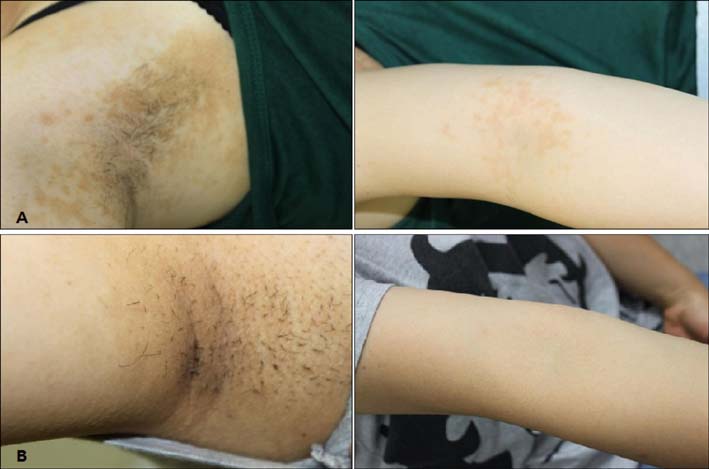
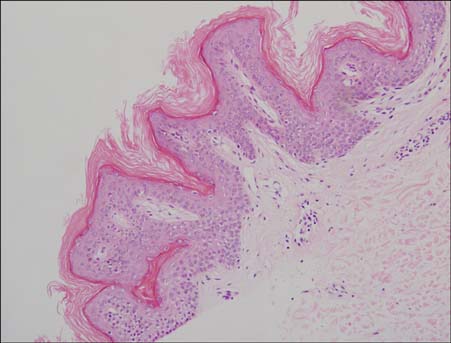
Ann Dermatol.
2014 Jun;26(3):409-410.
Updated Diagnosis Criteria for Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hsyoon79@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. A study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 154:287–293.
Article2. Lee D, Cho KJ, Hong SK, Seo JK, Hwang SW, Sung HS. Two cases of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis with an unusual location. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009; 89:84–85.
Article3. Davis RF, Harman KE. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis successfully treated with amoxicillin. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:583–584.
Article4. Kim MR, Kim SC. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis on the arm successfully treated with minocycline. J Dermatol. 2010; 37:749–750.
Article5. Stein JA, Shin HT, Chang MW. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis associated with tinea versicolor in three siblings. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005; 22:331–333.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis: Treatment with Etretinate
- A Case of Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis Treated with Oral Isotretinoin
- Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis without Papillomatosis
- Three Cases of Concomitant Acanthosis Nigricans with Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis in Obese Patients
- Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis Limited to the Forearm