Int J Thyroidol.
2017 May;10(1):66-69. 10.11106/ijt.2017.10.1.66.
Surgical Treatment for Riedel's Thyroiditis: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyjung@kumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2379365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2017.10.1.66
Abstract
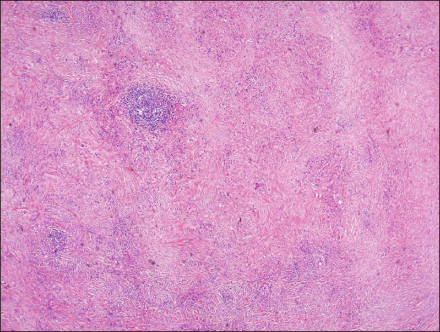
- Riedel's thyroiditis is a rare fibrotic condition that results in the destruction of the thyroid and infiltration into surrounding tissues. The exact etiology is not yet clear, although systemic fibrosing disorder, a variant of Hashimoto's thyroiditis, a primary inflammatory disorder of the thyroid, and even a manifestation of end-stage subacute thyroiditis has been suggested. Although various treatments have been applied, no definitive treatment has yet been established. We report a case of Riedel's thyroiditis treated without complications using microscopic surgery. A 54-year-old man visited our clinic presenting with neck tightness and a left neck mass. A gun biopsy revealed a benign thyroid mass, although the radiologic findings showed a malignant thyroid tumor with invasion into the trachea and strap muscles. The patient underwent a left hemi-thyroidectomy and shaving of the trachea, esophagus and recurrent laryngeal nerve under microscopy. The final pathology revealed Riedel's thyroiditis combined with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The patient had symptomatic relief without vocal fold paralysis and hypocalcemia. Surgical treatment using microscopic dissection can be considered to be one of treatment option for Riedel's thyroiditis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yasmeen T, Khan S, Patel SG, Reeves WA, Gonsch FA, de Bustros A, et al. Clinical case seminar: Riedel's thyroiditis: report of a case complicated by spontaneous hypoparathyroidism, recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and Horner's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87(8):3543–3547.
Article2. Julie C, Vieillefond A, Desligneres S, Schaison G, Grunfeld JP, Franc B. Hashimoto's thyroiditis associated with Riedel's thyroiditis and retroperitoneal fibrosis. Pathol Res Pract. 1997; 193(8):573–577. discussion 8.
Article3. Heufelder AE, Hay ID. Evidence for autoimmune mechanisms in the evolution of invasive fibrous thyroiditis (Riedel's struma). Clin Investig. 1994; 72(10):788–793.
Article4. Dahlgren M, Khosroshahi A, Nielsen GP, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Riedel's thyroiditis and multifocal fibrosclerosis are part of the IgG4-related systemic disease spectrum. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62(9):1312–1318.
Article5. Frankenthaler R, Batsakis JG, Suarez PA. Tumefactive fibroinflammatory lesions of the head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993; 102(6):481–482.
Article6. Baloch ZW, Feldman MD, LiVolsi VA. Combined Riedel's disease and fibrosing hashimoto's thyroiditis: a report of three cases with two showing coexisting papillary carcinoma. Endocr Pathol. 2000; 11(2):157–163.
Article7. Hao SP, Chen JF, Yen KC. Riedel's thyroiditis associated with follicular carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1999; 256(9):470–472.
Article8. Hostalet F, Hellin D, Ruiz JA. Tumefactive fibroinflammatory lesion of the head and neck treated with steroids: a case report. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2003; 260(4):229–231.
Article9. Bagnasco M, Passalacqua G, Pronzato C, Albano M, Torre G, Scordamaglia A. Fibrous invasive (Riedel's) thyroiditis with critical response to steroid treatment. J Endocrinol Invest. 1995; 18(4):305–307.
Article10. Hennessey JV. Clinical review: Riedel's thyroiditis: a clinical review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96(10):3031–3041.11. Fatourechi MM, Hay ID, McIver B, Sebo TJ, Fatourechi V. Invasive fibrous thyroiditis (Riedel thyroiditis): the Mayo Clinic experience, 1976-2008. Thyroid. 2011; 21(7):765–772.
Article12. Papi G, Corrado S, Cesinaro AM, Novelli L, Smerieri A, Carapezzi C. Riedel's thyroiditis: clinical, pathological and imaging features. Int J Clin Pract. 2002; 56(1):65–67.13. Ng SA, Corcuera-Solano I, Gurudutt VV, Som PM. A rare case of Reidel thyroiditis with associated vocal cord paralysis: CT and MR imaging features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32(11):E201–E202.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Riedel's Thyroiditis in a Patient with a History of Subacute Thyroiditis
- Riedel Thyroiditis in a Patient with Graves Disease
- A case of Riedel's thyroiditis
- Invasive Fibrous (Riedel's) Thyroiditis
- Case of concurrent Riedel's thyroiditis, acute suppurative thyroiditis, and micropapillary carcinoma