J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2016 Aug;51(4):301-307. 10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.4.301.
Clinical Results of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation in the Coronal Plane Articular Fracture of the Distal Humerus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. aabga@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- 3Goodssen Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2348636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.4.301
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the surgical outcomes according to the Ring's classification system in patients with the distal humeral coronal plane articular fracture after treatment with open reduction and internal fixation (OR/IF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients with the distal humeral coronal plane articular fracture treated with OR/IF in the three hospitals were reviewed retrospectively. The patients were evaluated clinically and radiographically according to the Ring's classification system.
RESULTS
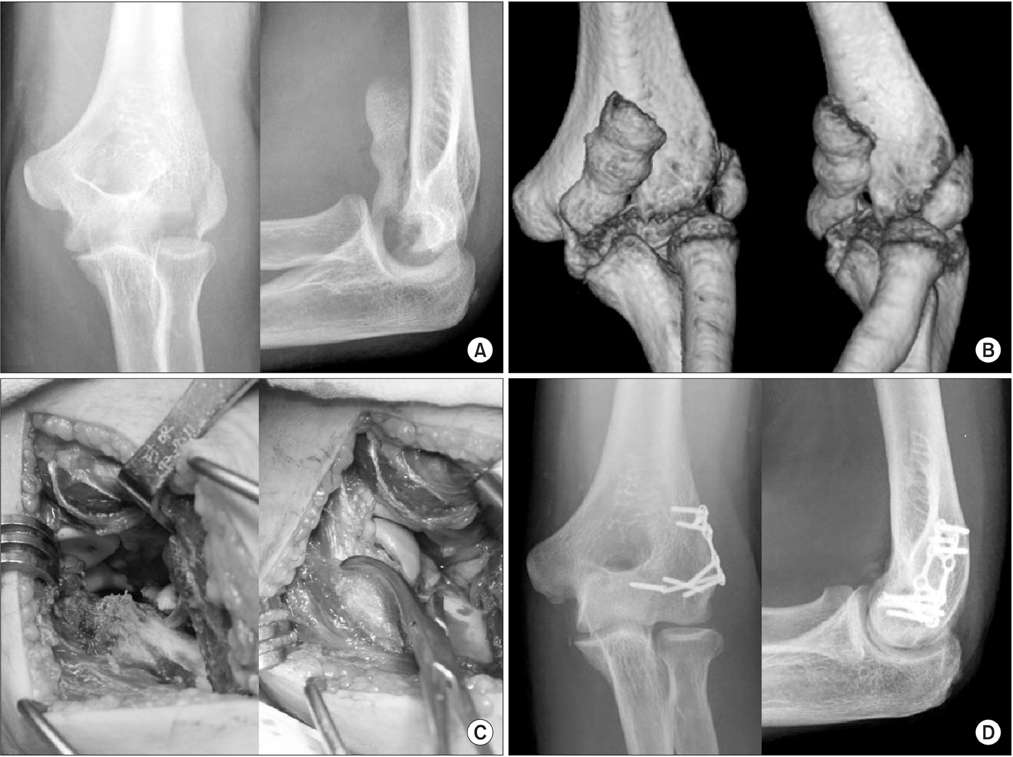
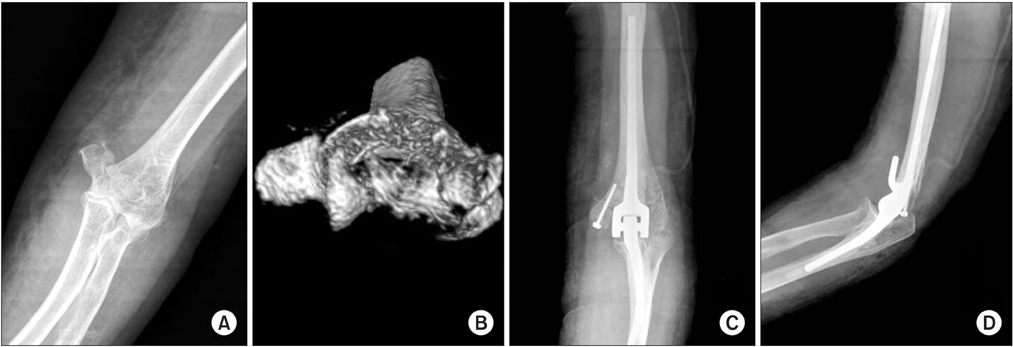
Eleven patients, including three males and eight female patients, with a mean age of 55 years (15-88 years) were enrolled in this study. Average Mayo elbow performance score was 85 (60-100), four patients had excellent, four had good, and three had fair results. Fracture union was achieved in ten of 11 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation. In the analysis of the results according to Ring's classification, patients presenting fracture of the posterior aspect of the lateral column showed worse clinical results than those who did not. It was the same for the patient presenting fracture of the posterior aspect of the trochlea.
CONCLUSION
The open reduction and internal fixation provides good clinical and radiologic outcomes for the distal humeral coronal plane articular fracture. Our results suggest that the type of fracture involvement with posterior aspect of trochlear or capitellum can result in poor clinical outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. McKee MD, Jupiter JB, Bamberger HB. Coronal shear fractures of the distal end of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:49–54.
Article2. Sabo MT, Fay K, McDonald CP, Ferreira LM, Johnson JA, King GJ. Effect of coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus on elbow kinematics and stability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19:670–680.
Article3. Ring D, Jupiter JB, Gulotta L. Articular fractures of the distal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A:232–238.
Article4. Brouwer KM, Jupiter JB, Ring D. Nonunion of operatively treated capitellum and trochlear fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36:804–807.
Article5. Dubberley JH, Faber KJ, Macdermid JC, Patterson SD, King GJ. Outcome after open reduction and internal fixation of capitellar and trochlear fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:46–54.
Article6. Goodman HJ, Choueka J. Complex coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2005; 62:85–89.7. Mosheiff R, Liebergall M, Elyashuv O, Mattan Y, Segal D. Surgical treatment of fractures of the capitellum in adults: a modified technique. J Orthop Trauma. 1991; 5:297–300.8. Sano S, Rokkaku T, Saito S, Tokunaga S, Abe Y, Moriya H. Herbert screw fixation of capitellar fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005; 14:307–311.
Article9. Stamatis E, Paxinos O. The treatment and functional outcome of type IV coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus: a retrospective review of five cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:279–284.
Article10. Mighell M, Virani NA, Shannon R, Echols EL Jr, Badman BL, Keating CJ. Large coronal shear fractures of the capitellum and trochlea treated with headless compression screws. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19:38–45.
Article11. O'Driscoll SW, Jupiter JB, Cohen MS, Ring D, McKee MD. Difficult elbow fractures: pearls and pitfalls. Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52:113–134.12. Lapner M, King GJ. Elbow arthroplasty for distal humeral fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2014; 63:15–26.13. Ali A, Shahane S, Stanley D. Total elbow arthroplasty for distal humeral fractures: indications, surgical approach, technical tips, and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19:2 Suppl. 53–58.
Article14. Kamineni S, Morrey BF. Distal humeral fractures treated with noncustom total elbow replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A:940–947.
Article15. Sen RK, Tripahty SK, Goyal T, Aggarwal S. Coronal shear fracture of the humeral trochlea. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013; 21:82–86.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of the distal radius fractures with open reduction and internal fixation
- Treatment of comminuted distal humeral intercondylar fracture using transolecranon approach
- Distal Radius Fracture treated with Distraction Plate Technique
- Refracture of Forearm Bone after Plate Removal
- Operative Treatment of Intraarticular Fracture of Distal Humerus in Adults