J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2017 Sep;22(3):196-201. 10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.196.
Pyogenic Arthritis of the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Treated with External Fixation in Adolescent
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dongshin General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jikocmc@naver.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Good Samsun Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2391217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.196
Abstract
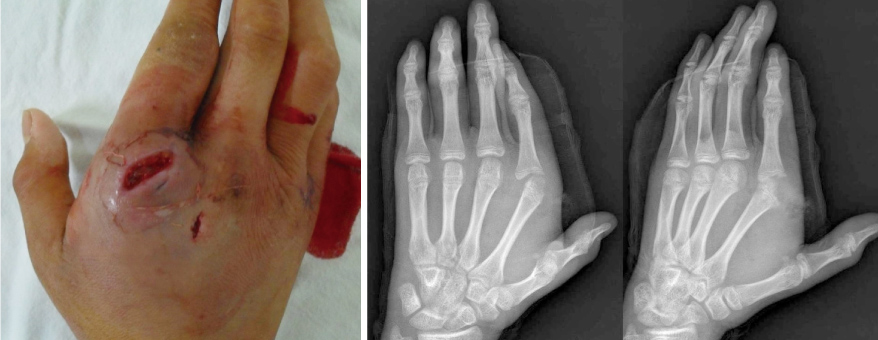
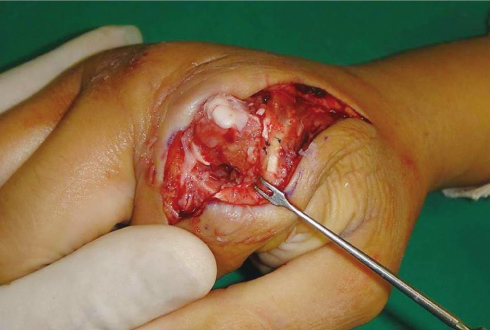
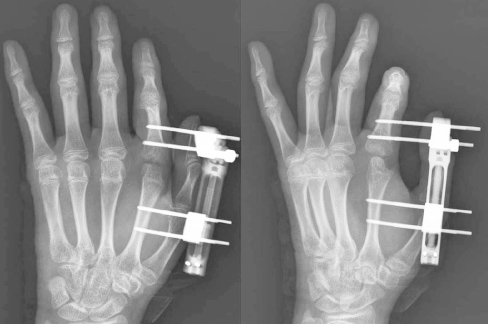
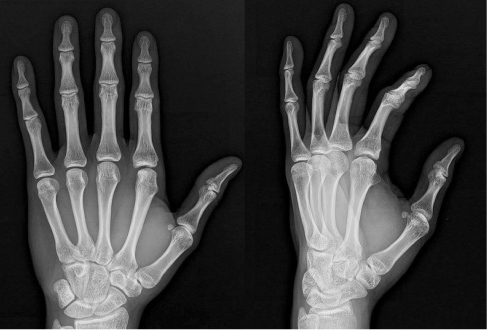
- When hand injuries caused by human bite are overlooked and they can progress to pyogenic arthritis. Pyogenic arthritis is difficult to treat and can make severe sequelae in the joints. We report a case of pyogenic arthritis of the hand that occurred after human bite injury in adolescent treated with wide debridement and external fixator. Our literature searches revealed that the use of external fixator is good treatment option for the treatment of pyogenic arthritis of the hand.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kennedy SA, Stoll LE, Lauder AS. Human and other mammalian bite injuries of the hand: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015; 23:47–57.2. Giuffre JL, Jacobson NA, Rizzo M, Shin AY. Pyarthrosis of the small joints of the hand resulting in arthrodesis or amputation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36:1273–1281.
Article3. de Vries H, van der Werken C. Septic arthritis of the hand. Injury. 1993; 24:32–34.
Article4. Sinha M, Jain S, Woods DA. Septic arthritis of the small joints of the hand. J Hand Surg Br. 2006; 31:665–672.
Article5. Wittels NP, Donley JM, Burkhalter WE. A functional treatment method for interphalangeal pyogenic arthritis. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:894–898.
Article6. Chadaev AP, Jukhtin VI, Butkevich AT, Emkuzhev VM. Treatment of infected clench-fist human bite wounds in the area of metacarpophalangeal joints. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21:299–303.
Article7. Murray PM. Septic arthritis of the hand and wrist. Hand Clin. 1998; 14:579–587.
Article8. Mennen U, Howells CJ. Human fight-bite injuries of the hand: a study of 100 cases within 18 months. J Hand Surg Br. 1991; 16:431–435.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pyogenic Arthritis of the Shoulder Associated with Brachial Plexus Palsy: A Case Report
- Simultaneous Fracture-Dislocation of the Carpometacarpal and Metacarpophalangeal joint of the Thumb
- Pyogenic Arthritis of the Facet Joint with Concurrent Epidural and Paraspinal Abscess: A Case Report
- Arthroscopic Management for Septic Arthritis of the Hip Joint in Adults: A Report of Four Cases
- Lesion in the Sacro-iliac Joint