J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Sep;49(9):1365-1370.
Results of Conjunctiva-Muller Muscle Resection in Mild Eyelid Ptosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University, Kim's Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jjw@kimeye.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To assess surgical outcomes after adjusting the amount of resection of the conjunctiva and the Muller muscle according to 10% phenylephrine test results.
METHODS
The charts of 32 patients (32 eyes) with mild upper eyelid ptosis were reviewed retrospectively. They all had conjunctiva-Muller muscle resections. A preoperative 10% phenylephrine test was performed to determine the resection amount of the Muller muscle and conjunctiva. An 8 mm resection was performed when phenylephrine raised the ptotic lid to the same level as that of the contralateral lid. A 7 mm resection was performed when the ptotic lid was raised to a level higher than that of the contralateral lid. A 9 mm resection was performed when the ptotic lid was raised to a level not quite to the level of the contralateral lid.
RESULTS
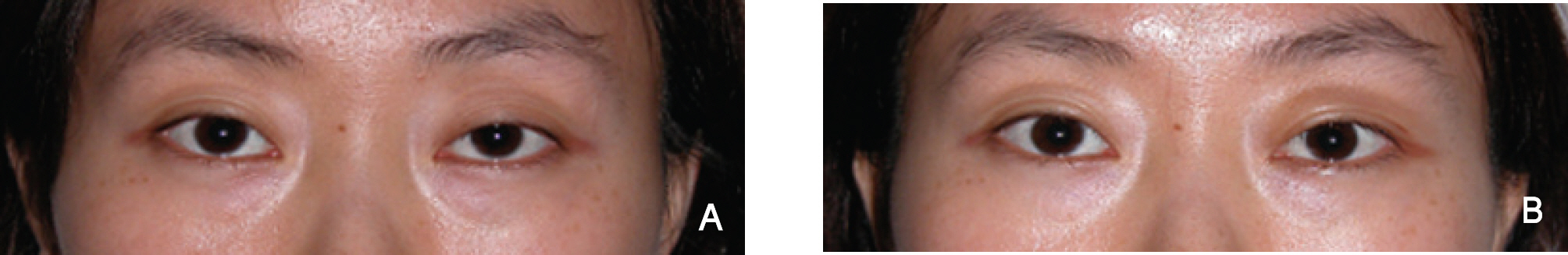
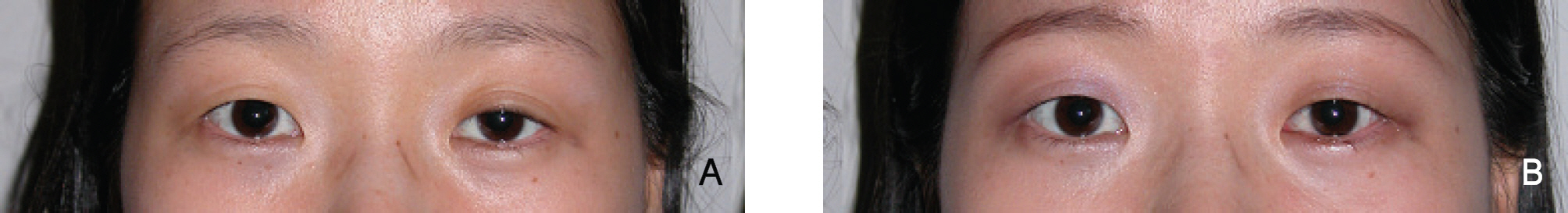
Of the 32 patients, 28 were female and 4 were male. The mean age of the patients was 30.8+/-10.2 years. Patients were followed up for an average of 40.2+/-36.8 days, postoperatively. Postoperative upper lid positions were exactly symmetrical in 26 of the 32 patients. Five patients showed undercorrection, and 1 patient showed overcorrection.
CONCLUSIONS
Excellent results were obtained by resecting the conjunctiva and Muller muscle according to the phenylephrine reaction of a ptotic eyelid.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Fasanella RM, Servat J. Levator resection for minimal ptosis: another simplified operation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961; 65:493–6.
Article2. Putterman AM, Urist MJ. Müller muscle-conjunctiva resection: technique for treatment of blepharoptosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:619–23.3. Putterman AM, Urist MJ. Müller’s muscle-conjunctival resection ptosis procedure. Ophthalmic Surg. 1978; 9:27–32.4. Weinstein GS, Buerger GF Jr. Modifications of the Müller’s muscle-conjunctival resection operation for blepharoptosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982; 93:647–51.
Article5. Putterman AM, Fett DR. Müller’s muscle in the treatment of upper eyelid ptosis: a ten-year study. Ophthalmic Surg. 1986; 17:354–60.
Article6. Glatt HJ, Putterman AM, Fett DR. Müller’s muscle- conjunctival resection procedure in the treatment of ptosis in Horner’s syndrome. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990; 21:93–6.7. Song WS, Kim YH, Lee SJ. Morphologic study of upper eyelid contour and functional evaluation of levator palpebrae. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1523–9.8. Whitnall SE. The anatomy of the human orbit. 2nd. Vol. 1. London: Oxford University Press;1932. p. 145.9. Dutton JJ. Atlas of clinical and surgical orbital anatomy. Philadelphia: WB Saunders co;1994. p. 113–38.10. Obear MF, Smith B. Tarsal grafting to elevate the lower eyelid margin. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 59:1088–90.11. Guyron B, Davies B. Experience with the modified Putterman procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988; 82:775–80.12. Dresner SC. Further modifications of the Müller’s muscle- conjunctival resection procedure for blepharoptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991; 7:114–22.13. Mercandetti M, Putterman AM, Cohen ME. . Internal levator advancement by Müller’s muscle-conjunctival resection. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001; 3:104–10.
Article14. Kanski JJ. Clinical ophthalmology. 6th. Vol. 1. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann;2007. p. 134.15. Kim SY, Chung WS. Analysis of the causes of ptosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1649–54.16. Jeong SK, Lemke BN, Dortzbach RK. . The Asian upper eyelid: an anatomical study with comparison to the Caucasian eyelid. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:907–12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcomes of Conjunctiva-Muller Muscle Resection and Factors Which Affect Success
- Clinical Effects of Conjunctiva-Muller Muscle Resection in Anophthalmic Ptosis
- Muller's Muscle-Levator Aponeurosis Advancement Procedure for Blepharoptosis
- Various Modifications of Muller's Muscle-Conjunctival Resection for Ptosis Repair
- Balanced Tucking of the Levator Muscle and Muller's Muscle in Blepharoptosis