J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Aug;42(4):182-186. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.182.
Mini-plate removal in maxillofacial trauma patients during a five-year retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. sgckim@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2350069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.182
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to analyze the incidence of indications for the removal of mini-plates over a five-year period in maxillofacial trauma patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The medical records of 530 patients who underwent treatment with mini-plate fixation after maxillofacial trauma were reviewed for a five-year period (May 2007 to May 2012). Patients were evaluated concerning the number of mini-plates removed, age and gender distributions, time between insertion and removal, indication for removal, and site of removal.
RESULTS
The plates of 120 patients were removed (26 females and 94 males). The removal rate was 22.6%. The most frequent indication for removal was patient demand (81.7%), followed by tooth extraction (7.5%), and pain (3.3%). The most frequent removal site was the mandible (95.0%).
CONCLUSION
The number of mini-plates removed was small, and the most common indication for removal was patient demand. There is no evidence to support a recommendation for the routine removal of titanium mini-plates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
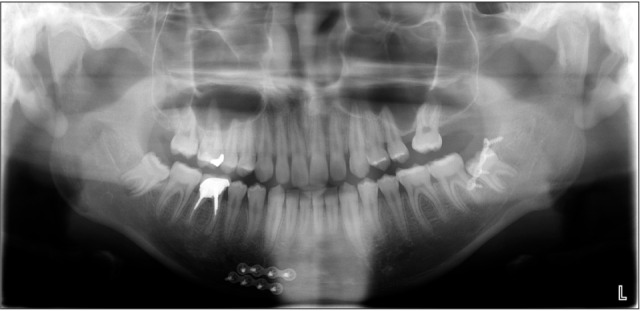
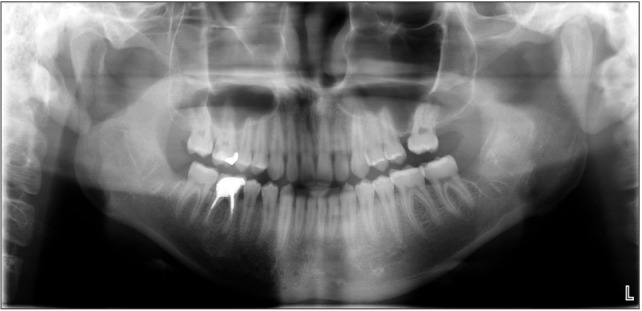
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haug RH. Retention of asymptomatic bone plates used for orthognathic surgery and facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:611–617. PMID: 8632246.
Article2. Champy M, Loddé JP, Schmitt R, Jaeger JH, Muster D. Mandibular osteosynthesis by miniature screwed plates via a buccal approach. J Maxillofac Surg. 1978; 6:14–21. PMID: 274501.
Article3. Breme J, Steinhäuser E, Paulus G. Commercially pure titanium Steinhäuser plate-screw system for maxillofacial surgery. Biomaterials. 1988; 9:310–313. PMID: 3214655.
Article4. Alpert B, Seligson D. Removal of asymptomatic bone plates used for orthognathic surgery and facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:618–621. PMID: 8632247.
Article5. Cawood JI. Small plate osteosynthesis of mandibular fractures. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985; 23:77–91. PMID: 3158338.
Article6. Michelet FX, Deymes J, Dessus B. Osteosynthesis with miniaturized screwed plates in maxillo-facial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg. 1973; 1:79–84. PMID: 4520558.
Article7. Bhatt V, Chhabra P, Dover MS. Removal of miniplates in maxillofacial surgery: a follow-up study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:756–760. PMID: 15944970.
Article8. Brown JS, Trotter M, Cliffe J, Ward-Booth RP, Williams ED. The fate of miniplates in facial trauma and orthognathic surgery: a retrospective study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989; 27:306–315. PMID: 2765458.
Article9. Matthew IR, Frame JW. Policy of consultant oral and maxillofacial surgeons towards removal of miniplate components after jaw fracture fixation: pilot study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999; 37:110–112. PMID: 10371312.
Article10. Islamoglu K, Coskunfirat OK, Tetik G, Ozgentas HE. Complications and removal rates of miniplates and screws used for maxillofacial fractures. Ann Plast Surg. 2002; 48:265–268. PMID: 11862030.
Article11. Nagase DY, Courtemanche DJ, Peters DA. Plate removal in traumatic facial fractures: 13-year practice review. Ann Plast Surg. 2005; 55:608–611. PMID: 16327461.12. Rallis G, Mourouzis C, Papakosta V, Papanastasiou G, Zachariades N. Reasons for miniplate removal following maxillofacial trauma: a 4-year study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2006; 34:435–439. PMID: 16963270.
Article13. Spiessl B. Internal fixation of the mandibule: a manual of AO/ASIF principles. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1989.14. Rosenberg A, Grätz KW, Sailer HF. Should titanium miniplates be removed after bone healing is complete? Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 22:185–188. PMID: 8340633.
Article15. Mosbah MR, Oloyede D, Koppel DA, Moos KF, Stenhouse D. Miniplate removal in trauma and orthognathic surgery--a retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 32:148–151. PMID: 12729774.
Article16. Langford RJ, Frame JW. Surface analysis of titanium maxillofacial plates and screws retrieved from patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002; 31:511–518. PMID: 12418567.
Article17. Winzenburg SM, Imola MJ. Internal fixation in pediatric maxillofacial fractures. Facial Plast Surg. 1998; 14:45–58. PMID: 10371893.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of screw number and length on internal fixation of mandibular fractures
- Treatments of comminuted mandibular fractures
- The Removal of Plates after Craniomaxillofacial Surgery: A Retrospective Study
- Removal of Broken Instruments in Soft Tissue at Mandibular Area Using a Dental Mini C-arm: Case Reports
- Mini-T Plate Fixation for Neer Type II Distal Clavicle Fracture