J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Apr;42(2):99-104. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.2.99.
Evaluation of safety and usefulness of submental intubation in panfacial trauma surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, ESIC Medical College and Postgraduates Institute of Medical Sciences and Research (PGIMSR), Chennai, India. mona13omfs@gmail.com
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, ESIC Medical College and Postgraduates Institute of Medical Sciences and Research (PGIMSR), Chennai, India.
- KMID: 2351732
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.2.99
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
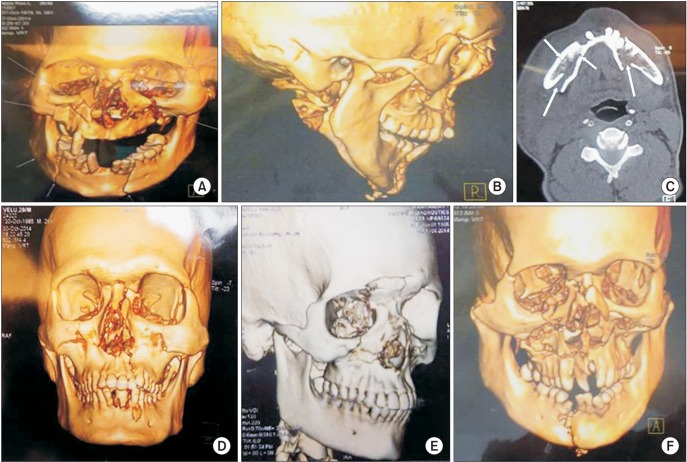
Submental intubation has been advocated as an alternative to classical tracheostomy for certain indicated panfacial trauma surgeries. Surgeons should have various options for airway management in maxillofacial trauma patients. Most maxillofacial injuries involve occlusal derangements, which might require intraoperative occlusal corrections; hence, orotracheal intubation is not ideal. Maxillofacial surgeons generally prefer nasotracheal intubation; however, in cases with concomitant skull base fracture or nasal bone fracture, nasotracheal intubation might not be suitable; in these situations, tracheostomy is typically performed. However, the possible complications of tracheostomy are well known. Due to trauma situations and to avoid the complications of tracheostomy, submental intubation would be an ideal alternative procedure in selected maxillofacial trauma surgery patients. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and usefulness of a submental intubation technique for panfacial trauma surgery. Moreover, we intended to share our experience of submental intubation and to recommend this simple, safe procedure for certain panfacial trauma surgeries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
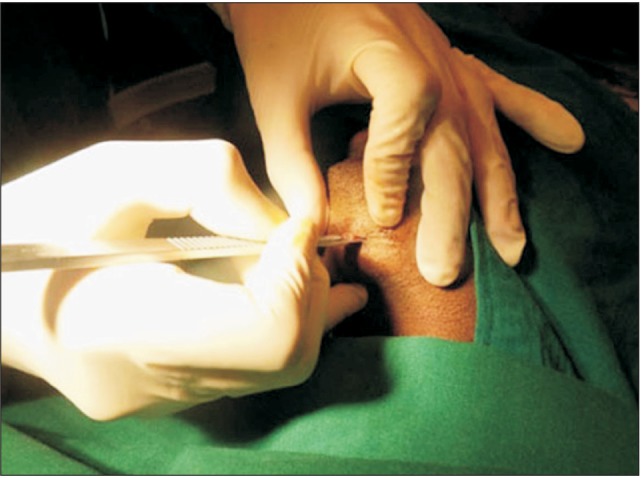
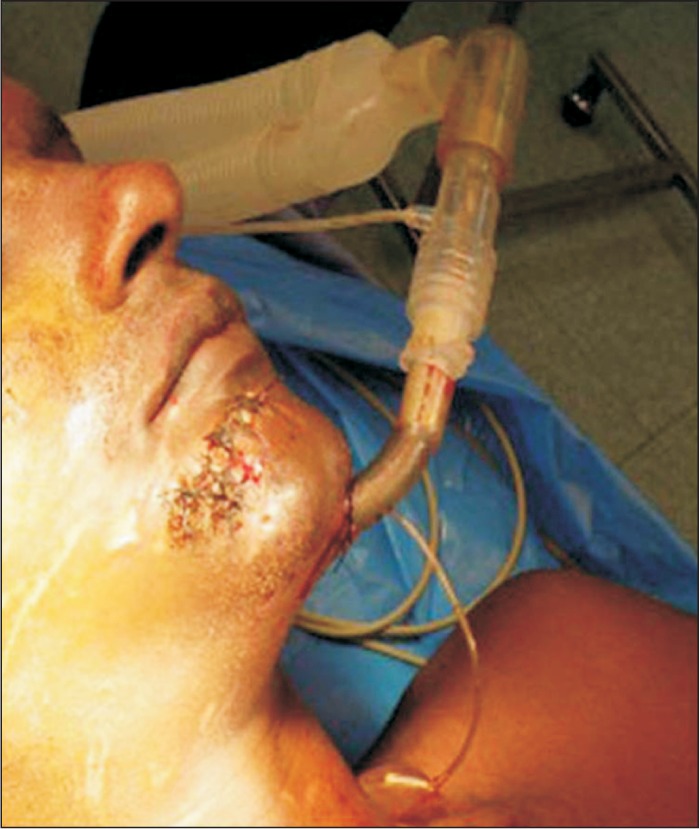
In five panfacial trauma patients, we performed submental intubation for airway management; the mean time required for the procedure was only eight minutes.
RESULTS
We were able to execute this procedure safely in a short time without any intraoperative or postoperative complications.
CONCLUSION
Submental intubation is a safe and simple technique for airway management in indicated panfacial trauma surgery patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Airway management through submental derivation: a safe and easily reproduced alternative for patients with complex facial trauma
Fernando González-Magaña, Héctor Omar Malagón-Hidalgo, Eugenio García-Cano, Roberto Vilchis-López, Adriana Fentanes-Vera, Fernan-Alejandra Ayala-Ugalde
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;44(1):12-17. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.1.12.
Reference
-
1. Hernández Altemir F. The submental route for endotracheal intubation: a new technique. J Maxillofac Surg. 1986; 14:64–65. PMID: 3456416.2. Kar C, Mukherjee S. Submental intubation: an alternative and costeffective technique for complex maxillofacial surgeries. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010; 9:266–269. PMID: 22190802.
Article3. Navaneetham A, Vinod Thangaswamy S, Rao N. Submental intubation: our experience. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010; 9:64–67. PMID: 23139571.
Article4. Taicher S, Givol N, Peleg M, Ardekian L. Changing indications for tracheostomy in maxillofacial trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:292–295. PMID: 8600235.
Article5. Amin M, Dill-Russel P, Manisali M, Lee R, Sinton I. Facial fractures and submental tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia. 2002; 57:1195–1199. PMID: 12479188.
Article6. MacInnis E, Baig M. A modified submental approach for oral endotracheal intubation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999; 28:344–346. PMID: 10535533.
Article7. Agrawal M, Kang LS. Midline submental orotracheal intubation in maxillofacial injuries: a substitute to tracheostomy where postoperative mechanical ventilation is not required. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 26:498–502. PMID: 21547178.8. Rungta N. Technique of retromolar and submental intubation in facio-maxillary trauma patients. Indian J Trauma Anaesth Crit Care. 2007; 8:573–575.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Modified Submental Intubation in Panfacial Bone Fracture Patients
- Submental Intubation in Panfacial Trauma Patient: A Case Report
- Submental intubation: alternative short-term airway management in maxillofacial trauma
- Airway management through submental derivation: a safe and easily reproduced alternative for patients with complex facial trauma
- Modified submental approach to oroendotracheal intubation in patients with panfacial bone fractures