J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Apr;52(4):502-506.
Ab Interno Trabeculotomy with Trabectome(R) for Refractory Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1HanGil Eye Hospital, Incheon, Korea. oijee@hanmail.net
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of ab interno trabeculotomy with Trabectome(R) (NeoMedix Corp., CA, USA) conducted on a refractory primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) patient.
CASE SUMMARY
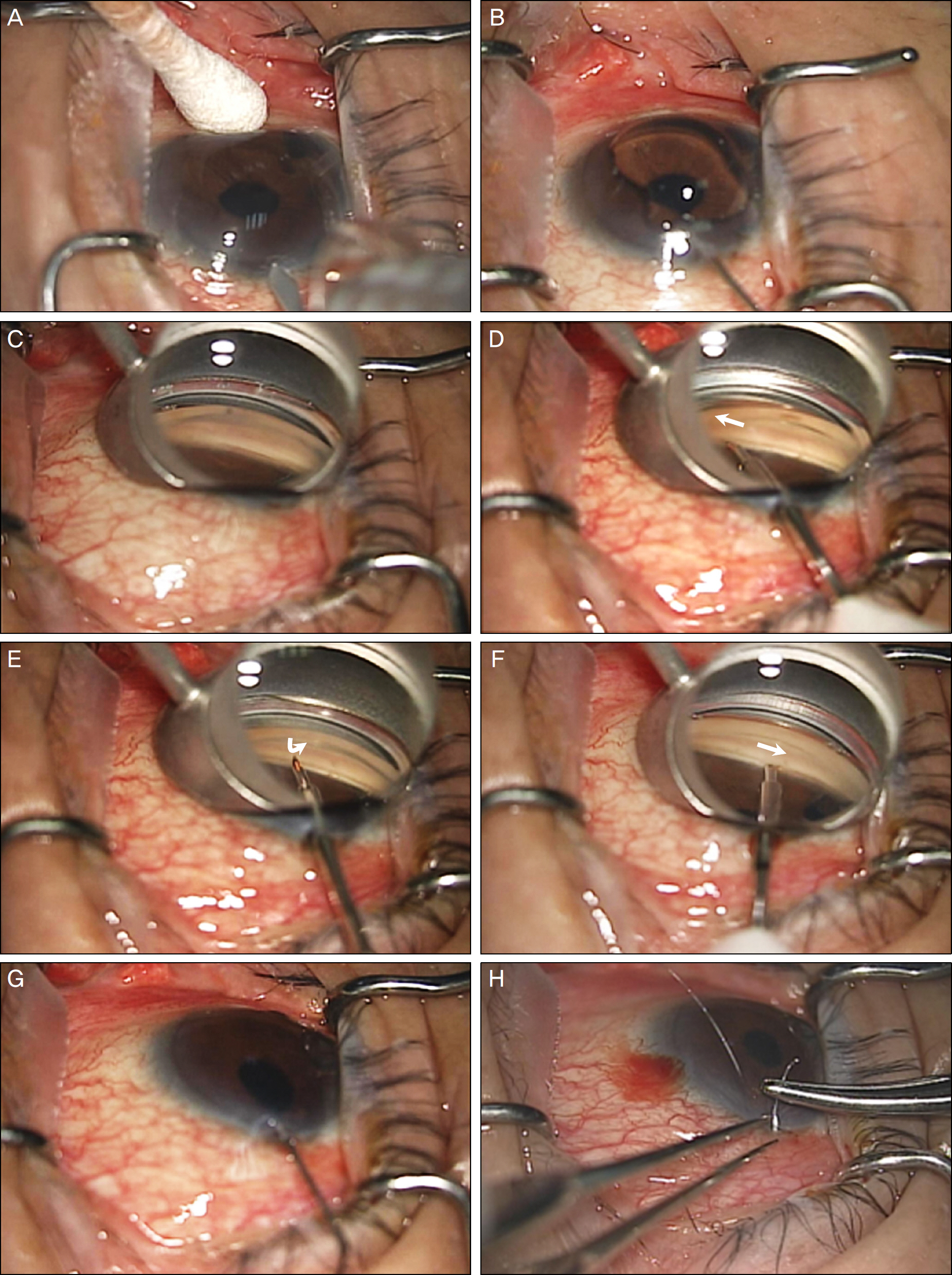
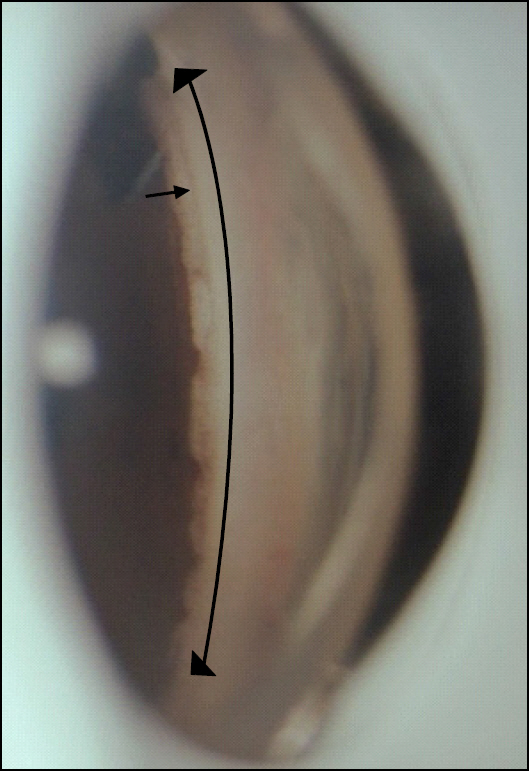
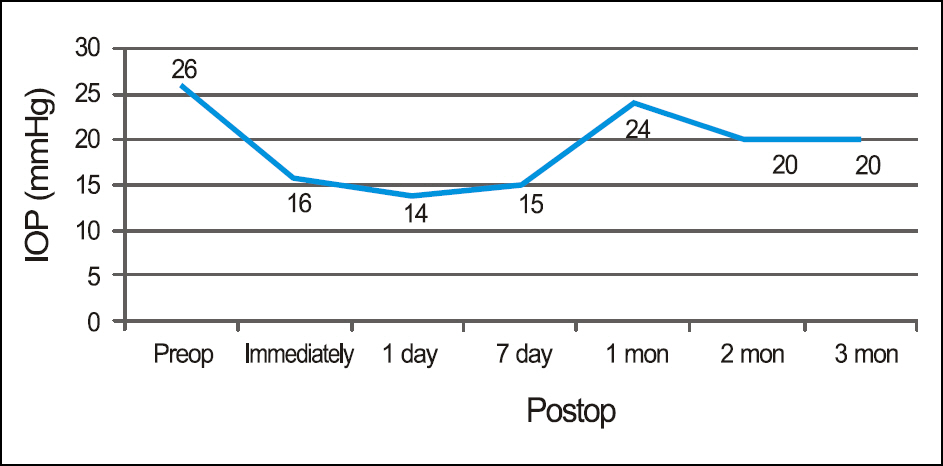
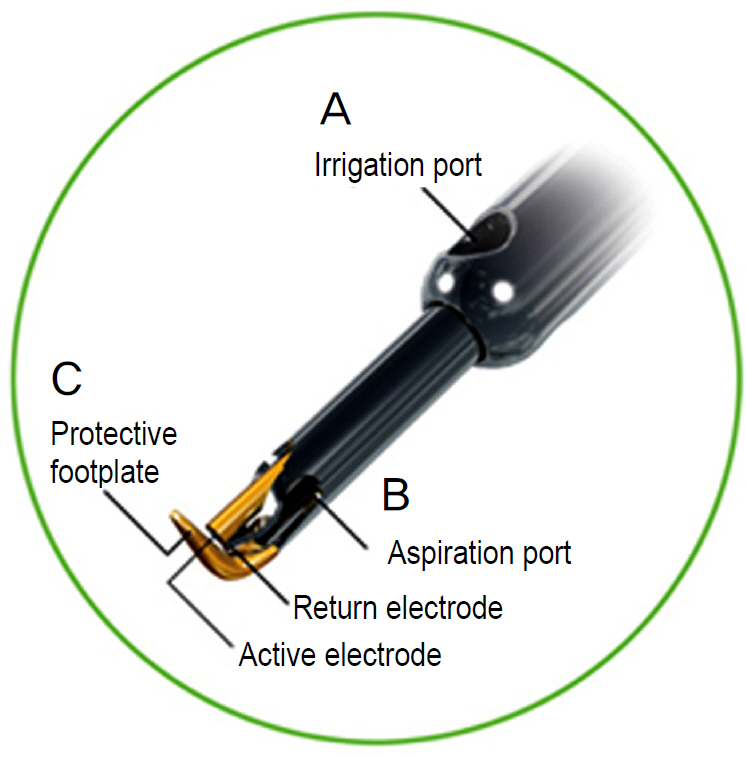
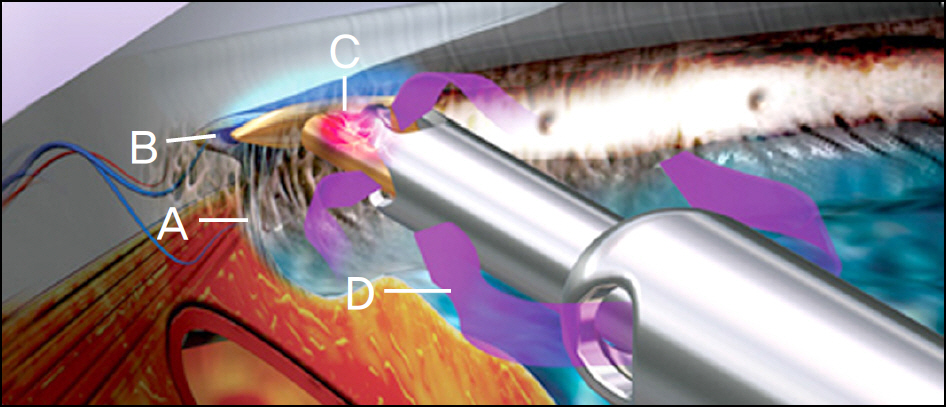
Trabectome(R) has microelectrocautery with simultaneous infusion and aspiration of debris and ablates a segment of trabecular meshwork and the inner wall of Schlemm's canal. The patient, a 54-year-old man had uncontrolled intraocular pressure (IOP) with topical anti-glaucoma medications after trabeculectomy and Ahmed valve implantation for POAG. For the patient, ab interno trabeculotomy with Trabectome(R) was performed. There were no other postoperative complications except for microhyphema immediately after surgery. The IOP was controlled between 14 to 24 mm Hg up to 3 months postoperatively with topical anti-glaucoma medications (Cosopt(R), Alphagan-P(R), Lumigan(R)).
CONCLUSIONS
Ab interno trabeculotomy with Trabectome(R) appears to offer a newer method of lowering IOP in POAG than conventional trabeculectomy and glaucoma drainage device surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. deLuise VP, Anderson DR. Primary infantile glaucoma (congenital glaucoma). Surv Ophthalmol. 1983; 28:1–19.
Article2. Luntz MH, Livingston DG. Trabeculotome ab externo and trabeculectomy in congenital and adult-onset glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1977; 83:174–9.3. Kobayashi H, Kobayashi K, Okinami S. A comparison of the intraocular pressure-lowering effect and safety of viscocanalostomy and trabeculotomy with mitomycin C in bilateral open-angle glaucoma. Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2003; 241:359–66.4. Nguyen QH. Trabectome: A novel approach to angle surgery in the treatment of glaucoma. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2008; 48:65–72.
Article5. Minckler DS, Hill RA. Use of novel devices for control of intraocular pressure. Exp Eye Res. 2009; 88:792–8.
Article6. Minckler DS, Mosaed S, Dustin L, et al. Trabectome (trabeculectomy- internal approach): additional experience and extended follow-up. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 106:149–60.7. Mosaed S. Ab interno trabeculotomy with the trabectome surgical device. Techn Opthalmol. 2007; 5:63–6.
Article8. Godfrey DG, Fellman RL, Neelakantan A. Canal surgery in adult glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009; 20:116–21.9. Francis BA, Minckler D, Dustin L, et al. Combined cataract extraction and trabeculotomy by internal approach for coexisting cataract and open-angle glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1096–103.10. Fontana H, Nouri-Mahdavi K, Caprioli J. Trabeculectomy with mitomycin C in pseudophakic patients with open angle glaucoma: outcomes and risk factors for failure. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:652–9.11. Filippopoulos T, Rhee DJ. Novel surgical procedures in glaucoma: advances in penetrating glaucoma surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:149–54.
Article12. Vold SD, Dustin L. Impact of laser trabeculoplasty on Trabectome® outcomes. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2010; 41:443–51.