J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs.
2014 Dec;25(4):225-236. 10.12799/jkachn.2014.25.4.225.
Development of an Assessment Tool for Drinking Motives and Problem Drinking in Female University Students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Howon University, Gunsan, Korea. wienona@hanmail.net
- 2Division of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2292702
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2014.25.4.225
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of the study is to develop a tool that can identify drinking motives and measure the degree of problem drinking in female university students.
METHODS
From June 25th, 2012 to September 21st, 2012, a methodological study was carried out on this subject. A basic questionnaire was made based on research literature and interviews with 8 female university students. The subjects who participated in the survey for factor analysis were 397 female university students from 2 universities in G Metropolitan City.
RESULTS
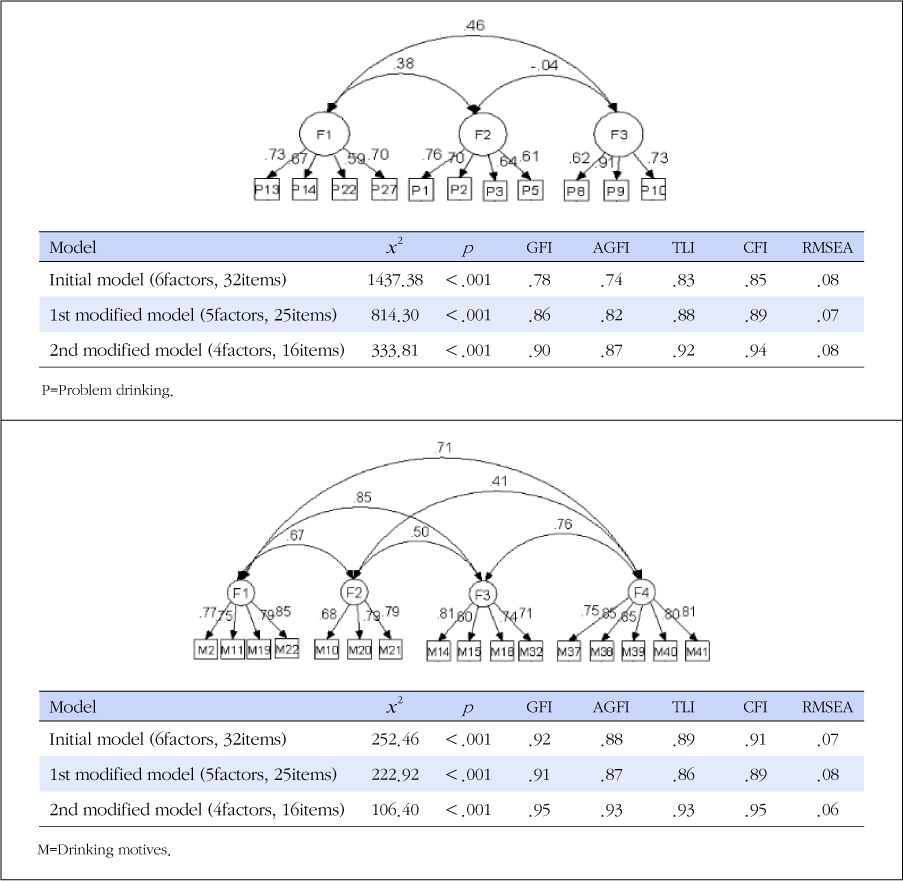
Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were conducted using PASW and AMOS 18.0. The developed tool was found to be acceptable in terms of construct validity and modeling suitability. The questionnaire comprised 16 questions on drinking motives in 4 sub-categories including 'relief' (4 questions), 'friendship' (3 questions), 'consolation' (4 questions), and 'escape' (5 questions). Problem drinking consisted of 11 questions in 3 different sub-categories including 'loss of control,' 'health hazards,' and 'sexual hazards.'
CONCLUSION
The questionnaire was proved to have reliability and validity. Finally, the researcher suggests that this questionnaire is adequate for assessing drinking motives and problem drinking of female university students.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shim SW, Lee JW, Sohn YK. An Approach on drinking reduction campaign strategic establishment of Korean women's college students: An application of the theory of planned behavior. Korean J Advert Public Relat. 2009; 11(1):204–247.2. Yang SH, Han KS. Drinking pattern, problem related drinking, perceived stress, ways of coping, and symptoms of stress of the female university students. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2003; 33(7):1057–1064.
Article3. Mun YH. Factors influencing drinking problems in female university students. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2007; 18(4):552–561.4. Park KM, Rhee MK. Effects of perceived stress, social support and drinking motives on drinking behaviors among college students. Korean J Health Psychol. 2005; 10(3):277–293.5. Kim HK, Choi ES, Ahn JS. Factors influencing alcohol consuming behavior of the female university students. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2004; 10(2):205–216.6. Ryu HS, Paek MJ. Factors influencing the drinking behavior in female university students. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2012; 23(3):307–315.
Article7. Park JS. A study on factors affecting problem drinking of university students. Korean Public Health Res. 2000; 26(4):393–413.8. Do EY, Kim YH, Kim JH. Comparison of problem drinking and alcohol expectancy among female college students, workers and housewives. J Korean Alcohol Sci. 2009; 10(1):93–106.9. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report No.: 11-1351159-000027-10. Korea health statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey report (KNHANES V-1). Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011.10. Kim IS, Lee YH. The effects of personality, social pressure and drinking motivation on drinking and drinking problems. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2003; 22(3):525–541.11. Tak JK. The effects of personality traits and life events on drinking motives. Korean J Health Psychol. 2000; 5(1):73–83.12. Cox WM, Klinger E. A motivational model of alcohol use. J Abnorm Psychol. 1988; 97(2):168–180.
Article13. Cooper ML, Russell M, Skinner JB, Windle M. Development and validation of a three-dimensional measure of drinking motives. Psychol Assess. 1992; 4(2):123–132. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.4.2.123.
Article14. Cooper ML. Motivations for alcohol use among adolescents: Development and validation of a four-factor model. Psychol Assess. 1994; 6(2):117–128. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.6.2.117.
Article15. Ooteman W, Koeter M, Verheul R, Schippers G, Van den Brink W. Development and validation of the amsterdam motives for drinking scale(AMDS): An attempt to distinguish relief and reward drinkers. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006; 41(3):284–292.16. Doyle SR, Donovan DM, Simpson TL. Validation of a nine-dimensional measure of drinking motives for use in clinical application: The desired effects of drinking scale. Addict Behav. 2011; 36(11):1052–1060. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.06.012.17. LaBrie JW, Hummer JF, Pedersen ER, Lac A, Chithambo T. Measuring college students' motives behind prepartying drinking: Development and validation of the prepartying motivations inventory. Addict Behav. 2012; 37(8):962–969. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.04.003.
Article18. Shin HW. The relationship between drinking motives and drinking problems. Korean J Psychol Soc Issues. 1999; 5(1):93–109.19. Chung SK. Factors influencing problem drinking among female college students in Korea. Ment Health Soc Work. 2007; 27:176–198.20. Kim JH, Kim MG, Hong SH. Writing scholarly papers with the structural equation modeling. Seoul: Communication Books;2009. p. 452.21. Um MY, Cho SU. Scale development in social work practice. Seoul: Hakjisa;2005. p. 240.22. Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate data analysis. 7th ed. New Jersey, NJ: Pearson;2010. p. 800.23. Kim GS. Structural equation modeling analysis. Seoul: Hannarae Academy;2011. p. 663.24. Shin HW, Han SY. A preliminary study for developing drinking motives scale. Korean J Psychol Soc Issues. 1999; 5(1):77–92.25. Yoon HM. Drinking behavior and factors that influence alcohol use among university students. J Hum Ecol. 2000; 3:1–15.26. Cooper ML, Frone MR, Russell M, Mudar P. Drinking to regulate positive and negative emotions: A motivational model of alcohol use. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1995; 69(5):990–1005.
Article27. Lee SH, Chung SE. Drinking experiences of female college students. Korean J Womens Health. 2011; 12(1):1–19.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How Do the Drinking Motives and Expectancies Relate to Drinking Problems among University Students?
- Factors Affecting Problem Drinking in Male Nursing Students
- Factors Influencing the Drinking Behavior in Female University Students
- Influences of Level of Alcohol Consumption and Motives for Drinking on Drinking Permissiveness in University Students
- Factors associated with Problem Drinking in Korean Male Employees for Drinking Motivation, Job Stress, and Drinking Refusal Self-efficacy