Korean J Gastroenterol.
2015 Oct;66(4):190-193. 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.4.190.
Colonoscopic Tattooing of Colonic Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimwonho@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2373340
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2015.66.4.190
Abstract
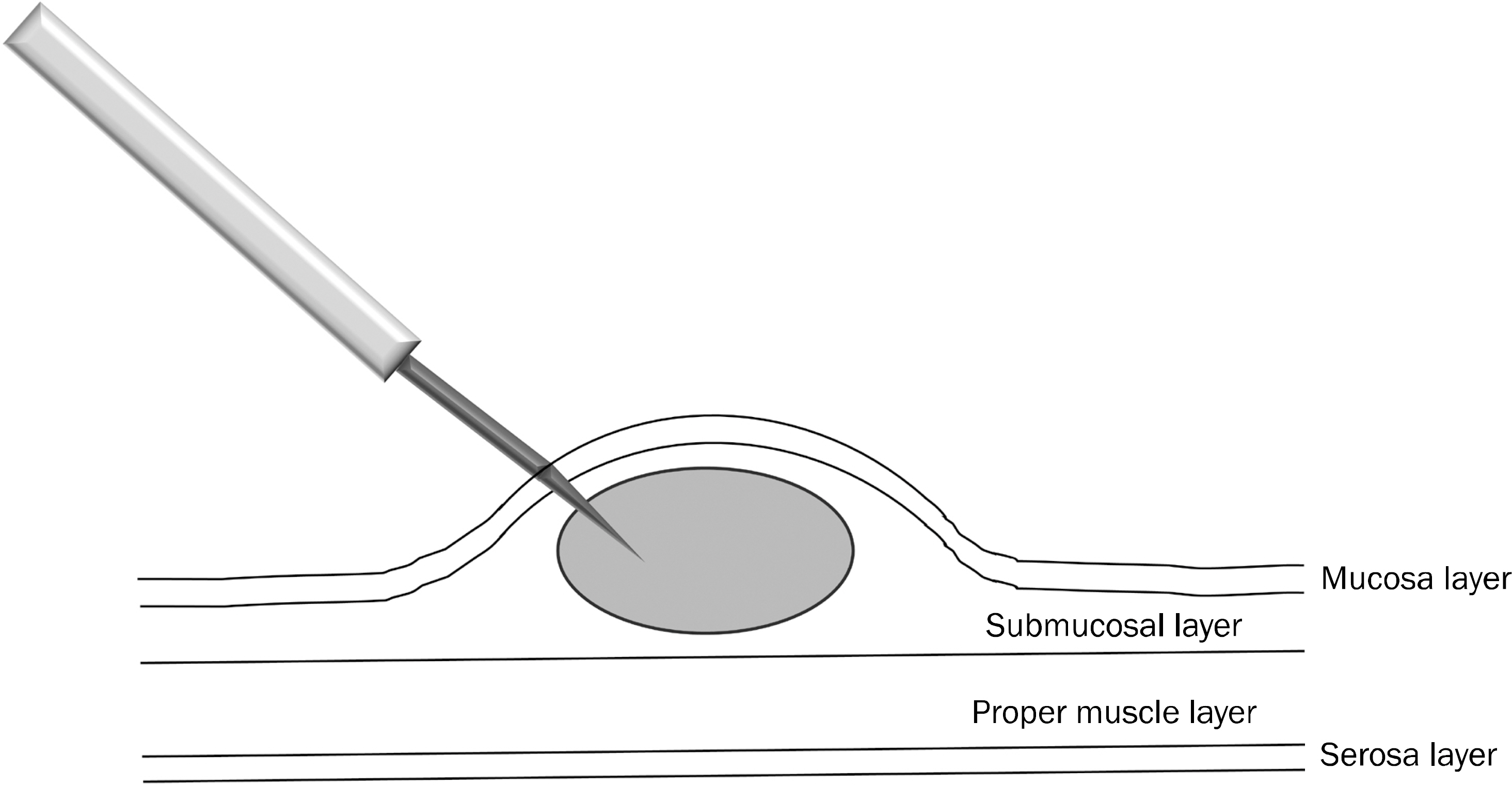
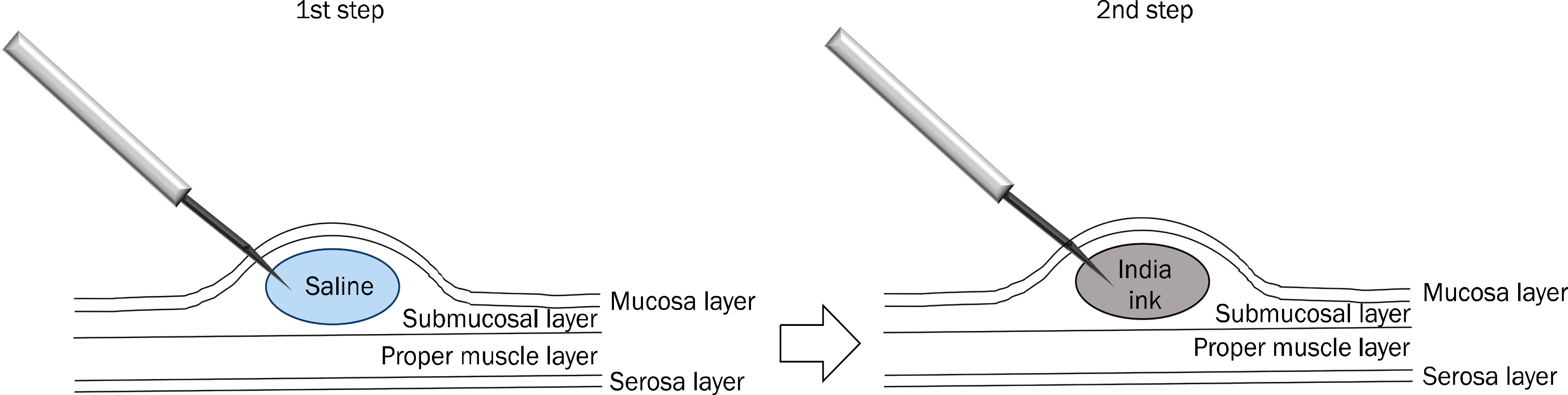
- With the development of minimal invasive surgery including laparoscopic and robot surgery, colonoscopic tattooing of colonic lesions is becoming more important to ensure easy localization of the lesion during surgery. Lack of accurate lesion identification during minimal invasive surgery may lead to resection of wrong segment of the bowel. In this article, some topics including proper materials, injection technique, and safety of colonoscopic tattooing are reviewed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Vignati P, Welch JP, Cohen JL. Endoscopic localization of colon cancers. Surg Endosc. 1994; 8:1085–1087.
Article2. Solon JG, Al-Azawi D, Hill A, Deasy J, McNamara DA. Colonoscopy and computerized tomography scan are not sufficient to localize right-sided colonic lesions accurately. Colorectal Dis. 2010; 12:e267–e272.
Article3. Ponsky JL, King JF. Endoscopic marking of colonic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1975; 22:42–43.
Article4. Nizam R, Siddiqi N, Landas SK, Kaplan DS, Holtzapple PG. Colonic tattooing with India ink: benefits, risks, and alternatives. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:1804–1808.5. Kethu SR, Banerjee S, Desilets D, et al. ASGE Technology Committee. Endoscopic tattooing. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:681–685.
Article6. Hammond DC, Lane FR, Welk RA, Madura MJ, Borreson DK, Passinault WJ. Endoscopic tattooing of the colon. An experimental study. Am Surg. 1989; 55:457–461.7. Askin MP, Waye JD, Fiedler L, Harpaz N. Tattoo of colonic neoplasms in 113 patients with a new sterile carbon compound. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:339–342.
Article8. Beretvas RI, Ponsky J. Endoscopic marking: an adjunct to laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery. Surg Endosc. 2001; 15:1202–1203.
Article9. Miyoshi N, Ohue M, Noura S, et al. Surgical usefulness of in-docyanine green as an alternative to India ink for endoscopic marking. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:347–351.
Article10. Hammond DC, Lane FR, Mackeigan JM, Passinault WJ. Endoscopic tattooing of the colon: clinical experience. Am Surg. 1993; 59:205–210.11. Tabibian N, Michaletz PA, Schwartz JT, et al. Use of an endoscopically placed clip can avoid diagnostic errors in colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988; 34:262–264.
Article12. Elarini T, Wexner SD, Isenberg GA. The need for standardization of colonoscopic tattooing of colonic lesions. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015; 58:264–267.
Article13. Frager DH, Frager JD, Wolf EL, Beneventano TC. Problems in the colonoscopic localization of tumors: continued value of the barium enema. Gastrointest Radiol. 1987; 12:343–346.
Article14. Lee SH, Kim do Y, Oh SY, Lee KJ, Suh KW. Preoperative localization of early colorectal cancer or a malignant polyp by using the patient's own blood. Ann Coloproctol. 2014; 30:115–117.
Article15. Jeong O, Cho SB, Joo YE, Ryu SY, Park YK. Novel technique for intraoperative tumor localization during totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy: endoscopic autologous blood tattooing. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:1778–1783.
Article16. Botoman VA, Pietro M, Thirlby RC. Localization of colonic lesions with endoscopic tattoo. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994; 37:775–776.
Article17. Sawaki A, Nakamura T, Suzuki T, et al. A two-step method for marking polypectomy sites in the colon and rectum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:735–737.
Article18. Fu KI, Fujii T, Kato S, et al. A new endoscopic tattooing technique for identifying the location of colonic lesions during laparoscopic surgery: a comparison with the conventional technique. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:687–691.
Article19. Hyman N, Waye JD. Endoscopic four quadrant tattoo for the identification of colonic lesions at surgery. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:56–58.
Article20. McArthur CS, Roayaie S, Waye JD. Safety of preoperation endoscopic tattoo with india ink for identification of colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 1999; 13:397–400.
Article21. Shatz BA, Weinstock LB, Swanson PE, Thyssen EP. Longterm safety of India ink tattoos in the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 45:153–156.
Article22. Park SI, Genta RS, Romeo DP, Weesner RE. Colonic abscess and focal peritonitis secondary to india ink tattooing of the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:68–71.
Article23. Gopal DV, Morava-Protzner I, Miller HA, Hemphill DJ. Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease associated with colonic tattooing with india ink preparation–case report and review of literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49:636–639.
Article24. Coman E, Brandt LJ, Brenner S, Frank M, Sablay B, Bennett B. Fat necrosis and inflammatory pseudotumor due to endoscopic tattooing of the colon with india ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:65–68.
Article25. Alba LM, Pandya PK, Clarkston WK. Rectus muscle abscess associated with endoscopic tattooing of the colon with India ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:557–558.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Small Efforts Can Prevent Big Mistakes: Preoperative Colonoscopic Tattooing Using Indocyanine Green
- Preoperative localization of potentially invisible colonic lesions on the laparoscopic operation field: using autologous blood tattooing
- Accuracy evaluation of preoperative indocyanine green tattooing and intraoperative colonoscopy in determining surgical resection margins for left-sided colorectal cancer: a retrospective study in Korea
- Preoperative Colonoscopic Tattooing with Autologous Blood in Laparoscopic Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Red-Flagging for an Invisible Enemy
- Preoperative Tattooing Using Indocyanine Green in Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery