Korean J Leg Med.
2018 May;42(2):56-61. 10.7580/kjlm.2018.42.2.56.
Age Estimation Based on Pulp Chamber Size of Mandibular First Molars from Intraoral Periapical Radiographs in Korean
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dental Clinic Center, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. ahnyongw@pusan.ac.kr
- 3Department of Oral Medicine, Inje University Pusan Paik Hospital, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2412861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2018.42.2.56
Abstract
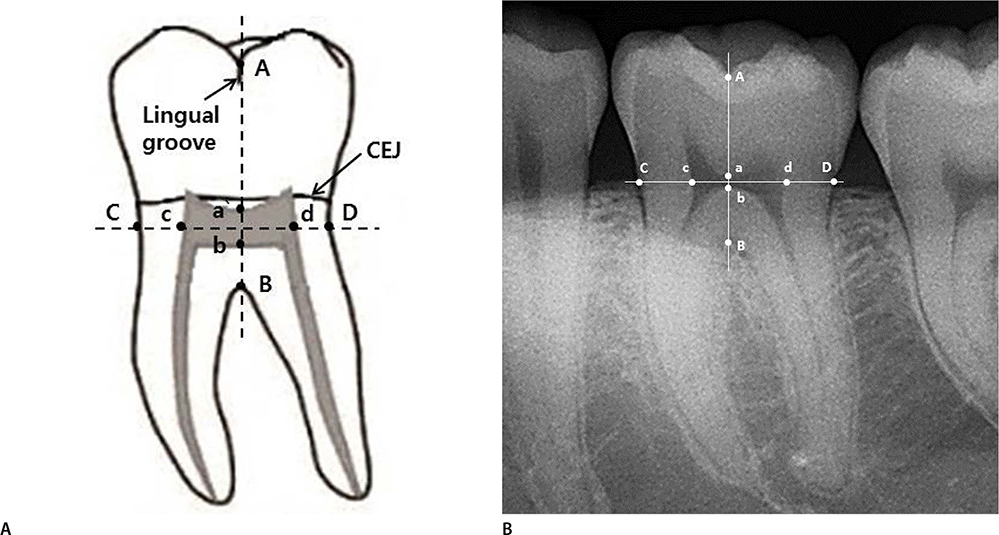
- The teeth are the hardest structures in the body and can be a biomarker of aging. The aging process and degenerative changes in the teeth are helpful for estimation of age in adults. One of the best-known features of dental aging is a reduction in the size of the pulp chamber as a result of secondary deposition of dentin. In this study, we developed new regression models to estimate chronological age in Korean adults using the mandibular first molars to examine the relationship between age and pulp cavity size on intraoral radiographs. Intraoral periapical digital radiographs of the mandibular first molars were collected from 243 patients (147 male, 96 female) of known age. The radiographic images were analyzed by using the Adobe Photoshop CS5 image editing program. The pulp chamber height ratio (PCHR), pulp chamber width ratio (PCWR) were calculated and found to have a significant negative correlation with age. The correlation was consistently higher for PCHR than for PCWR. The strongest correlation was found for PCHR in female patients (r=−0.824). Multiple regression models were derived using the PCHR and PCWR. The determination coefficients (R²) of the models ranged from 0.660 to 0.730. Our results indicate that the measurement of pulp chamber height and width in the mandibular first molar is a practical, simple and reliable method for estimation of age in Korean adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Application of Paewinsky et al.'s Age Estimation Method to Periapical Radiographs
Byung-Yoon Roh, Jeong-Uk Seo, Chang-Gyum Kim, Chang-Un Choi, Won-Joon Lee, Sang-Seob Lee
Korean J Leg Med. 2018;42(4):141-145. doi: 10.7580/kjlm.2018.42.4.141.
Reference
-
1. Kwon C, Byun JS, Jung JK, et al. An analysis of age estimation cases in Korea from the view of social aspects. J Oral Med Pain. 2013; 38:235–246.
Article2. Stavrianos C, Mastagas D, Stavrianou I, et al. Dental age estimation of adults: a review of methods and principals. Res J Med Sci. 2008; 2:258–268.3. Morse DR. Age-related changes of the dental pulp complex and their relationship to systemic aging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1991; 72:721–745.
Article4. Kvaal SI, Kolltveit KM, Thomsen IO, et al. Age estimation of adults from dental radiographs. Forensic Sci Int. 1995; 74:175–185.
Article5. Ikeda N, Umetsu K, Kashimura S, et al. Estimation of age from teeth with their soft X-ray findings. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 1985; 39:244–250.6. Drusini AG, Toso O, Ranzato C. The coronal pulp cavity index: a biomarker for age determination in human adults. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1997; 103:353–363.
Article7. Cameriere R, Ferrante L, Cingolani M. Variations in pulp/tooth area ratio as an indicator of age: a preliminary study. J Forensic Sci. 2004; 49:317–319.
Article8. Cameriere R, Cunha E, Sassaroli E, et al. Age estimation by pulp/tooth area ratio in canines: study of a Portuguese sample to test Cameriere's method. Forensic Sci Int. 2009; 193:128.e1. 128.e6.
Article9. Cameriere R, Cunha E, Wasterlain SN, et al. Age estimation by pulp/tooth ratio in lateral and central incisors by peri-apical X-ray. J Forensic Leg Med. 2013; 20:530–536.
Article10. Cameriere R, De Luca S, Aleman I, et al. Age estimation by pulp/tooth ratio in lower premolars by orthopantomography. Forensic Sci Int. 2012; 214:105–112.
Article11. Cameriere R, Ferrante L, Belcastro MG, et al. Age estimation by pulp/tooth ratio in canines by peri-apical X-rays. J Forensic Sci. 2007; 52:166–170.
Article12. Jeon HS, Tae IH, Ko MY, et al. Age estimation by dental radiographs in Korean adults. Korean J Oral Med. 2009; 34:179–188.13. Philippas GG, Applebaum E. Age factor in secondary dentin formation. J Dent Res. 1966; 45:778–789.
Article14. Bodecker CF. Depth tester for dental caries lesions. J Dent Res. 1952; 31:119–123.
Article15. Willems G. A review of the most commonly used dental age estimation techniques. J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2001; 19:9–17.16. Jeong EG, Heo JY, Ok SM, et al. Drusini's and Takei's methods for age estimation in Korean adults. Korean J Leg Med. 2015; 39:1–5.
Article17. Erbudak HO, Ozbek M, Uysal S, et al. Application of Kvaal et al.'s age estimation method to panoramic radiographs from Turkish individuals. Forensic Sci Int. 2012; 219:141–146.
Article18. Jafarzadeh H, Wu YN. The C-shaped root canal configuration: a review. J Endod. 2007; 33:517–523.
Article19. Mathew DG, Rajesh S, Koshi E, et al. Adult forensic age estimation using mandibular first molar radiographs: a novel technique. J Forensic Dent Sci. 2013; 5:56–59.
Article20. Jeon HM, Kim JH, Heo JY, et al. Age estimation by radiological measuring pulp chamber of mandibular first molar in Korean adults. J Oral Med Pain. 2015; 40:146–154.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age Estimation Using Attrition and Pulp Cavity Size of the Mandibular First Molar in Korean Population
- The Application of Paewinsky et al.'s Age Estimation Method to Periapical Radiographs
- The influence of periapical lesion on furcation involvement in mandibular molars
- A Clinical Study of Periapical Lesions
- Prediction of osteoporosis using fractal analysis on periapical and panoramic radiographs