Clin Endosc.
2018 Mar;51(2):156-160. 10.5946/ce.2017.085.
Management of Benign and Malignant Pancreatic Duct Strictures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA. mkahaleh@gmail.com
- KMID: 2410982
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.085
Abstract
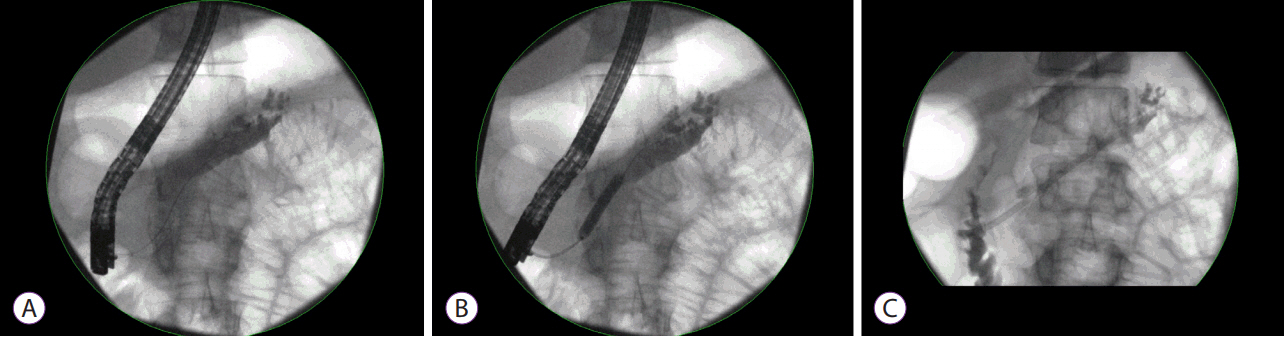
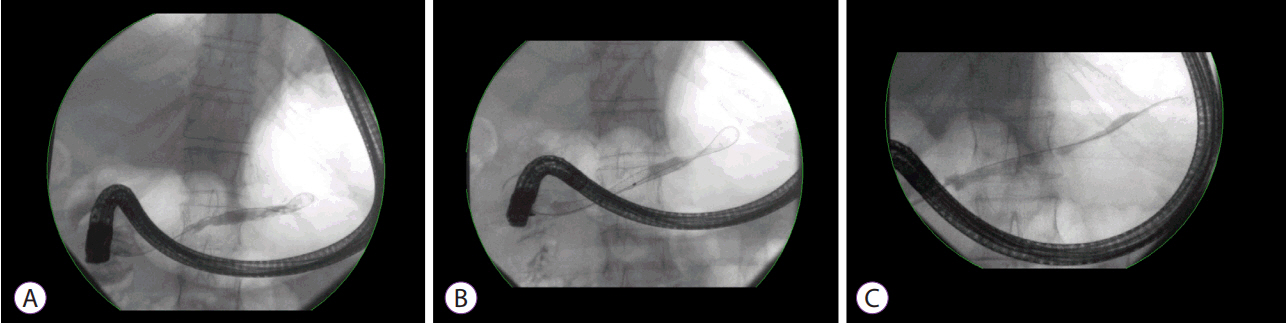
- The diagnosis and management of pancreatic strictures, whether malignant or benign, remain challenging. The last 2 decades have seen dramatic progress in terms of both advanced imaging and endoscopic therapy. While plastic stents remain the cornerstone of the treatment of benign strictures, the advent of fully covered metal stents has initiated a new wave of interest in calibrating the pancreatic duct with fewer sessions. In malignant disease, palliation remains the priority and further data are necessary before offering systematic pancreatic stenting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Catalano MF. Endoscopic treatment of pancreatic duct strictures. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 1:168–174.
Article2. Cohen SA, Siegel JH, Kasmin FE. Treatment of pancreatic strictures. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2007; 10:347–354.
Article3. Oza VM, Kahaleh M. Endoscopic management of chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 5:19–28.
Article4. Eloubeidi MA, Varadarajulu S, Desai S, Wilcox CM. Value of repeat endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for suspected pancreatic cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:567–570.
Article5. Varadarajulu S, Tamhane A, Eloubeidi MA. Yield of EUS-guided FNA of pancreatic masses in the presence or the absence of chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:728–736. ; quiz 751, 753.
Article6. Kahaleh M, Turner BG, Bezak K, et al. Probe-based confocal LASER endomicroscopy (pCLE) in the pancreatic duct provides direct visualization of ductal structures and AIDS in clinical management. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77(5 Suppl):AB165.7. Warshaw AL, Banks PA, Fernández-Del Castillo C. AGA technical review: treatment of pain in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1998; 115:765–776.
Article8. Weber A, Schneider J, Neu B, et al. Endoscopic stent therapy in patients with chronic pancreatitis: a 5-year follow-up study. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:715–720.
Article9. Talukdar R, Reddy DN. Pancreatic endotherapy for chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2015; 25:765–777.
Article10. Costamagna G, Bulajic M, Tringali A, et al. Multiple stenting of refractory pancreatic duct strictures in severe chronic pancreatitis: long-term results. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:254–259.
Article11. Dumonceau JM, Devière J, Le Moine O, et al. Endoscopic pancreatic drainage in chronic pancreatitis associated with ductal stones: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43:547–555.
Article12. Mangiavillano B, Pagano N, Baron TH, Luigiano C. Outcome of stenting in biliary and pancreatic benign and malignant diseases: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:9038–9054.
Article13. Gupta R, Reddy DN. Stent selection for both biliary and pancreatic strictures caused by chronic pancreatitis: multiple plastic stents or metallic stents? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011; 18:636–639.
Article14. Adler JM, Gardner TB. Endoscopic therapies for chronic pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2017; 62:1729–1737.
Article15. Sauer BG, Gurka MJ, Ellen K, Shami VM, Kahaleh M. Effect of pancreatic duct stent diameter on hospitalization in chronic pancreatitis: does size matter? Pancreas. 2009; 38:728–731.16. Eleftherladis N, Dinu F, Delhaye M, et al. Long-term outcome after pancreatic stenting in severe chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:223–230.
Article17. Tringali A, Boskoski I, Costamagna G. The role of endoscopy in the therapy of chronic pancreatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008; 22:145–165.
Article18. Tessier G, Bories E, Arvanitakis M, et al. EUS-guided pancreatogastrostomy and pancreatobulbostomy for the treatment of pain in patients with pancreatic ductal dilatation inaccessible for transpapillary endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:233–241.
Article19. François E, Kahaleh M, Giovannini M, Matos C, Devière J. EUS-guided pancreaticogastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:128–133.
Article20. Brauer BC, Chen YK, Fukami N, Shah RJ. Single-operator EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for difficult pancreaticobiliary access (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:471–479.
Article21. Tyberg A, Sharaiha RZ, Kedia P, et al. EUS-guided pancreatic drainage for pancreatic strictures after failed ERCP: a multicenter international collaborative study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:164–169.
Article22. Vila JJ, Pérez-Miranda M, Vazquez-Sequeiros E, et al. Initial experience with EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for biliary and pancreatic duct drainage: a Spanish national survey. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:1133–1141.
Article23. Fujii LL, Topazian MD, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. EUS-guided pancreatic duct intervention: outcomes of a single tertiary-care referral center experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:854–864.e1.
Article24. Adams DB, Ford MC, Anderson MC. Outcome after lateral pancreaticojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1994; 219:481–487. ; discussion 487-489.
Article25. Nealon WH, Thompson JC. Progressive loss of pancreatic function in chronic pancreatitis is delayed by main pancreatic duct decompression. A longitudinal prospective analysis of the modified puestow procedure. Ann Surg. 1993; 217:458–466. ; discussion 466-468.
Article26. Markowitz JS, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL. Failure of symptomatic relief after pancreaticojejunal decompression for chronic pancreatitis. Strategies for salvage. Arch Surg. 1994; 129:374–379. ; discussion 379-380.27. DiMagno EP, Reber HA, Tempero MA. AGA technical review on the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. American gastroenterological association. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:1464–1484.28. Wehrmann T, Riphaus A, Frenz MB, Martchenko K, Stergiou N. Endoscopic pancreatic duct stenting for relief of pancreatic cancer pain. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 17:1395–1400.
Article29. Mekaroonkamol P, Willingham FF, Chawla S. Endoscopic management of pain in pancreatic cancer. JOP. 2015; 16:33–40.30. Sharaiha RZ, Widmer J, Kahaleh M. Palliation of pancreatic ductal obstruction in pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2013; 23:917–923.
Article31. Yeoh KG, Zimmerman MJ, Cunningham JT, Cotton PB. Comparative costs of metal versus plastic biliary stent strategies for malignant obstructive jaundice by decision analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49(4 Pt 1):466–471.
Article32. Cremer M, Devière J, Delhaye M, Baize M, Vandermeeren A. Stenting in severe chronic pancreatitis: results of medium-term follow-up in seventy-six patients. Endoscopy. 1991; 23:171–176.
Article33. Rösch T, Daniel S, Scholz M, et al. Endoscopic treatment of chronic pancreatitis: a multicenter study of 1000 patients with long-term follow-up. Endoscopy. 2002; 34:765–771.
Article34. Vitale GC, Cothron K, Vitale EA, et al. Role of pancreatic duct stenting in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:1431–1434.
Article35. Weber A, Schneider J, Neu B, et al. Endoscopic stent therapy for patients with chronic pancreatitis: results from a prospective follow-up study. Pancreas. 2007; 34:287–294.36. Park DH, Kim MH, Moon SH, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK. Feasibility and safety of placement of a newly designed, fully covered self-expandable metal stent for refractory benign pancreatic ductal strictures: a pilot study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1182–1189.
Article37. Sauer B, Talreja J, Ellen K, Ku J, Shami VM, Kahaleh M. Temporary placement of a fully covered self-expandable metal stent in the pancreatic duct for management of symptomatic refractory chronic pancreatitis: preliminary data (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1173–1178.
Article38. Moon SH, Kim MH, Park DH, et al. Modified fully covered self-expandable metal stents with antimigration features for benign pancreatic-duct strictures in advanced chronic pancreatitis, with a focus on the safety profile and reducing migration. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:86–91.
Article39. Akbar A, Baron TH. Covered self-expanding metal stent use in the pancreatic duct: a case series. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:869–873.
Article40. Giacino C, Grandval P, Laugier R. Fully covered self-expanding metal stents for refractory pancreatic duct strictures in chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:874–877.
Article41. Landi R, Tringali A, Bove V, et al. Fully covered self-expandable metal stents to dilate pancreatic duct strictures due to chronic pancreatitis: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83(5 Suppl):AB251–AB252.42. Ogura T, Onda S, Takagi W, et al. Placement of a 6 mm, fully covered metal stent for main pancreatic head duct stricture due to chronic pancreatitis: a pilot study (with video). Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2016; 9:722–728.
Article43. Matsubara S, Sasahira N, Isayama H, et al. Prospective pilot study of fully covered self-expandable metal stents for refractory benign pancreatic duct strictures: long-term outcomes. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E1215–E1222.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Management of Benign Pancreatic Stricture Associated with Chronic Pancreatitis
- Difficulty of balloon dilatation in corrosive esophageal strictures
- Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Biliary Strictures
- Clinical Use of Gianturco Expandable Metallic Stent in Benign Biliary Stricture: Result of Longterm Follow-up
- Pancreatic cystic lesion-Surgery or follow-up evaluation