Anat Cell Biol.
2017 Mar;50(1):7-11. 10.5115/acb.2017.50.1.7.
Morphometric study of tensor of vastus intermedius in South Indian population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Pondicherry, India. dr_raveendra@rediffmail.com
- KMID: 2390420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2017.50.1.7
Abstract
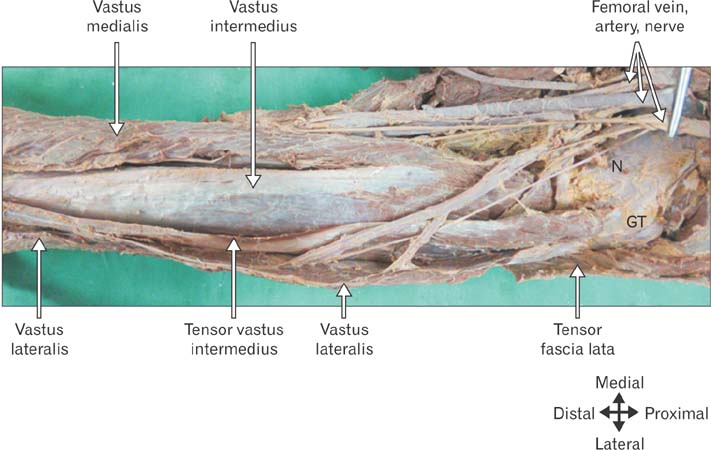
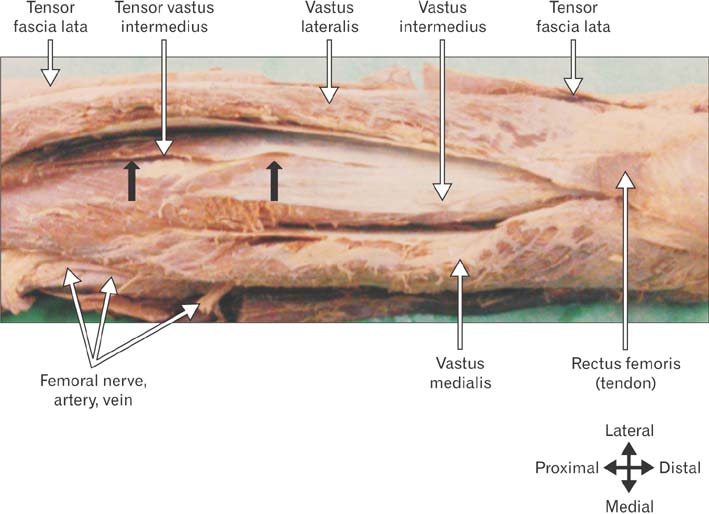
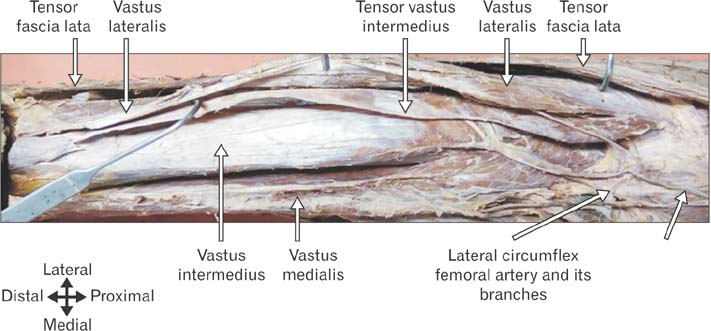
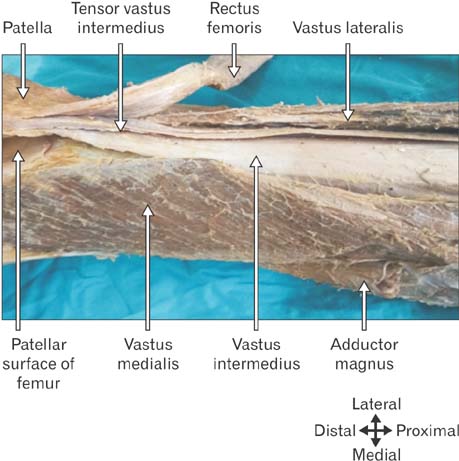
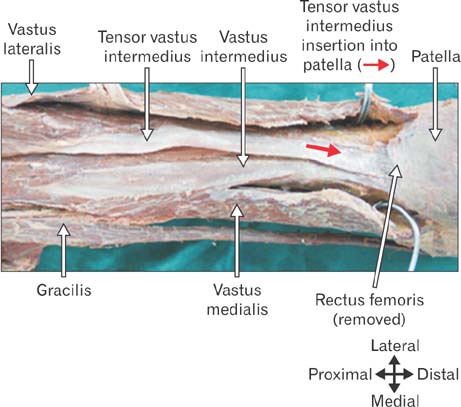
- Tensor of vastus intermedius is a newly discovered muscle located between vastus lateralis and vastus intermedius. The purpose of this study was to investigate the detailed morphology of tensor of vastus intermedius, specifically to provide data pertaining to the attachments, innervations, variation in the types and its morphometry in South Indian population. The tensor of vastus intermedius was studied in thirty six cadaveric lower limbs using macrodissection techniques. The origin of the muscle was from upper part of intertrochanteric line and anterior part of greater trochanter of femur inserted to medial aspect of upper border of patella. The muscle was classified into four types based on the origin and also the aponeurosis course with independent type (type 1) being common. The mean and standard deviation of the length of tensor of vastus intermedius and aponeurosis were 145.40±37.55 mm and 193.55±42.32 mm, respectively. The results of the study suggest that tensor of vastus intermedius is variable and the information provided regarding the attachments, types and quantitative data will contribute to the existing knowledge of the muscle.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grob K, Ackland T, Kuster MS, Manestar M, Filgueira L. A newly discovered muscle: the tensor of the vastus intermedius. Clin Anat. 2016; 29:256–263.2. Willan PL, Mahon M, Golland JA. Morphological variations of the human vastus lateralis muscle. J Anat. 1990; 168:235–239.3. Lin F, Wang G, Koh JL, Hendrix RW, Zhang LQ. In vivo and noninvasive three-dimensional patellar tracking induced by individual heads of quadriceps. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004; 36:93–101.4. Miao P, Xu Y, Pan C, Liu H, Wang C. Vastus medialis oblique and vastus lateralis activity during a double-leg semisquat with or without hip adduction in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:289.5. Lefebvre R, Leroux A, Poumarat G, Galtier B, Guillot M, Van-neuville G, Boucher JP. Vastus medialis: anatomical and functional considerations and implications based upon human and cadaveric studies. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2006; 29:139–144.6. Goh JC, Lee PY, Bose K. A cadaver study of the function of the oblique part of vastus medialis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:225–231.7. Grob K, Fretz C, Kuster MS, Gilbey H, Ackland T. Knee pain associated with rupture of tensor vastus intermedius, a newly discovered muscle: a case report. J Clin Case Rep. 2016; 6:828.8. Rajasekaran S, Hall MM. Sonographic appearance of the tensor of the vastus intermedius. PM R. 2016; 8:1020–1023.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Muscle Thickness and Echo Intensity of the Abdominal and Lower Extremity Muscles in Stroke Survivors
- A Computed Tomography-Based Assessment of the Anatomical Parameters Concerning S2-Alar Iliac Screw Insertion Using “Safe Trajectory Method” in Indian Population
- Exploring the atlantic part of the vertebral artery in the South Indian population and its implications in spine surgery
- Computed Tomography-Based Occipital Condyle Morphometry in an Indian Population to Assess the Feasibility of Condylar Screws for Occipitocervical Fusion
- Morphometric Study of C1 Pedicle and Feasibility Evaluation of C1 Pedicle Screw Placement with a Novel Clinically Relevant Radiological Classification in an Indian Population