Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Apr;38(2):286-291.
Magnetic Resonance Neurographic Findings in Classic Idiopathic Neuralgic Amyotrophy in Subacute Stage: A Report of Four Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yays.sung@samsung.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
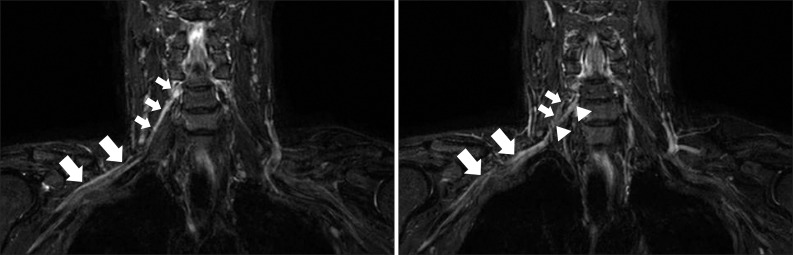
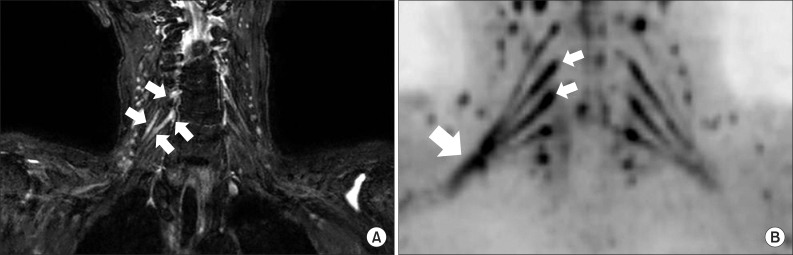
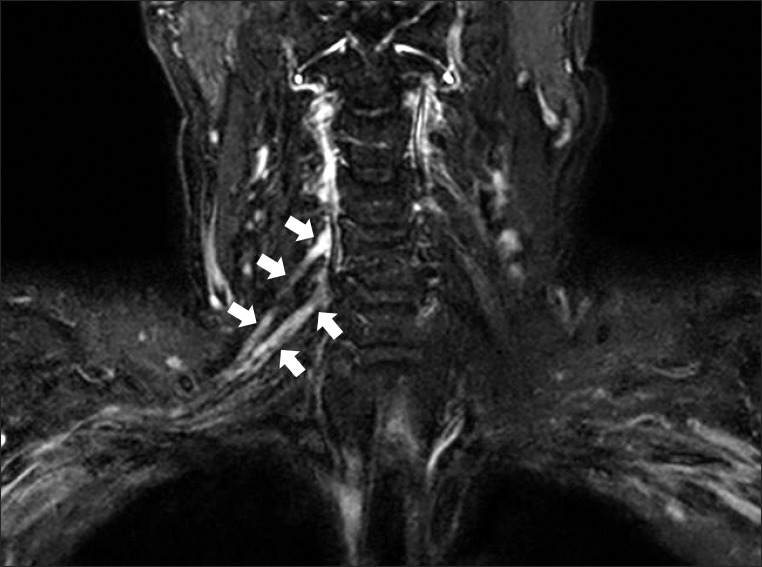
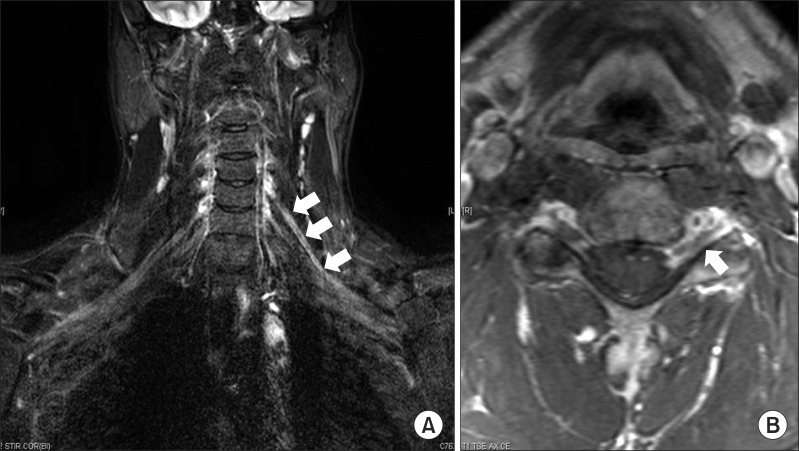
- Neuralgic amyotrophy (NA) is characterized by acute onset of severe pain, followed by muscular weakness and wasting of the shoulder girdle. While the diagnosis of NA mainly relies on the clinical history and examination, some investigations including electrophysiologic study and radiologic study may help to confirm the diagnosis. Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN), a new technique for the evaluation of peripheral nerve disorders, can be helpful in the diagnosis of NA. MRN presents additional benefits in comparison to conventional magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of idiopathic NA (INA). In this report, we present the first four cases of classic INA diagnosed with MRN in subacute stage. MRN imaging modality should be considered in patients clinically suspected of INA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. van Alfen N, van der Werf SP, van Engelen BG. Long-term pain, fatigue, and impairment in neuralgic amyotrophy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:435–439. PMID: 19254608.
Article2. Chance PF. Inherited focal, episodic neuropathies: hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies and hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Neuromolecular Med. 2006; 8:159–174. PMID: 16775374.3. van Alfen N, van Engelen BG. The clinical spectrum of neuralgic amyotrophy in 246 cases. Brain. 2006; 129(Pt 2):438–450. PMID: 16371410.
Article4. Duman I, Guvenc I, Kalyon TA. Neuralgic amyotrophy, diagnosed with magnetic resonance neurography in acute stage: a case report and review of the literature. Neurologist. 2007; 13:219–221. PMID: 17622915.5. Sarikaya S, Sumer M, Ozdolap S, Erdem CZ. Magnetic resonance neurography diagnosed brachial plexitis: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:1058–1059. PMID: 15895358.
Article6. van Alfen N. Clinical and pathophysiological concepts of neuralgic amyotrophy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011; 7:315–322. PMID: 21556032.
Article7. Miller JD, Pruitt S, McDonald TJ. Acute brachial plexus neuritis: an uncommon cause of shoulder pain. Am Fam Physician. 2000; 62:2067–2072. PMID: 11087188.8. Du R, Auguste KI, Chin CT, Engstrom JW, Weinstein PR. Magnetic resonance neurography for the evaluation of peripheral nerve, brachial plexus, and nerve root disorders. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112:362–371. PMID: 19663545.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Magnetic Resonance Neurography Findings in Idiopathic Neuralgic Amyotrophy
- Usability of Magnetic Resonance Neurography for Diagnosis of Neuralgic Amyotrophy in Acute Stage
- Idiopathic Neuralgic Amyotrophy in a Child Treated with Integrated Rehabilitation Program: A Case Report
- Diaphragmatic Dysfunction due to Neuralgic Amyotrophy After SARSCoV-2 Vaccination: A Case Report
- Neuroradiologic and Neurophysiologic Findings of Neuralgic Amyotrophy