Ann Lab Med.
2015 Nov;35(6):660-662. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.660.
Anti-Rods and Rings Autoantibodies in a Patient With Hepatitis C Virus Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. limyoung@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2363275
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.660
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
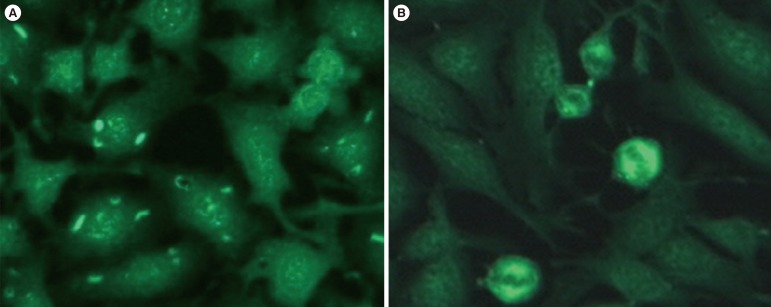
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vermeersch P, Bossuyt X. Prevalence and clinical significance of rare antinuclear antibody patterns. Autoimmun Rev. 2013; 12:998–1003. PMID: 23583982.
Article2. Liberal R, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Clinical significance of autoantibodies in autoimmune hepatitis. J Autoimmun. 2013; 46:17–24. PMID: 24016388.
Article3. Carcamo WC, Ceribelli A, Calise SJ, Krueger C, Liu C, Daves M, et al. Differential reactivity to IMPDH2 by anti-rods/rings autoantibodies and unresponsiveness to pegylated interferon-alpha/ribavirin therapy in US and Italian HCV patients. J Clin Immunol. 2013; 33:420–426. PMID: 23100146.
Article4. Covini G, Carcamo WC, Bredi E, von Mühlen CA, Colombo M, Chan EK. Cytoplasmic rods and rings autoantibodies developed during pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther. 2012; 17:805–811. PMID: 22293655.
Article5. Carcamo WC, Satoh M, Kasahara H, Terada N, Hamazaki T, Chan JY, et al. Induction of cytoplasmic rods and rings structures by inhibition of the CTP and GTP synthetic pathway in mammalian cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e29690. PMID: 22220215.
Article6. Stinton LM, Myers RP, Coffin CS, Fritzler MJ. Clinical associations and potential novel antigenic targets of autoantibodies directed against rods and rings in chronic hepatitis C infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013; 13:50. PMID: 23506439.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- A Study of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Patients with Hand Eczema
- Pre-S Defective Hepatitis B Virus in Patients with Acute and chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- A Case of Acute Transverse Myelitis with Hepatitis B Virus Infection