J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Mar;76(3):216-220. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.3.216.
Isolated Bronchial Artery Involvement by Polyarteritis Nodosa Presenting as Hemoptysis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. jhkwon17@naver.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2371689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.3.216
Abstract
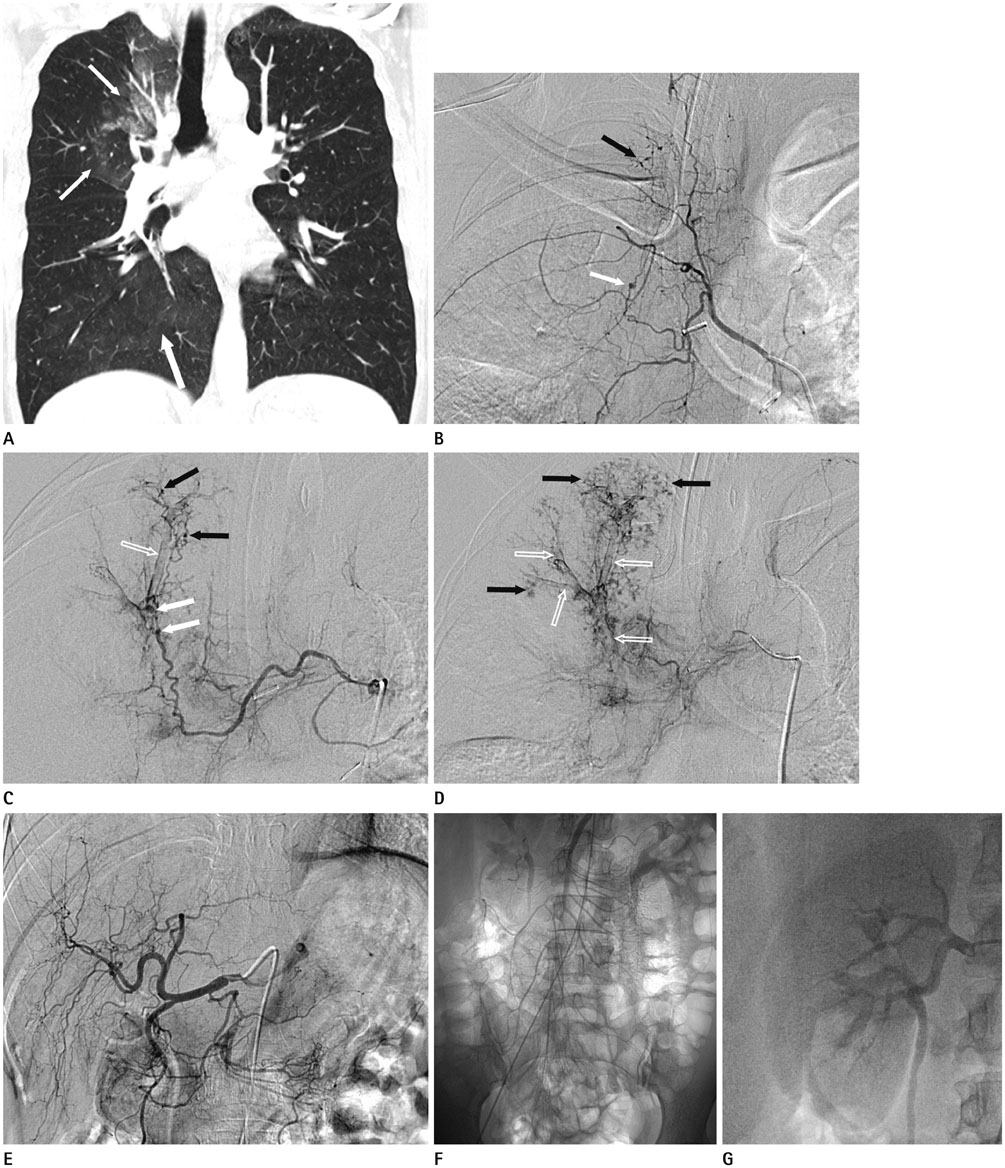
- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing vasculitis that involves medium- and small-sized arteries. PAN may affect any organ, and the presenting symptom of PAN varies depending on the organs affected. However, PAN generally spares the lung; thus, a report of PAN involving the bronchial artery is extremely rare, and hemoptysis has not been reported as the sole presenting symptom. Here, we report the case of a 39-year-old woman with hemoptysis who was diagnosed with PAN involving only the bronchial artery by angiography without involvement of the visceral arteries. Details of this case and a literature review are presented.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colmegna I, Maldonado-Cocco JA. Polyarteritis nodosa revisited. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2005; 7:288–296.2. Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Zvaifler NJ, McShane DJ, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1088–1093.3. Pagnoux C, Seror R, Henegar C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Le Guern V, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: a systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French Vasculitis Study Group Database. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:616–626.4. Stone JH. Polyarteritis nodosa. JAMA. 2002; 288:1632–1639.5. Lee YJ, Park SS, Kim SY, Lee JY, Koo HK, Yoon HI. A case of systemic polyarteritis nodosa involving bronchial artery. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2010; 27:164–168.6. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 37:187–192.7. Matsumoto T, Homma S, Okada M, Kuwabara N, Kira S, Hoshi T, et al. The lung in polyarteritis nodosa: a pathologic study of 10 cases. Hum Pathol. 1993; 24:717–724.8. Hernández-Rodríguez J, Alba MA, Prieto-González S, Cid MC. Diagnosis and classification of polyarteritis nodosa. J Autoimmun. 2014; 48-49:84–89.9. Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:222–227.10. Guillevin L, Cohen P, Mahr A, Arène JP, Mouthon L, Puéchal X, et al. Treatment of polyarteritis nodosa and microscopic polyangiitis with poor prognosis factors: a prospective trial comparing glucocorticoids and six or twelve cyclophosphamide pulses in sixty-five patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 49:93–100.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa in Childhood
- A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa Presented as Myositis
- Failure of Conservative Treatment in Two Cases of Polyarteritis Nodosa with Superior Mesenteric Artery Involvement Presenting with Abdominal Pain
- A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa Associated with Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Ischemic Pseudomembranous Colitis with Perforation due to Polyarteritis Nodosa