ohmi Medical Center, Higashi-Ohmi, Japan.
- 5Department of Gastroenterology, Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital, Chikushino, Japan.
- 6Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan.
- 7Division of Gastroenterology, Osaka City General Hospital, Osaka, Japan.
- 8Department of Intestinal Inflammation Research, Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
- 9Department of Gastroenterology, Kitasato University School of Medicine, Sagamihara, Japan.
- 10Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan.
- 11Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 12Department of Clinical Medicine (Biostatistics), Kitasato University School of Pharmacy, Tokyo, Japan.
- 13Division of Gastroenterology, Shiga University of Medical Science, Otsu, Japan.
- 14Department of Internal Medicine, Toho University Sakura Medical Centre, Sakura, Japan.
- 15Yokoyama IBD Clinic, Aichi, Japan.
- 16Department of Gastroenterology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan.
- 17Department of Endoscopy, Hiroshima University Hospital, Hiroshima, Japan.
- 18Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato University Kitasato Institute Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2417663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.16.3.494
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Exclusive enteral nutrition for induction of remission in anti-tumor necrosis factor refractory adult Crohn’s disease: the Indian experience
Ajit Sood, Arshdeep Singh, Ritu Sudhakar, Vandana Midha, Ramit Mahajan, Varun Mehta, Yogesh Kumar Gupta, Kirandeep Kaur
Intest Res. 2020;18(2):184-191. doi: 10.5217/ir.2019.00094.Enteral nutrition in the biologic era: learn from yesterday, live for today, hope for tomorrow
Tadakazu Hisamatsu
Intest Res. 2020;18(2):139-140. doi: 10.5217/ir.2019.09192.Efficacy and tolerability of exclusive enteral nutrition in adult patients with complicated Crohn’s disease
Sanchit Sharma, Arti Gupta, Saurabh Kedia, Samagra Agarwal, Namrata Singh, Sandeep Goyal, Saransh Jain, Vipin Gupta, Pabitra Sahu, Sudheer Kumar Vuyyuru, Bhaskar Kante, Raju Sharma, Rajesh Panwar, Peush Sahni, Govind Makharia, Vineet Ahuja
Intest Res. 2021;19(3):291-300. doi: 10.5217/ir.2019.09172.
Reference
-
1. Chan HC, Ng SC. Emerging biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol. 2017; 52:141–150. PMID: 27832357.
Article2. Akobeng AK, Thomas AG. Enteral nutrition for maintenance of remission in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; (3):CD005984. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005984.pub2. PMID: 17636816.
Article3. Yamamoto T, Nakahigashi M, Umegae S, Matsumoto K. Enteral nutrition for the maintenance of remission in Crohn's disease: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 22:1–8. PMID: 19707151.
Article4. Tsertsvadze A, Gurung T, Court R, Clarke A, Sutcliffe P. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of elemental nutrition for the maintenance of remission in Crohn's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2015; 19:1–138.
Article5. Hirai F, Ishihara H, Yada S, et al. Effectiveness of concomitant enteral nutrition therapy and infliximab for maintenance treatment of Crohn's disease in adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:1329–1334. PMID: 22926500.
Article6. Kamata N, Oshitani N, Watanabe K, et al. Efficacy of concomitant elemental diet therapy in scheduled infliximab therapy in patients with Crohn's disease to prevent loss of response. Dig Dis Sci. 2015; 60:1382–1388. PMID: 25532505.
Article7. Sazuka S, Katsuno T, Nakagawa T, et al. Concomitant use of enteral nutrition therapy is associated with sustained response to infliximab in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012; 66:1219–1223. PMID: 23010687.
Article8. Sugita N, Watanabe K, Kamata N, et al. Efficacy of a concomitant elemental diet to reduce the loss of response to adalimumab in patients with intractable Crohn's disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:631–637. PMID: 28857255.
Article9. Nguyen DL, Palmer LB, Nguyen ET, McClave SA, Martindale RG, Bechtold ML. Specialized enteral nutrition therapy in Crohn's disease patients on maintenance infliximab therapy: a meta-analysis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2015; 8:168–175.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting Surgical Treatment With Infliximab Therapy in Perianal Fistula With Crohn Disease
- Recent Trends of Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- Adalimumab or infliximab: which is better for perianal fistula in Crohn's disease?
- Adalimumab Treatment in Pediatric-Onset Crohn's Disease Patients after Infliximab Failure: A Single Center Study
- A Pityrosporum Fungal Infection Following Infliximab Therapy in a Crohn's Disease Patient