Blood Res.
2017 Mar;52(1):69-71. 10.5045/br.2017.52.1.69.
Is N-acetylcysteine infusion an effective treatment option in L-asparaginase associated hepatotoxicity?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, EskiÅŸehir Osmangazi University, Faculty of Medicine, EskiÅŸehir, Turkey. efecanan@yahoo.com
- 2Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Faculty of Medicine, EskiÅŸehir Osmangazi University, EskiÅŸehir, Turkey.
- KMID: 2375209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2017.52.1.69
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
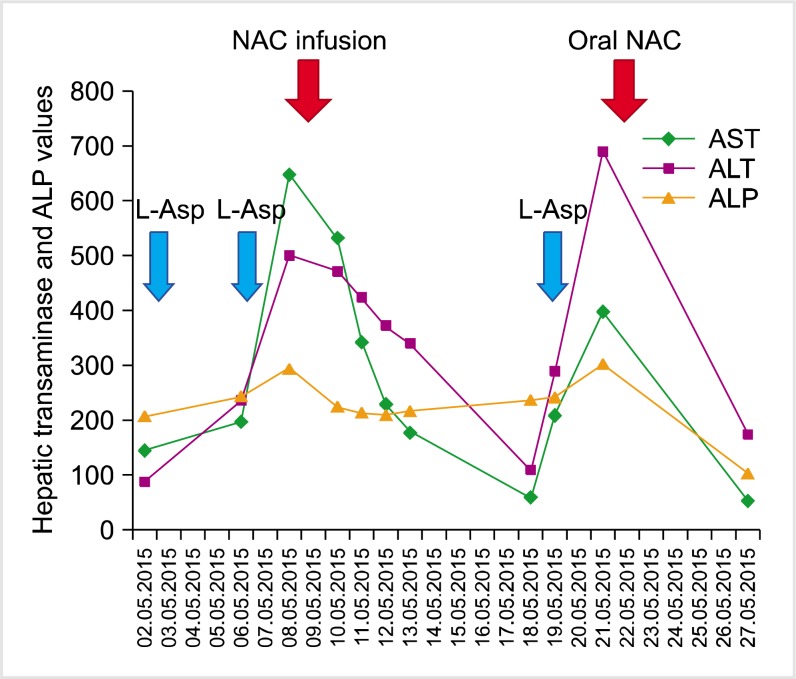
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clavell LA, Gelber RD, Cohen HJ, et al. Four-agent induction and intensive asparaginase therapy for treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1986; 315:657–663. PMID: 2943992.
Article2. Roesmann A, Afify M, Panse J, Eisert A, Steitz J, Tolba RH. L-carnitine ameliorates L-asparaginase-induced acute liver toxicity in steatotic rat livers. Chemotherapy. 2013; 59:167–175. PMID: 24192517.
Article3. Alshiekh-Nasany R, Douer D. L-Carnitine for treatment of pegasparaginase-induced hepatotoxicity. Acta Haematol. 2016; 135:208–210. PMID: 26841296.
Article4. Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et al. Successful treatment of L-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014; 55:1670–1674. PMID: 24090500.5. Pratt CB, Johnson WW. Duration and severity of fatty metamorphosis of the liver following L-asparaginase therapy. Cancer. 1971; 28:361–364. PMID: 5109448.
Article6. Durden DL, Salazar AM, Distasio JA. Kinetic analysis of hepatotoxicity associated with antineoplastic asparaginases. Cancer Res. 1983; 43:1602–1605. PMID: 6339039.7. Tsuji F, Miyake Y, Aono H, Kawashima Y, Mita S. Effects of bucillamine and N-acetyl-L-cysteine on cytokine production and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1999; 115:26–31. PMID: 9933417.
Article8. Firpi RJ, Nelson DR. Viral hepatitis: manifestations and management strategy. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006; 375–380. PMID: 17124086.
Article9. Nazer LH, Nazer HM. Drug-induced liver injury. In : Elzouki AY, Harfi HA, Nazer H, Oh W, Stapleton FB, Whitley RJ, editors. Textbook of clinical pediatrics. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer;2012. p. 2113–2117.10. Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999. p. 673–709.11. Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ. Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2002; 65:166–176. PMID: 11812920.
Article12. Marí M, Morales A, Colell A, García-Ruiz C, Kaplowitz N, Fernandez-Checa JC. Mitochondrial glutathione: features, regulation and role in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830:3317–3328. PMID: 23123815.
Article13. Baumgardner JN, Shankar K, Hennings L, Albano E, Badger TM, Ronis MJ. N-acetylcysteine attenuates progression of liver pathology in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Nutr. 2008; 138:1872–1879. PMID: 18806095.
Article14. Samuhasaneeto S, Thong-Ngam D, Kulaputana O, Patumraj S, Klaikeaw N. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on oxidative stress in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007; 90:788–797. PMID: 17487136.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- N-acetylcysteine for Acetaminophen Poisoning Without Hepatotoxicity: the Effect on the Prothrombin Time
- Acetaminophen Poisoning
- The Clinical Use of the Plasma Acetaminophen Halflife in NAC-treated Acetaminophen Overdose
- Effectiveness of premedication and rapid desensitization in hypersensitivity to L-asparaginase
- Oral vs. Intravenous Administration of N-acetylcysteine in the Acetaminophen Poisoning