J Korean Fract Soc.
2007 Jan;20(1):13-18. 10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.13.
Interlocking Intramedullary Nail in Distal Tibia Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. min1913@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2294373
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.13
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the effectivity of interlocking intramedullary nailing for distal tibia fracture and prognostic factor to bone healing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 2000 to June 2005, 21 cases who had distal tibia fracture were treated by interlocking intramedullary nail were analyzed. The duration of follow-up was more than 1 year. We evaluated clinical results by IOWA ANKLE rating system and union time by simple X-ray. Furthermore, we estimated prognostic factor to union time.
RESULTS
The bone union was achieved at average 18.5 weeks. At the last follow-up, there was no non-union and infection. Average IOWA ANKLE rating score was 91.3 point. The union time was delayed in open and segmental fracture at initial fracture. And severe soft tissue injury in open fracture revealed bad result.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that interlocking intramedullary nail is effective method for treatment of the distal tibial fractures. And, adequate soft tissue management is important to bone healing and clinical outcome.
MeSH Terms
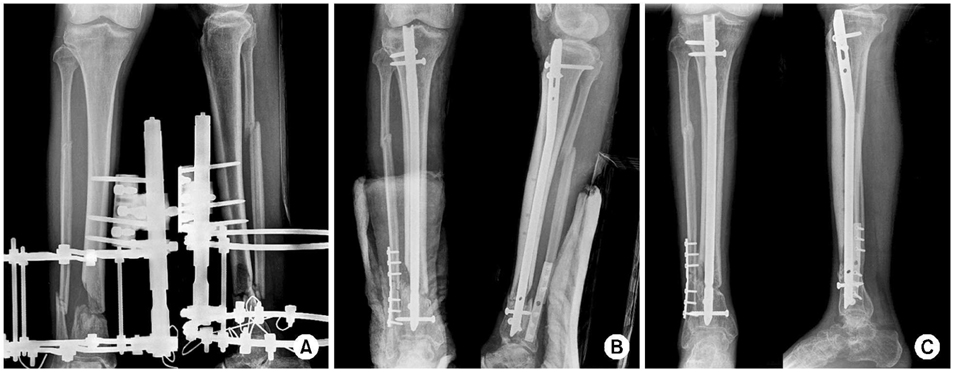
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Plate Fixation for Distal Tibia Fractures
JungHan Kim, Heui-Chul Gwak, Chang-Rack Lee, Yang-Hwan Jung
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2015;19(3):86-90. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2015.19.3.86.
Reference
-
1. Bone LB, Johnson KD. Treatment of tibial fractures by reaming and intra-medullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:877–887.
Article2. Bostman OM. Displaced malleolar fractures associated with spiral fractures of the tibial shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 228:202–207.3. Freedman EL, Johnson EE. Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; 315:25–33.
Article4. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58:453–458.
Article5. Hahn D, Bradbury N, Hartley R, Radford PJ. Intramedullary nail breakage in distal fracture of the tibia. Injury. 1996; 27:323–327.
Article6. Harvey FJ, Hodgkinson AH, Harvey PM. Intramedullary nailing in the treatment of open fractures of the tibia and fibula. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57:909–915.
Article7. Harvey JP Jr. Management of open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974; 105:154–166.
Article8. Hasenhuttl K. The treatment of unstable fractures of the tibia and fibula with flexible medullary wires. A review of two hundred and thirthy-five fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:921–931.
Article9. Holbrook JL, Swiontkowski MF, Sanders R. Treatment of open fractures of the tibial shaft: Ender nailing versus external fixation. A randomized, prospective comparison. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:1231–1238.10. Kim JR, Lee HS, Choi MK, Lee KB, Park JH, Lee JM. Treatment of distal tibial fractures by interlocking intramedullary nailing. J Korean Soc Fract. 2003; 16:348–355.
Article11. Konrath G, Hoed BR, Watson JT, Kaneshiro S, Karges DE, Cramer KE. Intramedullary nailing of unstable diaphyseal fractures of the tibia with distal intraarticular involvement. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:200–205.
Article12. McKibbin B. The biology of fracture healing in long bones. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978; 60:150–162.
Article13. Melis GC, Sotgiu F, Lepori M, Guido P. Intramedullary nailing in segmental tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:1310–1318.
Article14. Merchant TC, Dietz FR. Long-term follow-up after fractures of tibial and fibular shafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:599–606.15. Nicoll EA. Closed and open management of tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974; 105:144–153.
Article16. Park IH, Song KW, Shin SI, et al. Interlocking intramedullary nailing for treating most distal tibial fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 2003; 16:356–362.
Article17. Richter D, Hahn MP, Laun RA, Ekkernkamp A, Muhr G, Ostermann PA. Ankle para-articular tibial fracture. Is osteosynthesis with the unreamed intramedullary nail adequate? Chirurg. 1998; 69:563–570.18. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:781–787.
Article19. Rockwood CA, Green DP. Fractures. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippencott Co;1991. p. 1593–1663.20. Rzesacz EH, Konneker W, Reilmann H, Culemann U. Combination of intramedullary nail and covered screw osteosynthesis for managing distal tibial fracture with ankle joint involvement. Unfallchirurg. 1998; 101:907–913.
Article21. Shepherd LE, Costigan WM, Gardocki RJ, Ghiassi AD, Patzakis MJ, Stevanovic MV. Local or free muscle flaps and unreamed interlocked nails for open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 350:90–96.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative Fracture of the Tibia Associated with Removal of the Interlocking Intramedullary Nail: Report of 5 cases
- Posterior Cortical Fracture of Tibia during Tibial Interlocking Intramedurally Nail Extraction : A report of 3 cases
- Acase of Fatigue Fracture of the Interlocking nail in the Treatment of Fracture of the Femoral Shaft
- Treatment of Tibial Fractures by Interlocking Intramedullary Nailling
- Malalignment of Tibial Fracture Following Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing