J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Aug;54(8):1241-1247.
The Success Rate and Factors Influencing the Results of Pneumatic Retinopexy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. changmh@dankook.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the success rate of pneumatic retinopexy and the preoperative factors influencing the results in the rhegmatogenous retinal detachment patients.
METHODS
We analyzed retrospectively the preoperative and postoperative retinal findings and postoperative complication in 152 eyes of 150 patients with uncomplicated rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, who had undergone pneumatic retinopexy and were followed up for at least 3 months. We analyzed preoperative factors, including age, sex, location and numbers of retinal tears, duration of retinal detachment, lens status, and refractive error.
RESULTS
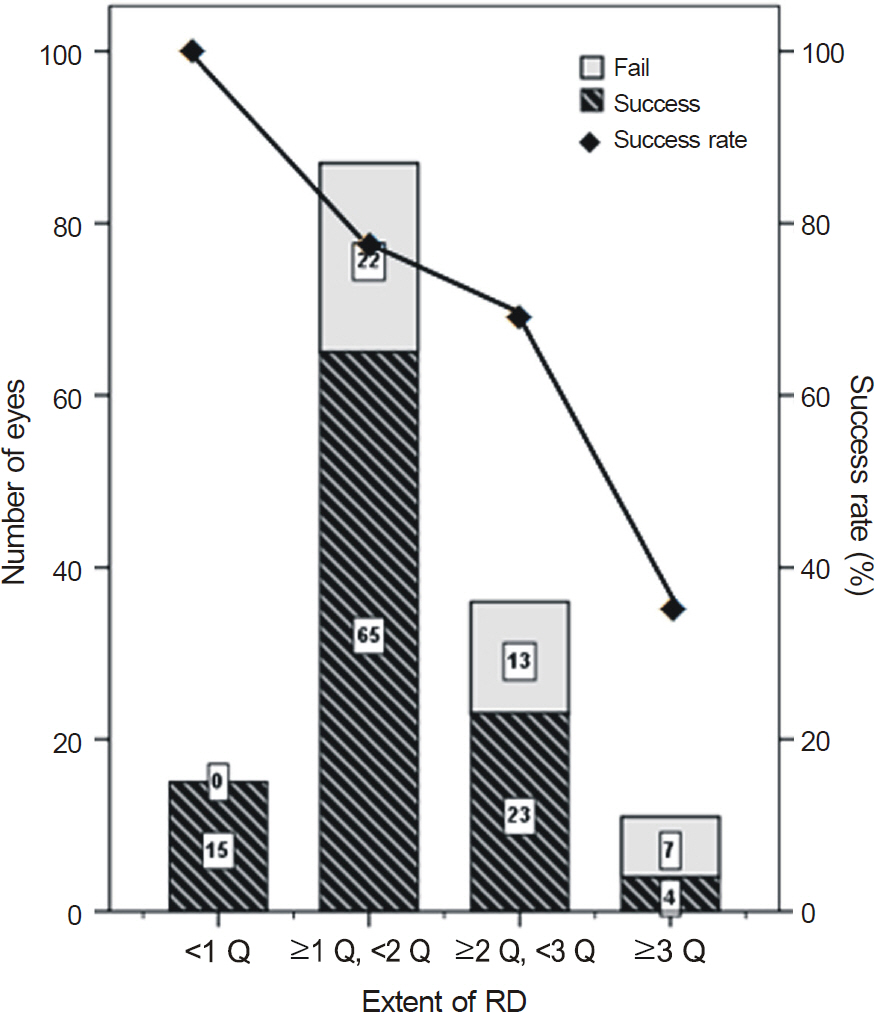
The success rate of the initial surgery was 72.37%. The success rate was significantly higher in non-high myopic and phakic eyes, and when the retinal detachment was less than 3 quadrants with the retinal break located superiorly. Accordingly, the success rate was 85.87% (79 of 92 eyes).
CONCLUSIONS
In the present study, the anatomical success rate of primary pneumatic retinopexy was more than 70%. If pneumatic retinopexy is performed to non-high myopic, phakic eyes, and retinal detachment is less than 3 quadrants with superior retinal break, the surgeon can expect good anatomical outcomes and consider pneumatic retinopexy as a first management in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hilton GF, Grizzard WS. Pneumatic retinopexy: a two-step out-patient operation without conjunctival incision. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:626–41.2. Brinton DA, Hilton GF. Pneumatic retinopexy and alternative reti-nal detachment techniques. In: Ryan SJ, Wilkinson CP, eds. Retina. St. Louis: CV Mosby;2001; v. 3:2047. 62:3. Hilton GF, Das T, Majji AB, Jalali S. Pneumatic retinopexy princi-ples and practice. Indian J Ophthalmol. 1996; 44:131–43.4. Regillo CD, Tornambe PE. Primary retinal detachment repair. In: Regillo CD, Brown GC, Flynn Jr HW, eds. Vitreoretinal Disease. 1st ed.New York: Thieme;1999; 640–2.5. Ohm J. Ueber die Behandlung der Netzhautablosung durch oper-ative Entleerung der subretinalen Flussigkeit und Einspiritzung von Luft in den Glaskorper. Graefes Arch Clin Ophthalmol. 1911; 79:442–50.6. Custodis E. Bedeutet die Plombenaufnahung auf die Sklera einen Fortschritt in der operativen Behandlung der Netzhautablosung? Ber Zusammenkunft Dtsch Ophthalmol Ges. 1953; 58:102–5.7. Custodis E. Scleral buckling without excision and with polyviol implant. In: Schepens CL, ed. Importance of the vitreous body in retinal surgery with special emphasis on reoperations. St. Louis: CV Mosby;1960; 175.8. Ross WH, Lavina A. Pneumatic retinopexy scleral buckling, and vitrectomy surgery in the management of pseudophakic retinal detachments. 2008; 43:65–72.
Article9. Poliner LS, Grand MG. Clinical experience. St. Louis: Missouri, In: Tornambe PE, Grizzard WS, eds. Pneumatic retinopexy: a clin-ical symposium. Des Plaines: Greenwood Publishing;1989; 127. 9:10. Dominguez DA, Boyd BF, Gordon S. Repeated insufflation of ex-pansive gas. Highlights Ophthalmol Lett. 1986; 14:1–14.11. McAllister IL, Meyers SM, Zegarra H. . Comparison of pneu-matic retinopexy with alternative surgical techniques. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:877–83.
Article12. Tornambe PE, Hilton GF. Pneumatic retinopexy: a multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial comparing pneumatic reti-nopexy with scleral buckling. The Retinal Detachment Study Group. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:772–84.13. Chan CK, Lin SG, Nuthi AS, Salib DM. Pneumatic retinopexy for the repair of retinal detachments: a comprehensive review (1986- 2007). Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53:443–78.14. Abecia E, Pinilla I, Olivan JM. . Anatomic results and compli-cations in a long-term follow-up of pneumatic retinopexy cases. Retina. 2000; 20:156–61.
Article15. Algvere P, Hallnäs K, Palmqvist BM. Success and complications of pneumatic retinopexy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:400–4.
Article16. Ambler JS, Meyers SM, Zegarra H, Paranandi L. Reoperations and visual results after failed pneumatic retinopexy. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97:786–90.
Article17. Assi AC, Charteris DG, Pearson RV, Gregor ZJ. Pneumatic reti-nopexy in the treatment of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Eye (Lond). 1999; 13:(Pt 6). 725–8.
Article18. Böhm P, Záhorcová M. [Pneumatic retinopexy-method of choice in treatment of retinal detachment]. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2003; 59:154–9.19. Han DP, Mohsin NC, Guse CE. . Comparison of pneumatic ret-inopexy and scleral buckling in the management of primary rheg-matogenous retinal detachment. Southern Wisconsin Pneumatic Retinopexy Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:658–68.
Article20. Grizzard WS, Hilton GF, Hammer ME, Taren D. A multivariate analysis of anatomic success of retinal detachment treated with scleral buckling. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthal. 1994; 232:1–7.21. Grizzard WS, Hilton GF, Hammer ME. . Pneumatic retinopexy failures: cause, prevention, timing, and management. Ophthalmology. 1995; 102:929–36.22. Tornambe PE. Pneumatic retinopexy: The evolution of case se-lection and surgical technique, a twelve-year study of 302 eyes. Trans Am Ophth Soc. 1997; 95:551–78.23. Kulkarni KM, Roth DB, Prenner JL. Current visual and anatomic outcomes of pneumatic retinopexy. Retina. 2007; 27:1065–70.
Article24. Yeo JH, Vidaurri-Leal J, Glaser BM. Extension of retinal detach-ments as a complication of pneumatic retinopexy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:1161–3.25. Campochiaro PA, Kaden IH, Vidaurri-Leal J, Glaser BM. Cryotherapy enhances intravitreal dispersion of viable retinal pig-ment epithelial cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:434–6.
Article26. Griffiths PG, Richardson J. Causes of proliferative retinopathy fol-lowing pneumatic retinopexy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:1515.
Article27. Hackett SF, Conway BP, Campochiaro PA. Subretinal fluid stim-ulation of retinal pigment epithelial cell migration and pro-liferation is dependent on certain features of the detachment or its treatment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:391–4.
Article28. Chen JC, Robertson JE, Coonan P. . Results and complications of pneumatic retinopexy. Ophthalmology. 1998; 95:601–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Factors Influencing to the Results of Pneumatic Retinopexy
- Treatment of Retinal Detachments by Pneumatic Retinopexy
- A Result of Pneumatic Retinopexy for Pseudophakic Retinal Detachment
- Choroidal Detachment after Pneumatic Retinopexy
- Two Cases of Pneumatic Retinopexy as a Primary Successful Intervention of Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment