J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2016 Dec;32(4):351-357. 10.14368/jdras.2016.32.4.351.
Maxillofacial rehabilitation of adenoid cystic carcinoma patient using full mouth fixed implant and pharyngeal obturator: a clinical report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. mcnihil@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2369077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2016.32.4.351
Abstract
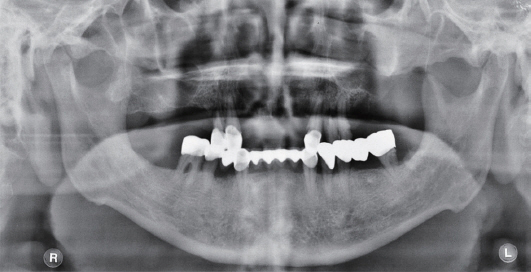
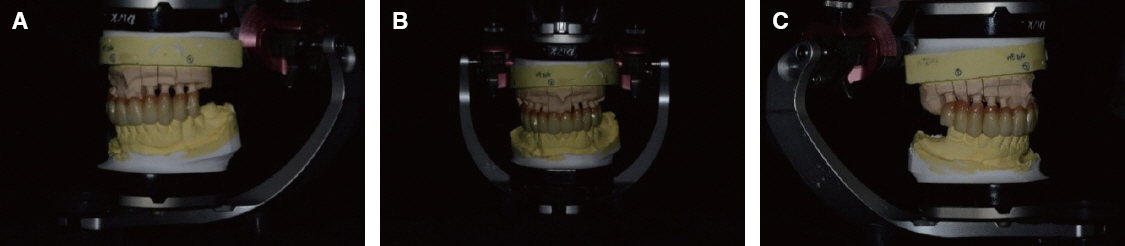
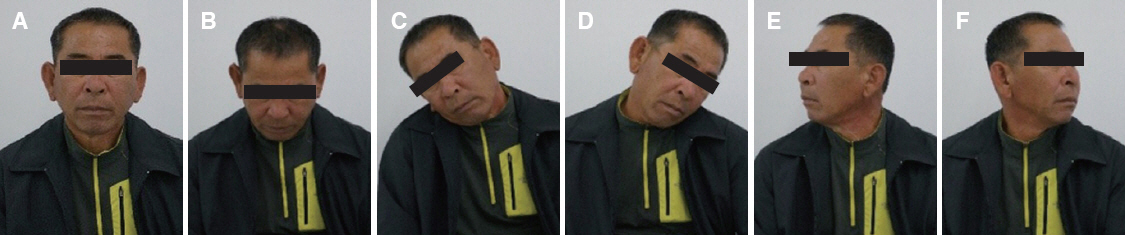
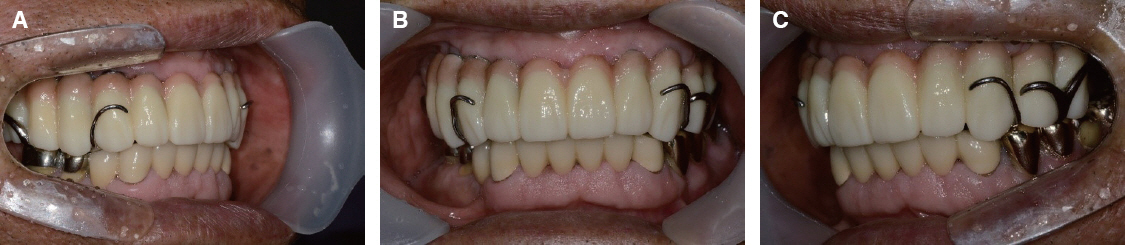
- Rehabilitation of maxillectomy patients is challenging. The maxillary defects need to functional restoration because of mastication, speech, swallowing problems. The goal of making obturator is to restore maxillary defects and give patients comfortable, esthetic prosthesis. This case report presents acquired masticatory and esthetic results and improved retention resulting from the pharyngeal obturator prosthesis using implant.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Strong EW. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary origin. A clinicopathologic study of 242 cases. Am J Surg. 1974; 128:512–20. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90265-7.2. Haralur SB, Shah FK. Prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient with adenoid cystic carcinoma with continuous orbital-maxillary defect. BMJ Case Rep 2013. Apr. 18. 2013; bcr2013009313. doi:10.1136/bcr2013-009313.3. Brown KE. Clinical considerations improving obturator treatment. J Prosthet Dent. 1970; 24:461–6. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(70)90085-5.4. Brown KE. Peripheral consideration in improving obturator retention. J Prosthet Dent. 1968; 20:17681. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(68)90143-1.5. Eckert SE, Desjardins RP, Taylor TD. Clinical maxillofacial prosthetics. 1st ed. Chicago: Quintessence publishing;2000. p. 125–31.6. Keyf F. Obturator prostheses for hemimaxillectomy patients. J Oral Rehabil. 2001; 28:821–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2001.00754.x. PMID: 11580820.7. Esposito SJ, Rieger J, Beumer J. Rehabilitation of soft palate defects. Beumer J, Marunick MT, Esposito SJ, editors. Maxillofacial rehabilitation: prosthodontic and surgical management of cancer-related, acquired, and congenital defects of the head and neck. 3rd ed. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing;2011. p. 213.8. Ackerman AJ. The prosthetic management of oral and facial defects following cancer surgery. J Prosthet Dent. 1955; 5:413–32. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(55)90050-0.9. Desjardins RP. Obturator prosthesis design for acquired maxillary defects. J Prosthet Dent. 1978; 39:424–35. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3913(78)80161-9.10. Kaires AK. Effect of partial denture design on bilateral force distribution. J Prosthet Dent. 1956; 6:373–85. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(56)90058-0.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Full-mouth rehabilitation by immediate implantation combined with orthognathic surgery: a clinical report
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma presenting as an ulcer on the floor of the mouth: a rare case report
- Full mouth fixed implant rehabilitation in a patient with generalized aggressive periodontitis
- Full mouth rehabilitation of fully edentulous patient with implant-supported fixed prosthesis preceding bone graft: A case report
- Palliative Radiotherapy in a Patient with Pulmonary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma