J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Oct;63(4):311-318.
Comparative Study of the CT Findings and Clinical Features in Pediatric and Adult Sialadenitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Korea. mdhjk@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We wanted to compare the CT findings and clinical features of parotitis and submandibular sialadenitis in children and adults and to evaluate the statistical significance of these in different age groups and the usefulness of a CT scan
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ninety-seven adults and 36 pediatric patients with sialadenitis were included in this retrospective study. Regardless of the site of involvement, we evaluated the CT findings and clinical manifestations between the pediatric and adult groups, and between the pediatric and adult parotitis and submandibular sialadenitis groups. At last, all the patients were classified into seven age groups.
RESULTS
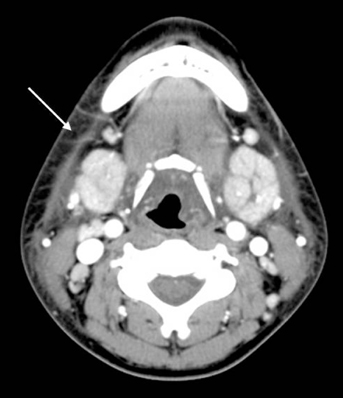
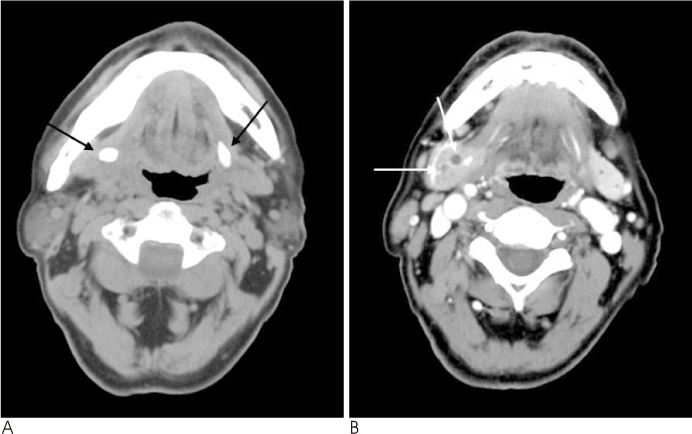
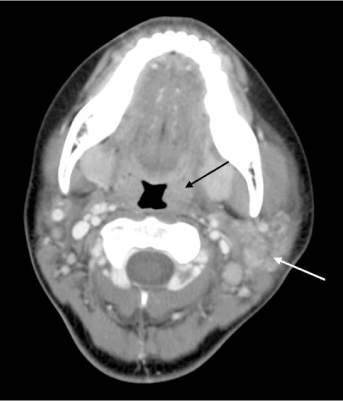
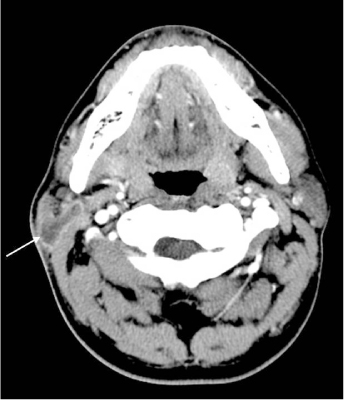
Abscess formations were more prominent in the parotitis groups, and sialiths were more common in the submandibular sialadenitis group with the lowest incidence in the young children group (< or = 10 years). Cellulitis seen on a CT scan showed a higher incidence in the adult parotitis group, and this finding was closely connected with pain. A number of patients showed cervical lymphadenitis on a CT scan and this coincided with lymph node palpation. Tonsillitis associated sialadenitis was common in the pediatric group. The therapeutic durations were longer in the pediatric parotitis patient group and the adult submandibular sialadenitis group.
CONCLUSION
CT scans were very helpful to evaluate for abscess, stone, lymphadenitis and estimating the associated clinical manifestations such as swelling, palpable lymph nodes, pain with operation and the therapeutic plan.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sumi M, Izumi M, Yonetsu K, Nakamura T. The MR imaging assessment of submandibular gland sialadenitis secondary to sialolithiasis: correlation with CT and histopathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1737–1743.2. Even TE, Niv A, Kraus M, Nash M. Candida parotitis with abscess formation. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; 126:334–336.3. Kaneta T, Minami M, Ozawa K, Akimoto Y, Kawana T, Yamamoto H, et al. MR of the submandibular gland: normal and pathologic states. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1575–1581.4. Chung MK, Jeong HS, Ko MH, Cho HJ, Ryu NG, Cho DY, et al. Pediatric sialolithiasis: what is different from adult sialolithiasis? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 71:787–791.5. Waseem Z, Forte V. An unusual case of bilateral submandibular sialolithiasis in a young female patient. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 69:691–694.6. Bova R, Walker P. Neonatal submandibular sialadenitis progressing to submandibular gland abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2000; 53:73–75.7. Bryan RN, Miller RH, Ferreyro RI, Sessions RB. Computed tomography of the major salivary glands. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982; 139:547–554.8. Mandel L, Bijoor R. Imaging (computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, sialography) in a case of recurrent parotitis in children. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:984–988.9. Mandel L, Hatzis G. The role of computerized tomography in the diagnosis and therapy of parotid stones: a case report. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000; 131:479–482.10. Laskawi R, Schaffranietz F, Arglebe C, Ellies M. Inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands in infants and adolescents. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 70:129–136.11. Becker M, Marchal F, Becker CD, Dulguerov P, Georgakopoulos G, Lehmann W, et al. Sialolithiasis and salivary ductal stenosis: diagnostic accuracy of MR sialography with a three-dimensional extended-Phase conjugate-symmetry rapid spin-echo sequence. Radiology. 2000; 217:347–358.12. Stong BC, Sipp JA, Sobol SE. Pediatric parotitis: a 5-year review at a tertiary care pediatric institution. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 70:541–544.13. Sitheeque M, Sivachandran Y, Varathan V, Ariyawardana A, Ranasinghe A. Juvenile recurrent parotitis: clinical, sialographic and ultrasonographic features. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2007; 17:98–104.14. Miziara ID, Campelo VE. Infantile recurrent parotitis: follow up study of five cases and literature review. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 71:570–575.15. Saarinen RT, Kolho KL, Pitkaranta A. Cases presenting as parotid abscesses in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 71:897–901.16. Faure F, Querin S, Dulguerov P, Froehlich P, Disant F, Marchal F. Pediatric salivary gland obstructive swelling: sialendoscopic approach. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:1364–1367.17. Nahlieli O, Eliav E, Hasson O, Zagury A, Baruchin AM. Pediatric sialolithiasis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000; 90:709–712.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Neonatal Suppurative Submandibular Sialadenitis: Complicated with Multiple Deep Neck Abscess
- Acute Sialadenitis in Children and Adolescents: CT Findings and Clinical Manifestations according to Glandular Involvement
- Sialography And Salivary Scan Study Of Salivary Diseases
- A Case of Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis with Facial Palsy Mimicking Malignancy
- Obstructive Sialadenitis associated with Injectable Facial Fillers