Korean J Pain.
2010 Mar;23(1):74-77.
Post-traumatic Back Pain Revealed as Tuberculous Spondylitis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chsung@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
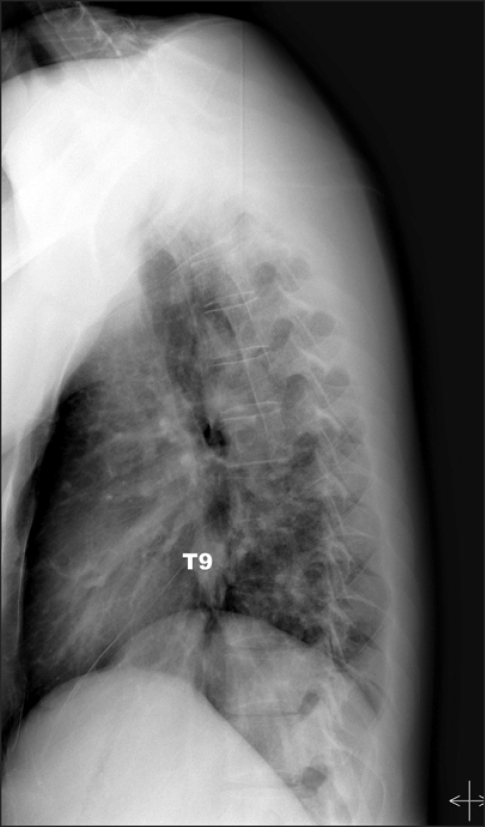
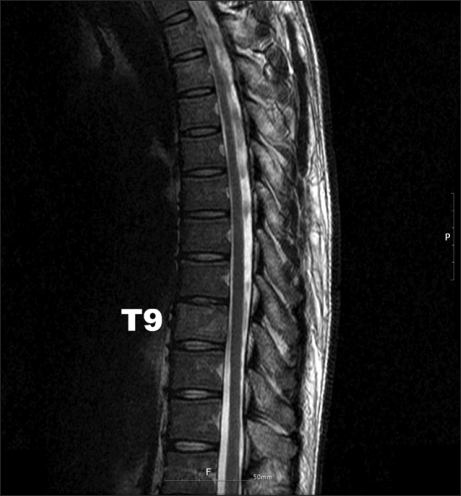
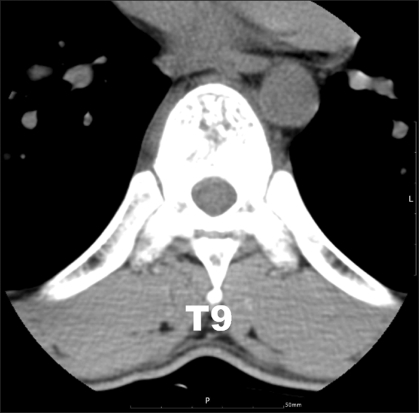
- Tuberculous spondylitis is a very rare disease, but it can result in bone destruction, kyphotic deformity, spinal instability, and neurologic complications unless early diagnosis and proper management are done. Because the most common symptom of tuberculous spondylitis is back pain, it can often be misdiagnosed. Atypical tuberculous spondylitis can be presented as a metastatic cancer or a primary vertebral tumor. We must make a differential diagnosis through adequate biopsy. A 30-year-old man visited our clinic due to back and chest pain after a recent traffic accident. About 1 year ago, he had successfully recovered from tuberculous pleurisy after taking anti-tuberculosis medication. We performed epidural and intercostal blocks but the pain was not relieved. For the further evaluation, several imaging and laboratory tests were done. Finally, we confirmed tuberculous spondylitis diagnosis with the biopsy results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Snider GL. Tuberculosis then and now: a personal perspective on the last 50 years. Ann Intern Med. 1997; 126:237–243. PMID: 9027277.
Article2. Okuyama Y, Nakaoka Y, Kimoto K, Ozasa K. Tuberculous spondylitis (Pott's disease) with bilateral pleural effusion. Intern Med. 1996; 35:883–885. PMID: 8968802.
Article3. Chang DJ, Yoon DM, Kang YS, Yoon KB. Chronic back pain proven to be spinal tuberculosis: a report of 2 cases. Korean J Pain. 2008; 21:74–79.
Article4. Ahmadi J, Bajaj A, Destian S, Segall HD, Zee CS. Spinal tuberculosis: atypical observations at MR imaging. Radiology. 1993; 189:489–493. PMID: 8210378.
Article5. Naim-Ur-Rahman , Al-Arabi KM, Khan FA. Atypical forms of spinal tuberculosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1987; 88:26–33. PMID: 3425410.
Article6. Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, Erickson DL, Seljeskog EL. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg. 1995; 83:243–247. PMID: 7616269.
Article7. Verver S, Warren RM, Beyers N, Richardson M, van der, Borgdorff MW, et al. Rate of reinfection tuberculosis after successful treatment is higher than rate of new tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:1430–1435. PMID: 15831840.
Article8. Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, Daley CL, Etkind SC, Friedman LN, et al. American thoracic society/centers for disease control and prevention/infectious diseases society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:603–662. PMID: 12588714.
Article9. Schlesinger N, Lardizabal A, Rao J, Rao J, McDonald R. Tuberculosis of spine: experience in an inner city hospital. J Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 11:17–20. PMID: 16357692.10. Yoo SS, Kwon JS, Kang YR, Lee JW, Cha SI, Park JY, et al. The clinical characteristics and outcomes of short-term treatment in patients with recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008; 64:341–346.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Tuberculous Spondylitis of the Lumbosacral Junction by Transperitoneal Approach
- Surgical Treatment of Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Tuberculous Spondylitis after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Misdiagnosis or Complication?
- A Case of Traumatic Spinal Epidural Hematoma in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Total Hip Arthroplasty for Ankylosed Hip