J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2016 Jun;32(2):123-129. 10.14368/jdras.2016.32.2.123.
Management for traumatic neuropathy after dental treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Dental Research Institute, Yangsan, Republic of Korea. oksoomin@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Medicine, Pusan National University Dental Hospital, Dental Research Institute, Yangsan, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Oral Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2328894
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2016.32.2.123
Abstract
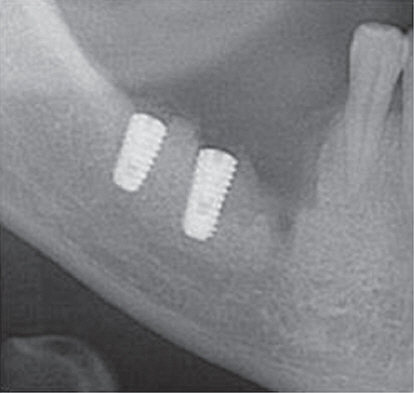
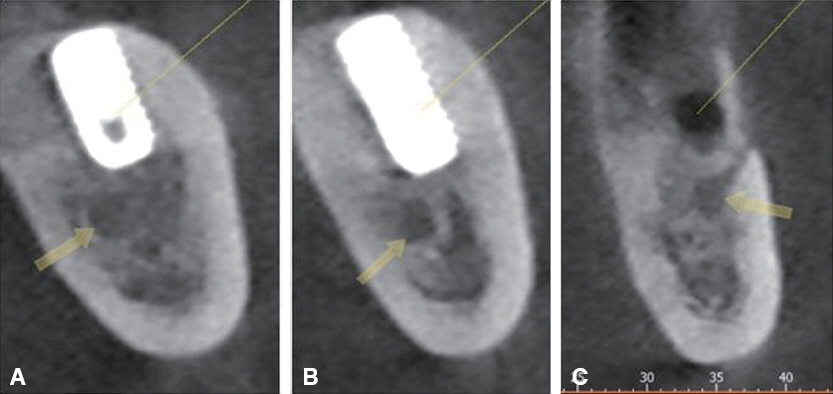
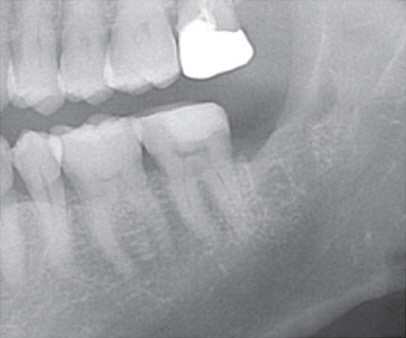
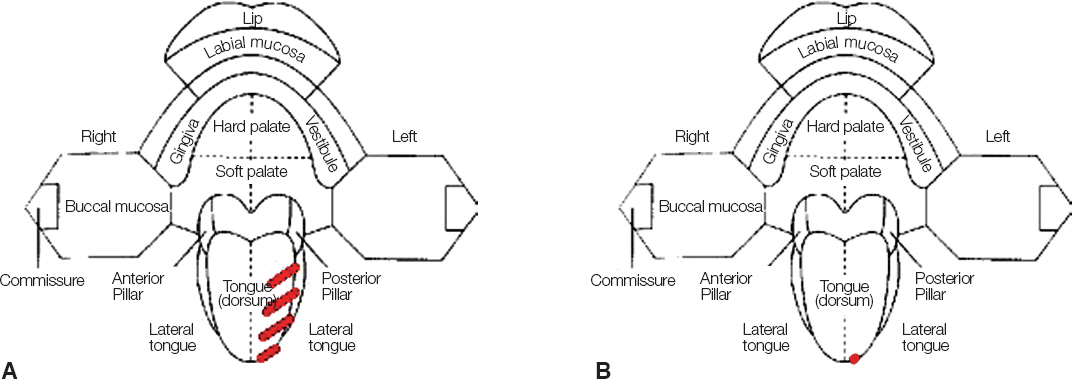
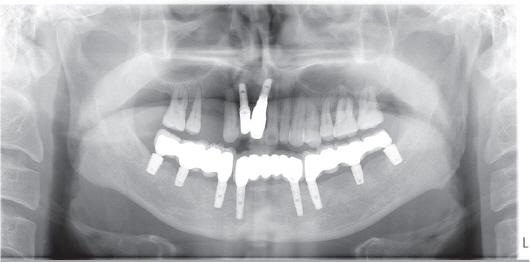
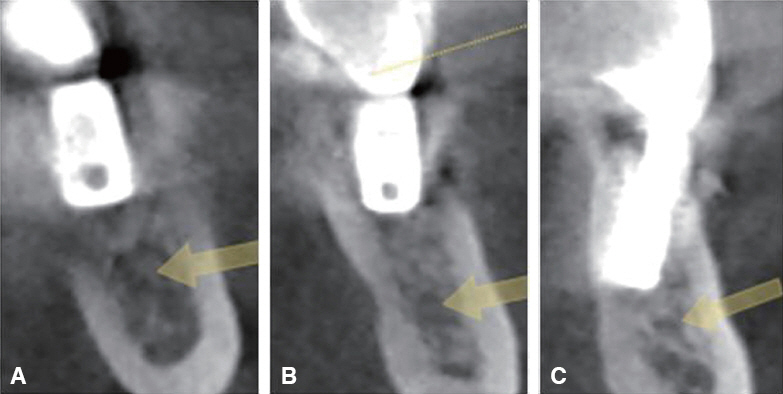
- Whereas a somatic pain notifies tissue damage, a neuropathic pain presents disorder of the nerve itself. The causes of neuropathic pains are trauma, infection, chronic irritation by adjacent tissue and so on. The iatrogenic trauma or infection also causes traumatic neuropathy, which may exert a bad influence on doctor-patient relationship. Some of related dental treatments are implantation (directly or indirectly through heating), root canal treatment, teeth extraction, block anesthesia, mandibular surgery. If inappropriate management is performed after nerve trauma, there will be many chances to develop chronic neuropathy for the patient. It is important that the sign of nerve trauma have to be caught by the practitioner as soon as possible and treated properly.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Merskey HE. Classification of chronic pain: descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. Prepared by the International Association for the Study of Pain, Subcommittee on Taxonomy. Pain Suppl. 1986; 3:S1–226.2. Sunderland S. A classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function. Brain. 1951; 74:491–516. DOI: 10.1093/brain/74.4.491. PMID: 14895767.3. Seddon HJ. Three types of nerve injury. Brain. 1943; 66:247–88. DOI: 10.1093/brain/66.4.237.4. Juodzbalys G, Wang HL, Sabalys G. Injury of the inferior alveolar nerve during implant placement: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2011; 2:e1. DOI: 10.5037/jomr.2011.2101. PMID: 24421983. PMCID: PMC3886063.5. Abarca M, van Steenberghe D, Malevez C, De Ridder J, Jacobs R. Neurosensory disturbances after immediate loading of implants in the anterior mandible: an initial questionnaire approach followed by a psychophysical assessment. Clin Oral Investig. 2006; 10:269–77. DOI: 10.1007/s00784-006-0065-0. PMID: 16937108. PMCID: PMC1705496.6. Benoliel R, Sharav Y. Chronic orofacial pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2010; 14:33–40. DOI: 10.1007/s11916-009-0085-y. PMID: 20425212.7. Yoon JA, Kang JK, Ahn HJ, Choi JH, Kim CY. A study on types and counterplans of medical accident experienced by dentists in Seoul (2004). J Oral Med Pain. 2005; 30:163–200.8. Han SR, Yeo SP, Lee MK, Bae YC, Ahn DK. Early dexamethasone relieves trigeminal neuropathic pain. 2010; 89:915–20.9. Alves FR, Coutinho MS, Gonçalves LS. Endodontic-related facial paresthesia: systematic review. J Can Dent Assoc. 2014; 80:e13. PMID: 24598329.10. Libersa P, Savignat M, Tonnel A. Neurosensory disturbances of the inferior alveolar nerve: a retrospective study of complaints in a 10-year period. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:1486–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2007.03.023. PMID: 17656272.11. Peñarrocha Diago M, Boronat López A, Lamas Pelayo J. Update in dental implant periapical surgery. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006; 11:E429–32. PMID: 16878068.12. Galloway EB 3rd, Jensen RL, Dailey AT, Thompson BG, Shelton C. Role of topical steroids in reducing dysfunction after nerve injury. Laryngoscope. 2000; 110:1907–10. DOI: 10.1097/00005537-200011000-00026. PMID: 11081608.13. Jancsó G, Kiraly E, Jancsó-Gábor A. Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurones. Nature. 1977; 270:741–3. DOI: 10.1038/270741a0. PMID: 593396.14. Kohnelein KE, Ocker K, Seitz HD. Experimental rails to inhibit neuroma formation. Chir Plast (Berl). 1980; 5:207–11.