J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 Nov;59(6):655-658. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.6.655.
Multiple Spinal Revision Surgery in a Patient with Parkinson's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, VHS Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. apuzzo@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2417352
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.6.655
Abstract
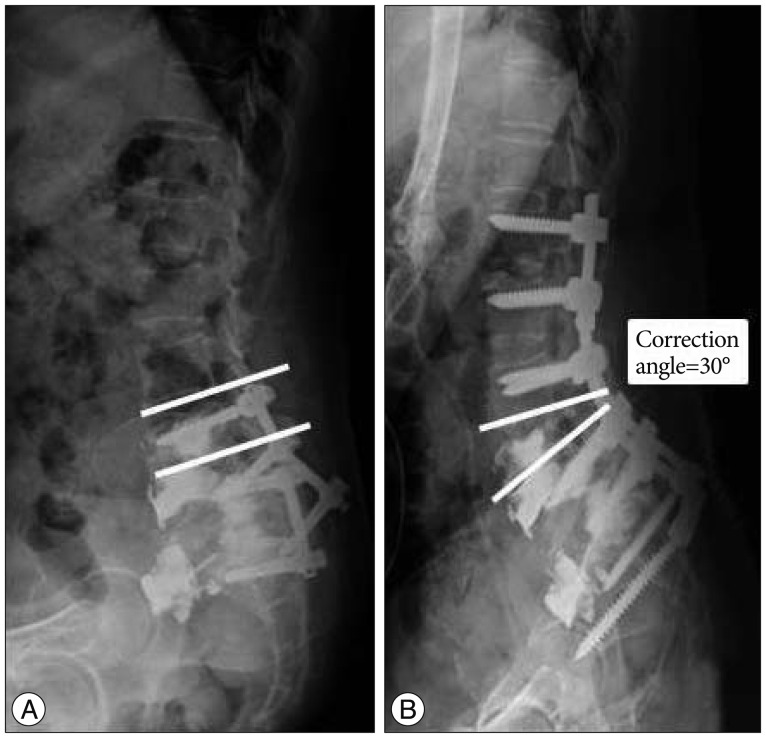
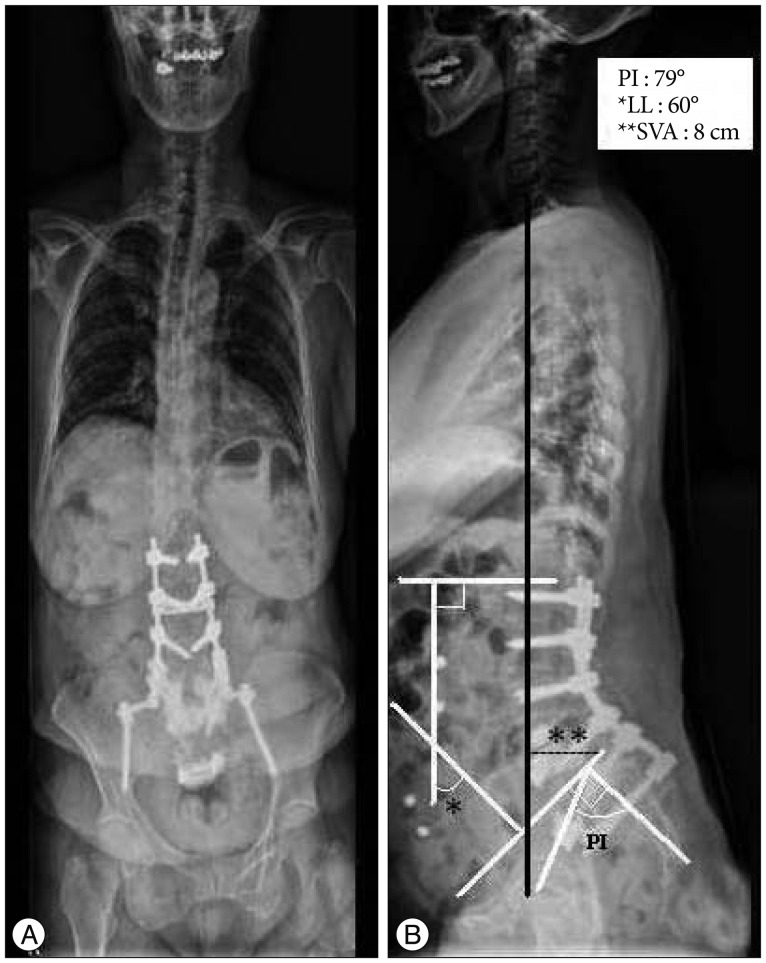
- Parkinson's disease (PD) patients frequently have several spinal deformities leading to postural instabilities including camptocormia, myopathy-induced postural deformity, Pisa syndrome, and progressive degeneration, all of which adversely affect daily life activities. To improve these postural deformities and relieve the related neurologic symptoms, patients often undergo spinal instrumentation surgery. Due to progressive degenerative changes related to PD itself and other complicating factors, patients and surgeons are faced with instrument failure-related complications, which can ultimately result in multiple revision surgeries yielding various postoperative complications and morbidities. Here, we report a representative case of a 70-year-old PD patient with flat back syndrome who had undergone several revision surgeries, including anterior and posterior decompression and fusion for a lumbosacral spinal deformity. The patient ultimately benefitted from a relatively short segment fixation and corrective fusion surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ashour R, Jankovic J. Joint and skeletal deformities in Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord. 2006; 21:1856–1863. PMID: 16941460.
Article2. Babat LB, McLain RF, Bingaman W, Kalfas I, Young P, Rufo-Smith C. Spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson's disease : construct failure and progressive deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:2006–2012. PMID: 15371701.
Article3. Bourghli A, Guérin P, Vital JM, Aurouer N, Luc S, Gille O, et al. Posterior spinal fusion from T2 to the sacrum for the management of major deformities in patients with Parkinson disease : a retrospective review with analysis of complications. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25:E53–E60. PMID: 22460399.4. Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Lewis SJ. Treatment of spinal stenosis and fixed sagittal imbalance. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 384:35–44.
Article5. Christodoulou E, Chinthakunta S, Reddy D, Khalil S, Apostolou T, Drees P, et al. Axial pullout strength comparison of different screw designs : fenestrated screw, dual outer diameter screw and standard pedicle screw. Scoliosis. 2015; 10:15. PMID: 25949274.6. Goost H, Deborre C, Wirtz DC, Burger C, Prescher A, Fölsch C, et al. PMMA-augmentation of incompletely cannulated pedicle screws : a cadaver study to determine the benefits in the osteoporotic spine. Technol Health Care. 2014; 22:607–615. PMID: 24837053.
Article7. Jankovic J. Parkinson's disease : clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008; 79:368–376. PMID: 18344392.8. Koller H, Acosta F, Zenner J, Ferraris L, Hitzl W, Meier O, et al. Spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson's disease : experiences with the challenges posed by sagittal imbalance and the Parkinson's spine. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:1785–1794. PMID: 20422434.
Article9. Moon SH, Lee HM, Chun HJ, Kang KT, Kim HS, Park JO, et al. Surgical outcome of lumbar fusion surgery in patients with Parkinson disease. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25:351–355. PMID: 21685805.
Article10. Paré PE, Chappuis JL, Rampersaud R, Agarwala AO, Perra JH, Erkan S, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel fenestrated pedicle screw augmented with bone cement in osteoporotic spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E1210–E1214. PMID: 21325986.
Article11. Peek AC, Quinn N, Casey AT, Etherington G. Thoracolumbar spinal fixation for camptocormia in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80:1275–1278. PMID: 19864661.
Article12. Sato M, Sainoh T, Orita S, Yamauchi K, Aoki Y, Ishikawa T, et al. Posterior and anterior spinal fusion for the management of deformities in patients with Parkinson's disease. Case Rep Orthop. 2013; 2013:140916. PMID: 24073349.
Article13. Schwab F, Blondel B, Chay E, Demakakos J, Lenke L, Tropiano P, et al. The comprehensive anatomical spinal osteotomy classification. Neurosurgery. 2014; 74:112–120. PMID: 24356197.
Article14. Tiple D, Fabbrini G, Colosimo C, Ottaviani D, Camerota F, Defazio G, et al. Camptocormia in Parkinson disease : an epidemiological and clinical study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80:145–148. PMID: 18931011.
Article15. Upadhyaya CD, Starr PA, Mummaneni PV. Spinal deformity and Parkinson disease : a treatment algorithm. Neurosurg Focus. 2010; 28:E5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Failure of Long Spinal Construct and Pseudarthrosis in a Patient with Parkinson Disease for the Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disorder: Case Report
- Revision Surgery for Spinal Stenosis Developed at the Adjacent Segment after Lumbar Fusion
- A Comparison of Adjacent Segment Diseases Above One Versus Above Two Vertebral Segment after Spinal Fusion of the Degenerative Lumbar Disease
- An Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Parkinson's Disease Who Underwent Whipple's Operation by Enteral Levodopa Administration
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease