World J Mens Health.
2016 Aug;34(2):148-152. 10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.2.148.
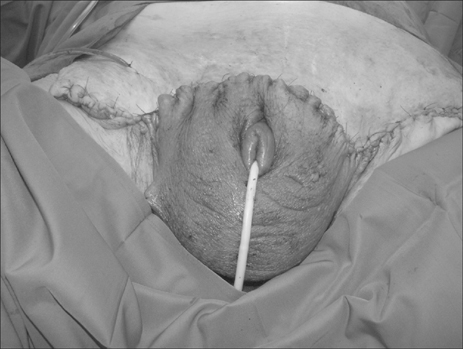
Gigantic Suprapubic Lymphedema: A Case Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany. marcushorstmann@gmx.ch
- 2Institute of Radiology, Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany.
- KMID: 2349852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.2.148
Abstract
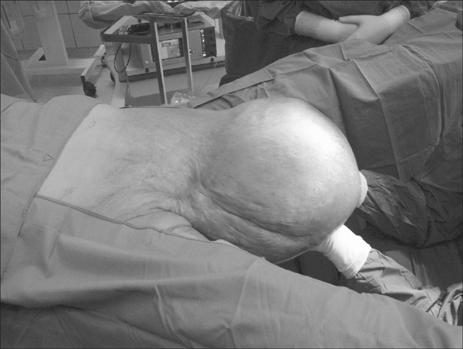
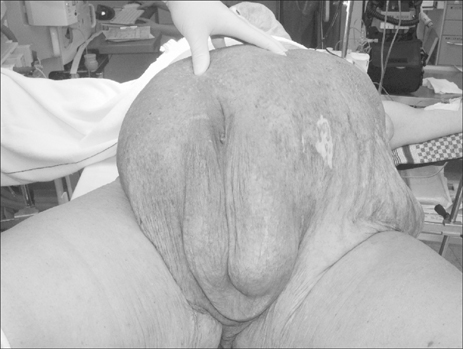
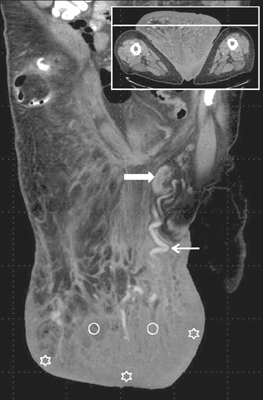
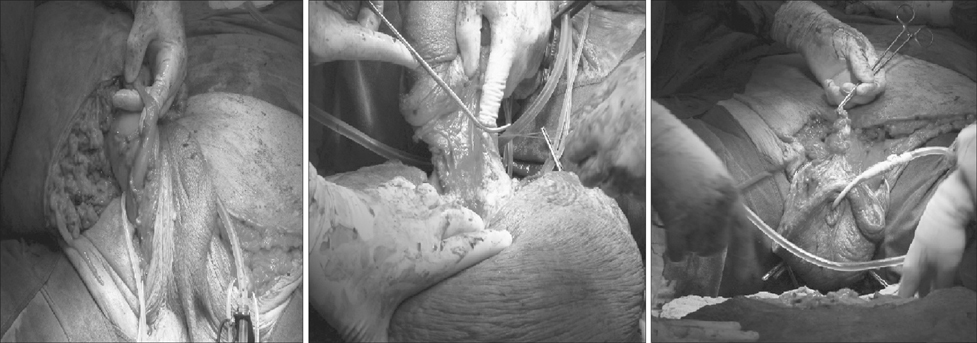
- We present the first case study of idiopathic gigantic suprapubic lymphedema and buried penis treated with puboscrotal reconstruction in a patient with initial extreme obesity after an extensive weight reduction (120 kg). Massive localized lymphedema of the suprapubic region should be differentiated from the scrotal type. Severe lymphedema could not resolve on its own and weight reduction does not seem to be helpful in such cases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chopra K, Tadisina KK, Brewer M, Holton LH, Banda AK, Singh DP. Massive localized lymphedema revisited: a quickly rising complication of the obesity epidemic. Ann Plast Surg. 2015; 74:126–132.2. Brewer MB, Singh DP. Massive localized lymphedema: review of an emerging problem and report of a complex case in the mons pubis. Ann Plast Surg. 2012; 68:101–104.3. Mattsson B, Vollmer C, Schwab C, Padevit C, Horton K, John H, et al. Complications of a buried penis in an extremely obese patient. Andrologia. 2012; 44:Suppl 1. 826–828.
Article4. Hammoud AO, Walker JM, Gibson M, Cloward TV, Hunt SC, Kolotkin RL, et al. Sleep apnea, reproductive hormones and quality of sexual life in severely obese men. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011; 19:1118–1123.
Article5. Jagielski AC, Brown A, Hosseini-Araghi M, Thomas GN, Taheri S. The association between adiposity, mental well-being, and quality of life in extreme obesity. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92859.
Article6. Duval K, Marceau P, Lescelleur O, Hould FS, Marceau S, Biron S, et al. Health-related quality of life in morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2006; 16:574–579.
Article7. Janiszewski PM, Janssen I, Ross R. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity are associated with erectile dysfunction independent of body mass index. J Sex Med. 2009; 6:1990–1998.8. Mehrara BJ, Greene AK. Lymphedema and obesity: is there a link? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 134:154e–160e.9. Garaffa G, Christopher N, Ralph DJ. The management of genital lymphoedema. BJU Int. 2008; 102:480–484.
Article10. Greene AK, Grant FD, Maclellan RA. Obesity-induced lymphedema nonreversible following massive weight loss. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015; 3:e426.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Considerations of Gigantic Lipoma
- A Case of Conjunctival and Lid Lymphedema Confirmed with Lymphoscintigraphy
- Primary (Congenital) Lymphedema of the External Genitalia
- Post Traumatic Chronic Lymphedema: A case report
- Acute Traumatic Lymphedema without Tissue Injury Detected by Lymphoscintigraphy