Hip Pelvis.
2016 Dec;28(4):201-207. 10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.201.
Accuracy and Reliability of Preoperative On-screen Templating Using Digital Radiographs for Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. kuentak@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2364697
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.201
Abstract
- PURPOSE
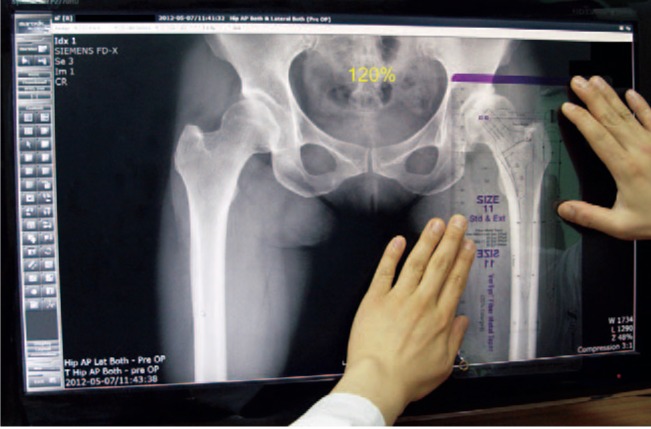
Preoperative on-screen templating is a method of using acetate templates on digital images. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the accuracy, intra- and interobserver reliabilities of preoperative on-screen templating using digital radiographs for total hip arthroplasty (THA).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two hundred patients with hip disease who were treated with primary cementless THA were retrospectively evaluated. The accuracy of on-screen templating was assessed by comparing the predicted prosthesis sizes with the actual sizes used operatively. The inter- and intraobserver reliabilities of the templating results were also evaluated.
RESULTS
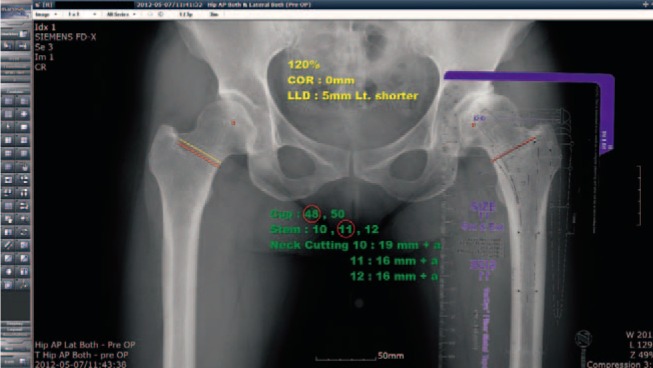
The prosthesis prediction accuracy within ±one size was 96.6% for the cup size and 97.8% for the stem size. The inter- and intraobserver reliabilities for the implant size were substantial (kappa>0.70). The intra- and interobserver reliabilities for the leg length discrepancy and femoral offset difference using the intraclass correlation coefficient ranged from 0.89 to 0.97.
CONCLUSION
Preoperative on-screen templating using digital radiographs showed substantial accuracy and reliability for implant prediction. It is an effective method for predicting the size of implant, correcting the leg length discrepancy and restoring the femoral offset.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Three-dimensional-printing Technology in Hip and Pelvic Surgery: Current Landscape
Seong-Hwan Woo, Myung-Jin Sung, Kyung-Soon Park, Taek-Rim Yoon
Hip Pelvis. 2020;32(1):1-10. doi: 10.5371/hp.2020.32.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Crooijmans HJ, Laumen AM, van Pul C, van Mourik JB. A new digital preoperative planning method for total hip arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:909–916. PMID: 18781367.
Article2. Iorio R, Siegel J, Specht LM, Tilzey JF, Hartman A, Healy WL. A comparison of acetate vs digital templating for preoperative planning of total hip arthroplasty: is digital templating accurate and safe? J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:175–179. PMID: 18534425.3. Suh KT, Cheon SJ, Kim DW. Comparison of preoperative templating with postoperative assessment in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004; 75:40–44. PMID: 15022804.
Article4. Unnanuntana A, Wagner D, Goodman SB. The accuracy of preoperative templating in cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:180–186. PMID: 18534455.
Article5. Archibeck MJ, Cummins T, Tripuraneni KR, et al. Inaccuracies in the use of magnification markers in digital hip radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474:1812–1817. PMID: 26797909.
Article6. Charles MN, Bourne RB, Davey JR, Greenwald AS, Morrey BF, Rorabeck CH. Soft-tissue balancing of the hip: the role of femoral offset restoration. Instr Course Lect. 2005; 54:131–141. PMID: 15948440.7. Gamble P, de Beer J, Petruccelli D, Winemaker M. The accuracy of digital templating in uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:529–532. PMID: 19493647.
Article8. González Della Valle A, Comba F, Taveras N, Salvati EA. The utility and precision of analogue and digital preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008; 32:289–294. PMID: 17404731.
Article9. The B, Diercks RL, van Ooijen PM, van Horn JR. Comparison of analog and digital preoperative planning in total hip and knee arthroplasties. A prospective study of 173 hips and 65 total knees. Acta Orthop. 2005; 76:78–84. PMID: 15788312.10. Kim MS, Jeong MC, Ji NG, Lee JS, Kim JI, Suh KT. Preoperative templating in PACS for total hip replacement. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011; 46:472–477.
Article11. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174. PMID: 843571.
Article12. Bono JV. Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A(Suppl 2):118–122.
Article13. Krishnamoorthy VP, Perumal R, Daniel AJ, Poonnoose PM. Accuracy of templating the acetabular cup size in Total Hip Replacement using conventional acetate templates on digital radiographs. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015; 6:215–219. PMID: 26566332.
Article14. Berstock JR, Webb JC, Spencer RF. A comparison of digital and manual templating using PACS images. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:73–74. PMID: 20056068.
Article15. Meyer C, Kotecha A, Richards O, Isbister E. Acetate templating for total hip arthroplasty using PACS. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2009; 91:162–163. PMID: 19317940.
Article16. Oddy MJ, Jones MJ, Pendegrass CJ, Pilling JR, Wimhurst JA. Assessment of reproducibility and accuracy in templating hybrid total hip arthroplasty using digital radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:581–585. PMID: 16645101.
Article17. Petretta R, Strelzow J, Ohly NE, Misur P, Masri BA. Acetate templating on digital images is more accurate than computer-based templating for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473:3752–3759. PMID: 25910779.
Article18. Whiddon DR, Bono JV. Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2008; 57:273–279. PMID: 18399591.19. Bertz A, Indrekvam K, Ahmed M, Englund E, Sayed-Noor AS. Validity and reliability of preoperative templating in total hip arthroplasty using a digital templating system. Skeletal Radiol. 2012; 41:1245–1249. PMID: 22588597.
Article20. Davila JA, Kransdorf MJ, Duffy GP. Surgical planning of total hip arthroplasty: accuracy of computer-assisted EndoMap software in predicting component size. Skeletal Radiol. 2006; 35:390–393. PMID: 16572344.
Article21. Eggli S, Pisan M, Müller ME. The value of preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:382–390. PMID: 9619923.
Article22. Knight JL, Atwater RD. Preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Quantitating its utility and precision. J Arthroplasty. 1992; 7(Suppl):403–409. PMID: 1431923.23. Kumar PG, Kirmani SJ, Humberg H, Kavarthapu V, Li P. Reproducibility and accuracy of templating uncemented THA with digital radiographic and digital TraumaCad templating software. Orthopedics. 2009; 32:815. PMID: 19902895.
Article24. Shaarani SR, McHugh G, Collins DA. Accuracy of digital preoperative templating in 100 consecutive uncemented total hip arthroplasties: a single surgeon series. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:331–337. PMID: 22854351.25. Steinberg EL, Shasha N, Menahem A, Dekel S. Preoperative planning of total hip replacement using the TraumaCad™ system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130:1429–1432. PMID: 20069428.
Article26. Bracey DN, Seyler TM, Shields JS, Leng X, Jinnah RH, Lang JE. A comparison of acetate and digital templating for hip resurfacing. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014; 43:E19–E24. PMID: 24490189.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Conventional and Digital Templating Technique in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Comparison of Digital Templating with Manual Templating for Total hip Replacement
- Surgeon’s Experience and Accuracy of Preoperative Digital Templating in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Useful Method for Minimizing Leg Length Discrepancies in Hip Arthroplasty: Use of an Intraoperative X-ray
- Preoperative Templating in PACS for Total Hip Replacement