J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Jan;51(1):106-111.
Clinical Significance of Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Early Stage of Traumatic Hyphema
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, KyungHee University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khjinmd@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Kangwon University, College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
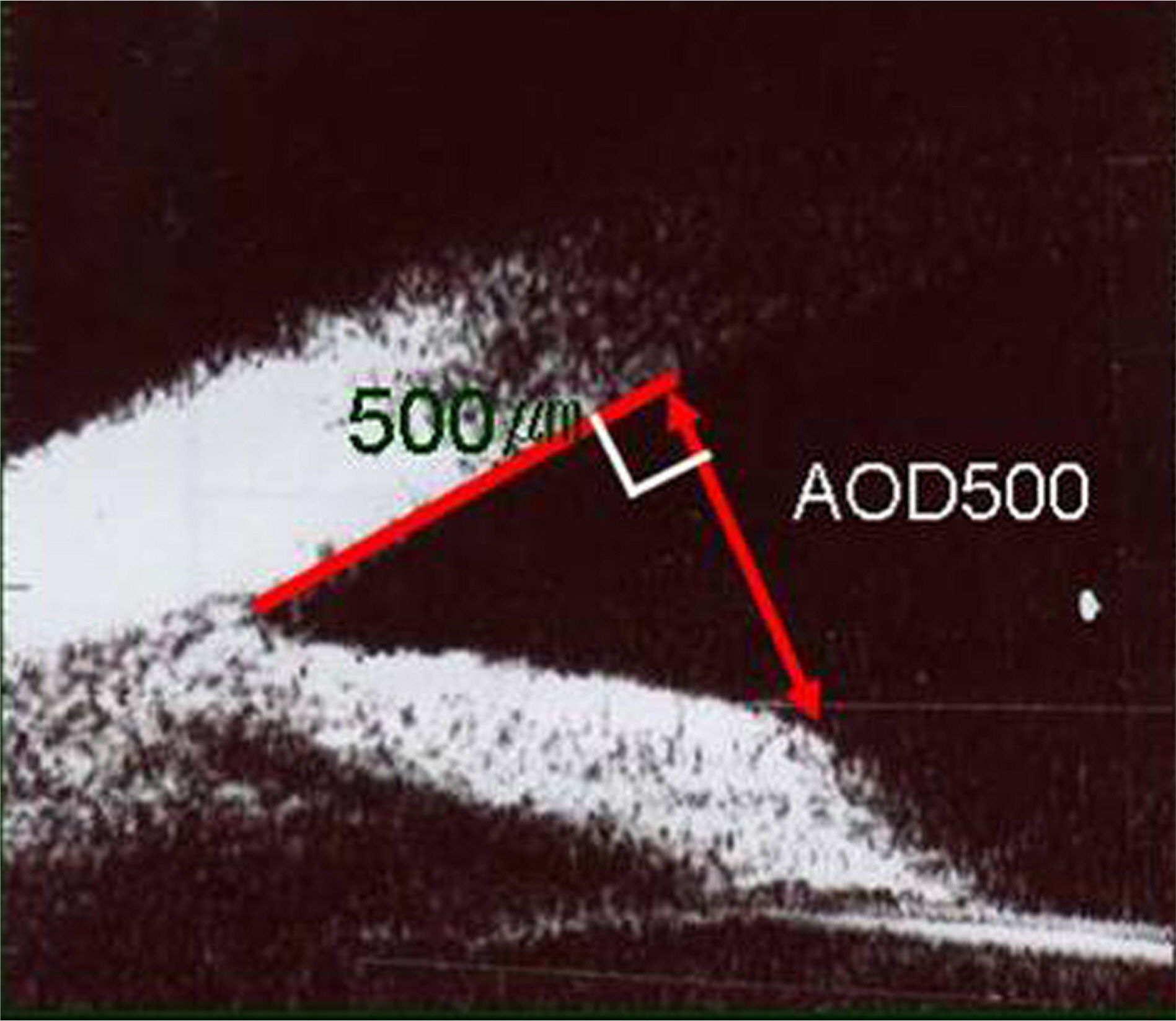
To evaluate the clinical significance of angle-opening distance 500 (AOD500) using ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) in the early stage of traumatic hyphema.
METHODS
The participants of this study were 46 hospitalized traumatic hyphema patients. We measured the quantity of initial blood clotting using a slit-lamp and the range of angle recession, AOD500 using UBM and then reviewed the relationship between the two.
RESULTS
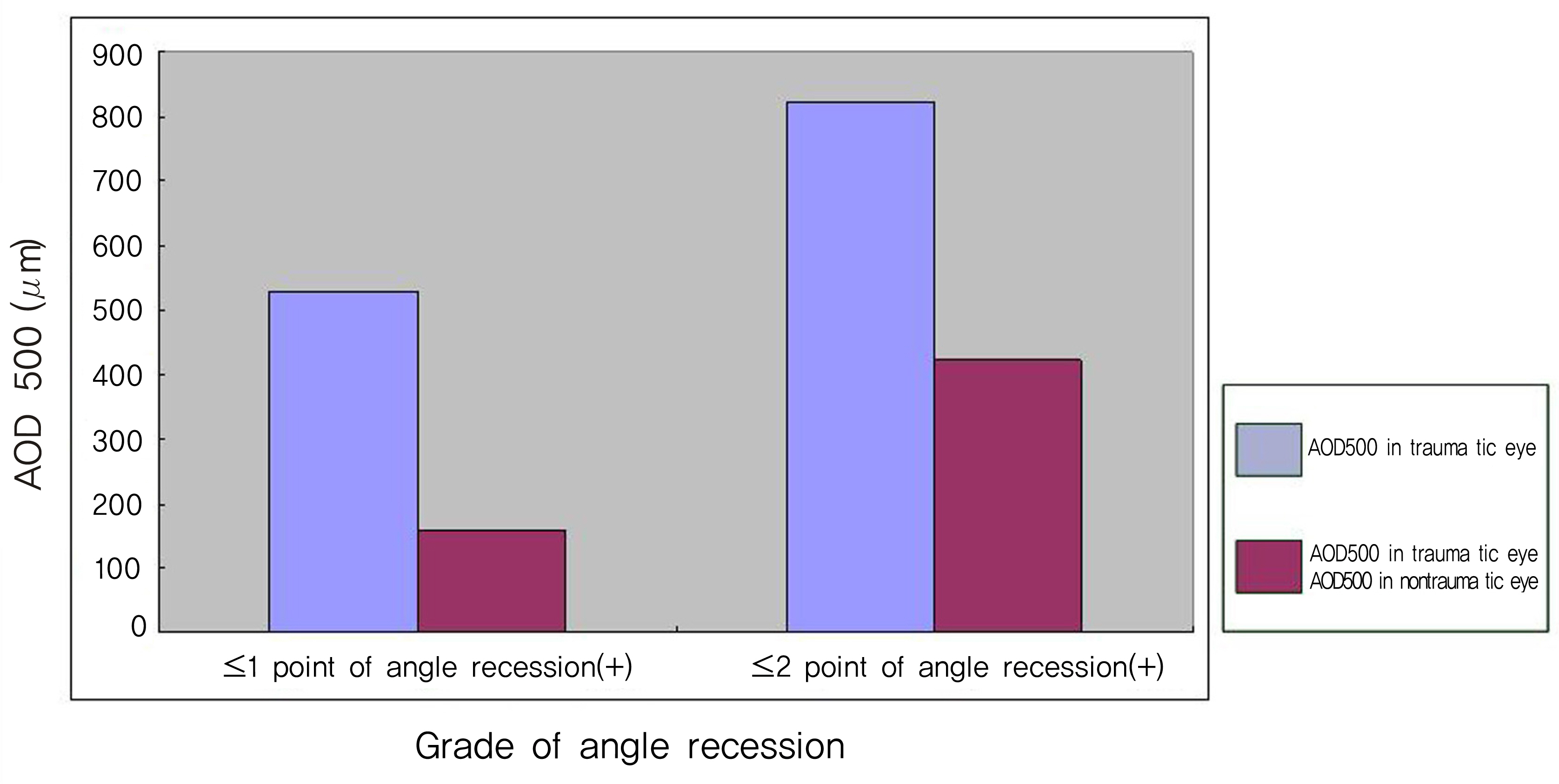
The difference of AOD500 in the traumatic and the non-traumatic eye measured by UBM at admission increased significantly in the wider recessed angle group (p=0.008), but did not increase at a statistically significantly level in the larger initial blood clot grade group (> or =Grade 2).
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that the measurement of the angle-opening distance of both eyes using UBM will aid in evaluating the range of angle recession in patients in the early stage of traumatic hyphema.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tesluk GC, Spaeth GL. The occurrence of primary open-angle glaucoma in the fellow eye of patients with unilateral angle-cleavage glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1985; 92:904–11.
Article2. Pettit TH, Keates EU. Traumatic cleavage of the chamber angle. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963; 69:438–44.
Article3. Kaufman JH, Tolpin DW. Glaucoma after traumatic angle recession. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974; 78:648–54.4. Sihota R, Kumar S, Gupta V, et al. Early predictors of traumatic glaucoma after closed globe injury: trabecular pigmentation, widened angle recess, and higher baseline intraocular pressure. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 126:921–6.5. Kobayashi H, Ono H, Kiryu J, et al. Ultrasound biomicroscopic measurement of development of anterior chamber angle. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:559–62.
Article6. Agapitos PJ, Noel LP, Clarke WN. Traumatic hyphema in children. Ophthalmology. 1987; 94:1238–41.
Article7. Jung KS, Hong SW, Chang HK. The incidence of complication and decreased visual acuity in traumatic hyphema patients aberrations to the amount of blood clot. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:1852–9.8. Edwards WC, Layden WE. Traumatic hyphema. Am J aberrations. 1973; 75:110.
Article9. Crouch ER Jr, Crouch ER. Management of traumatic hyphema: therapeutic options. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1999; 36:238–50.
Article10. Cho JS, Jun BK, Lee YJ, et al. Factors associated with the poor final visual outcome after traumatic hyphema. J Korean aberrations Soc. 1998; 12:122–9.
Article11. Pavlin CJ, Harasiewicz K, Sherar MD, Foster FS. Clinical use of ultrasound biomicroscopy. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:287–95.
Article12. Foster FS, Palvin CJ, Harasiewicz KA, et al. Advances in ultrasound biomicroscopy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2000; 26:1–27.
Article13. Ozdal MP, Mansour M, Deschenes J. Ultrasound biomicroscopic evaluation of the traumatized eyes. Eye. 2003; 17:467–72.
Article14. Berinstein DM, Gentile RC, Sidoti PA, et al. Ultrasound aberrations in anterior ocular trauma. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1997; 28:201–7.15. Genovesi-Ebert F, Rizzo S, Chiellini S, et al. Ultrasound aberrations in the assessment of penetrating or blunt anterior-aberrations trauma. Ophthalmologica. 1998; 212:6–7.16. Lee KW, Park CH, Hahn DK. Anterior chamber angle recession and elevation of intraocular pressure. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1987; 28:595–8.