J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Apr;18(2):115-117. 10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.2.115.
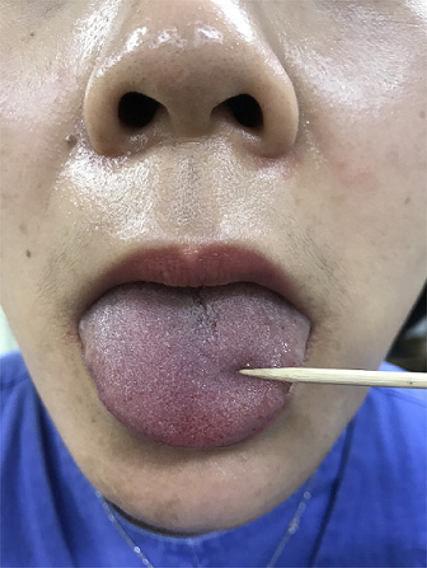
Dexamethasone treatment for bilateral lingual nerve injury following orotracheal intubation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea. jeon68@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2410145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.2.115
Abstract
- Lingual nerve injury is a rare complication of general anesthesia. The causes of lingual nerve injury following general anesthesia are multifactorial; possible mechanisms may include difficult laryngoscopy, prolonged anterior mandibular displacement, improper placement of the oropharyngeal airway, macroglossia and tongue compression. In this report, we have described a case of bilateral lingual nerve injury that was associated with orotracheal intubation for open reduction and internal fixation of the left distal radius fracture in a 61-year-old woman. In this case, early treatment with dexamethasone effectively aided the recovery of the injured lingual nerve.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fung BK, Chan MY. Incidence of oral tissue trauma after the administration of general anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2001; 39:163–167.2. Gaut A, Williams M. Lingual nerve injury during suspension microlaryngoscopy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 126:669–671.
Article3. Alling CC 3rd. Dysesthesia of the lingual and inferior alveolar nerves following third molar surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986; 44:454–457.
Article4. McGeachie JK. Anatomy of the lingual nerve in relation to possible damage during clinical procedures. Ann R Australas Coll Dent Surg. 2002; 16:109–110.5. Silva DA, Colingo KA, Miller R. Lingual nerve injury following laryngoscopy. Anesthesiology. 1992; 76:650–651.
Article6. Kim KJ, Park JW, Baek CW, Jung YH, Koo GH. Hypoglossal nerve palsy following general anesthesia: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005; 49:702–704.
Article7. Hwang BS, Hwang BM. Tongue Numbness following Endotracheal General Anesthesia: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008; 54:350–352.
Article8. Majumder S, Hopkins PM. Bilateral lingual nerve injury following the use of the laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia. 1998; 53:184–186.
Article9. Lang MS, Waite PD. Bilateral lingual nerve injury after laryngoscopy for intubation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 59:1497–1499.
Article10. Lagalla G, Logullo F, Di Bella P, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG. Influence of early high-dose steroid treatment on Bell's palsy evolution. Neurol Sci. 2002; 23:107–112.11. Gozali P, Boonsiriseth K, Kiattavornchareon S, Khanijou M, Wongsirichat NJ. Decreased post-operative pain using a sublingual injection of dexamethasone (8 mg) in lower third molar surgery. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2017; 17:47–53.
Article12. Sun H, Yang T, Li Q. Dexamethasone and vitamin B12 synergistically promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats by upregulating the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Arch Med Sci. 2012; 8:924–930.13. Kim HJ, Ahn HS, Lee JY, Choi SS, Cheong YS, Kwon K. Effects of applying nerve blocks to prevent postherpetic neuralgia in patients with acute herpes zoster: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J Pain. 2017; 30:3–17.
Article14. Kadry MA, Popat MT. Lingual nerve injury after use of a cuffed oropharyngeal airway. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2001; 18:264–266.
Article15. Teichner RL. Lingual nerve injury: a complication of orotracheal intubation. Case report. Br J Anaesth. 1971; 43:413–414.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tongue Numbness following Endotracheal General Anesthesia: A case report
- Unrecognized Bilateral Dislocation of Temporomandibular Joint during Orotracheal Intubation
- Transient Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy after Septorhinoplasty: A case report
- Compression Neuropathy of the Hypoglossal Nerve Following Orotracheal Intubation: A case report
- How Many Attempts are Needed for Learning Fiberoptic Orotracheal Intubation?