J Clin Neurol.
2014 Apr;10(2):108-118. 10.3988/jcn.2014.10.2.108.
Idiopathic Small Fiber Neuropathy: Phenotype, Etiologies, and the Search for Fabry Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge, Stockholm, Sweden. kristin.samuelsson@ki.se
- 2Division of Neurology and Clinical Neurophysiology, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, Linkoping University, Linkoping, Sweden.
- 3Albrecht-Kossel Institute for Neuroregeneration, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany.
- KMID: 2287528
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.2.108
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The etiology of small fiber neuropathy (SFN) often remains unclear. Since SFN may be the only symptom of late-onset Fabry disease, it may be underdiagnosed in patients with idiopathic polyneuropathy. We aimed to uncover the etiological causes of seemingly idiopathic SFN by applying a focused investigatory procedure, to describe the clinical phenotype of true idiopathic SFN, and to elucidate the possible prevalence of late-onset Fabry disease in these patients.
METHODS
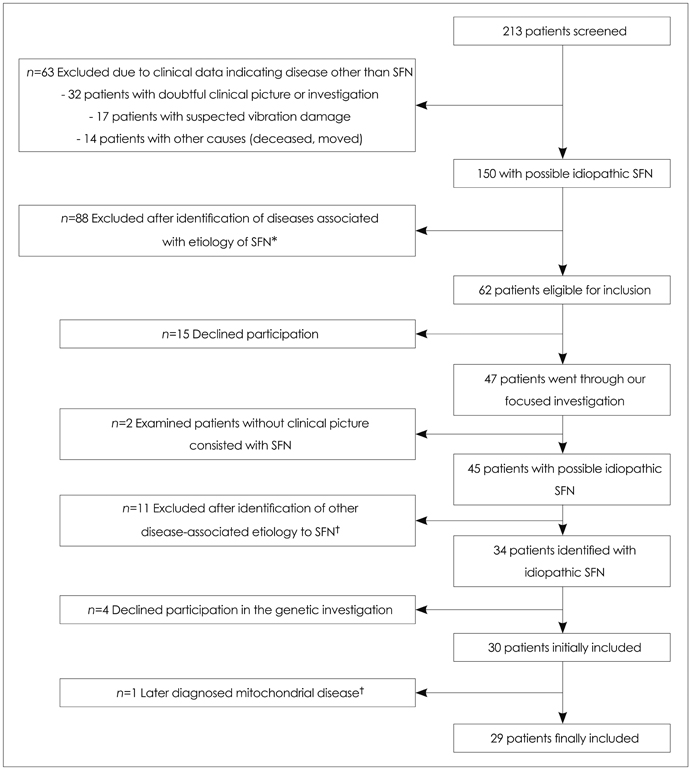
Forty-seven adults younger than 60 years with seemingly idiopathic pure or predominantly small fiber sensory neuropathy underwent a standardized focused etiological and clinical investigation. The patients deemed to have true idiopathic SFN underwent genetic analysis of the alpha-galactosidase A gene (GLA) that encodes the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A (Fabry disease).
RESULTS
The following etiologies were identified in 12 patients: impaired glucose tolerance (58.3%), diabetes mellitus (16.6%), alcohol abuse (8.3%), mitochondrial disease (8.3%), and hereditary neuropathy (8.3%). Genetic alterations of unknown clinical significance in GLA were detected in 6 of the 29 patients with true idiopathic SFN, but this rate did not differ significantly from that in healthy controls (n=203). None of the patients with genetic alterations in GLA had significant biochemical abnormalities simultaneously in blood, urine, and skin tissue.
CONCLUSIONS
A focused investigation may aid in uncovering further etiological factors in patients with seemingly idiopathic SFN, such as impaired glucose tolerance. However, idiopathic SFN in young to middle-aged Swedish patients does not seem to be due to late-onset Fabry disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, Camozzi F, Lombardi R, Melli G, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008; 131(Pt 7):1912–1925.
Article2. Lacomis D. Small-fiber neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:173–188.
Article3. Novak V, Freimer ML, Kissel JT, Sahenk Z, Periquet IM, Nash SM, et al. Autonomic impairment in painful neuropathy. Neurology. 2001; 56:861–868.
Article4. Bednarik J, Vlckova-Moravcova E, Bursova S, Belobradkova J, Dusek L, Sommer C. Etiology of small-fiber neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2009; 14:177–183.
Article5. Singleton JR, Smith AG, Bromberg MB. Painful sensory polyneuropathy associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Muscle Nerve. 2001; 24:1225–1228.
Article6. Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M. The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology. 2003; 60:108–111.
Article7. Gøransson LG, Tjensvoll AB, Herigstad A, Mellgren SI, Omdal R. Small-diameter nerve fiber neuropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol. 2006; 63:401–404.
Article8. Lopate G, Pestronk A, Al-Lozi M, Lynch T, Florence J, Miller T, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in an outpatient cohort of patients with Sjögrens' syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2006; 33:672–676.
Article9. Chin RL, Sander HW, Brannagan TH, Green PH, Hays AP, Alaedini A, et al. Celiac neuropathy. Neurology. 2003; 60:1581–1585.
Article10. Khan S, Zhou L. Characterization of non-length-dependent small-fiber sensory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 45:86–91.
Article11. Magri F, Buonocore M, Oliviero A, Rotondi M, Gatti A, Accornero S, et al. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density reduction as a marker of preclinical asymptomatic small-fiber sensory neuropathy in hypothyroid patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010; 163:279–284.
Article12. Barbieri S, Sandroni P, Nobile-Orazio E, Cappellari A, Cavestro C, Baldini L, et al. Small fibre involvement in neuropathy associated with IgG, IgA and IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995; 35:39–44.13. Periquet MI, Novak V, Collins MP, Nagaraja HN, Erdem S, Nash SM, et al. Painful sensory neuropathy: prospective evaluation using skin biopsy. Neurology. 1999; 53:1641–1647.
Article14. Polydefkis M, Yiannoutsos CT, Cohen BA, Hollander H, Schifitto G, Clifford DB, et al. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density in HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. Neurology. 2002; 58:115–119.
Article15. Yoon MS, Obermann M, Dockweiler C, Assert R, Canbay A, Haag S, et al. Sensory neuropathy in patients with cryoglobulin negative hepatitis-C infection. J Neurol. 2011; 258:80–88.
Article16. Adams D. Hereditary and acquired amyloid neuropathies. J Neurol. 2001; 248:647–657.
Article17. Peltier AC, Russell JW. Advances in understanding drug-induced neuropathies. Drug Saf. 2006; 29:23–30.
Article18. Zambelis T, Karandreas N, Tzavellas E, Kokotis P, Liappas J. Large and small fiber neuropathy in chronic alcohol-dependent subjects. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005; 10:375–381.
Article19. Verhoeven K, Timmerman V, Mauko B, Pieber TR, De Jonghe P, Auer-Grumbach M. Recent advances in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies. Curr Opin Neurol. 2006; 19:474–480.
Article20. Stewart JD, Low PA, Fealey RD. Distal small fiber neuropathy: results of tests of sweating and autonomic cardiovascular reflexes. Muscle Nerve. 1992; 15:661–665.
Article21. De Sousa EA, Hays AP, Chin RL, Sander HW, Brannagan TH 3rd. Characteristics of patients with sensory neuropathy diagnosed with abnormal small nerve fibres on skin biopsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006; 77:983–985.
Article22. Gemignani F, Giovanelli M, Vitetta F, Santilli D, Bellanova MF, Brindani F, et al. Non-length dependent small fiber neuropathy. A prospective case series. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010; 15:57–62.
Article23. Holland NR, Crawford TO, Hauer P, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW, McArthur JC. Small-fiber sensory neuropathies: clinical course and neuropathology of idiopathic cases. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44:47–59.
Article24. Laaksonen SM, Röyttä M, Jääskeläinen SK, Kantola I, Penttinen M, Falck B. Neuropathic symptoms and findings in women with Fabry disease. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:1365–1372.
Article25. MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 60 obligate carrier females. J Med Genet. 2001; 38:769–775.
Article26. Sugawara K, Ohno K, Saito S, Sakuraba H. Structural characterization of mutant alpha-galactosidases causing Fabry disease. J Hum Genet. 2008; 53:812–824.
Article27. Monserrat L, Gimeno-Blanes JR, Marín F, Hermida-Prieto M, García-Honrubia A, Pérez I, et al. Prevalence of fabry disease in a cohort of 508 unrelated patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50:2399–2403.
Article28. Nakao S, Takenaka T, Maeda M, Kodama C, Tanaka A, Tahara M, et al. An atypical variant of Fabry's disease in men with left ventricular hypertrophy. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:288–293.
Article29. Rolfs A, Böttcher T, Zschiesche M, Morris P, Winchester B, Bauer P, et al. Prevalence of Fabry disease in patients with cryptogenic stroke: a prospective study. Lancet. 2005; 366:1794–1796.
Article30. Sawada K, Mizoguchi K, Hishida A, Kaneko E, Koide Y, Nishimura K, et al. Point mutation in the alpha-galactosidase A gene of atypical Fabry disease with only nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1996; 45:289–294.31. Yang CC, Lai LW, Whitehair O, Hwu WL, Chiang SC, Lien YH. Two novel mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene in Chinese patients with Fabry disease. Clin Genet. 2003; 63:205–209.
Article32. Dütsch M, Marthol H, Stemper B, Brys M, Haendl T, Hilz MJ. Small fiber dysfunction predominates in Fabry neuropathy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 19:575–586.
Article33. Luciano CA, Russell JW, Banerjee TK, Quirk JM, Scott LJ, Dambrosia JM, et al. Physiological characterization of neuropathy in Fabry's disease. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:622–629.
Article34. Spada M, Pagliardini S, Yasuda M, Tukel T, Thiagarajan G, Sakuraba H, et al. High incidence of later-onset fabry disease revealed by newborn screening. Am J Hum Genet. 2006; 79:31–40.
Article35. Tanislav C, Kaps M, Rolfs A, Böttcher T, Lackner K, Paschke E, et al. Frequency of Fabry disease in patients with small-fibre neuropathy of unknown aetiology: a pilot study. Eur J Neurol. 2011; 18:631–636.
Article36. Hilz MJ, Brys M, Marthol H, Stemper B, Dütsch M. Enzyme replacement therapy improves function of C-, Adelta-, and Abeta-nerve fibers in Fabry neuropathy. Neurology. 2004; 62:1066–1072.
Article37. Lidove O, West ML, Pintos-Morell G, Reisin R, Nicholls K, Figuera LE, et al. Effects of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease--a comprehensive review of the medical literature. Genet Med. 2010; 12:668–679.
Article38. Desnick RJ, Allen KY, Desnick SJ, Raman MK, Bernlohr RW, Krivit W. Fabry's disease: enzymatic diagnosis of hemizygotes and heterozygotes. Alpha-galactosidase activities in plasma, serum, urine, and leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1973; 81:157–171.39. Jansen T, Brokalaki E, Hillen U, Hentschke M, Grabbe S. [Manifestation of Fabry disease in a heterozygous female patient. New perspectives using enzyme replacement therapy]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2006; 131:1590–1593.40. Üçeyler N, He L, Schönfeld D, Kahn AK, Reiners K, Hilz MJ, et al. Small fibers in Fabry disease: baseline and follow-up data under enzyme replacement therapy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011; 16:304–314.
Article41. Froissart R, Guffon N, Vanier MT, Desnick RJ, Maire I. Fabry disease: D313Y is an alpha-galactosidase A sequence variant that causes pseudodeficient activity in plasma. Mol Genet Metab. 2003; 80:307–314.
Article42. Gaspar P, Herrera J, Rodrigues D, Cerezo S, Delgado R, Andrade CF, et al. Frequency of Fabry disease in male and female haemodialysis patients in Spain. BMC Med Genet. 2010; 11:19.
Article43. Yasuda M, Shabbeer J, Benson SD, Maire I, Burnett RM, Desnick RJ. Fabry disease: characterization of alpha-galactosidase A double mutations and the D313Y plasma enzyme pseudodeficiency allele. Hum Mutat. 2003; 22:486–492.
Article44. Biegstraaten M, Hollak CE, Bakkers M, Faber CG, Aerts JM, van Schaik IN. Small fiber neuropathy in Fabry disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2012; 106:135–141.
Article45. Hughes RA, Umapathi T, Gray IA, Gregson NA, Noori M, Pannala AS, et al. A controlled investigation of the cause of chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 8):1723–1730.
Article46. Lindh J, Tondel M, Osterberg A, Vrethem M. Cryptogenic polyneuropathy: clinical and neurophysiological findings. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005; 10:31–37.
Article47. Notermans NC, Wokke JH, Franssen H, van der, Vermeulen M, van der Graaf Y, et al. Chronic idiopathic polyneuropathy presenting in middle or old age: a clinical and electrophysiological study of 75 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993; 56:1066–1071.
Article48. Wolfe GI, Baker NS, Amato AA, Jackson CE, Nations SP, Saperstein DS, et al. Chronic cryptogenic sensory polyneuropathy: clinical and laboratory characteristics. Arch Neurol. 1999; 56:540–547.49. Liedberg GM, Vrethem M. Polyneuropathy, with and without neurogenic pain, and its impact on daily life activities--a descriptive study. Disabil Rehabil. 2009; 31:1402–1408.
Article50. Lindh J, Tondel M, Persson B, Vrethem M. Health-related quality of life in patients with cryptogenic polyneuropathy compared with the general population. Disabil Rehabil. 2011; 33:617–623.
Article51. Hoitsma E, Reulen JP, de Baets M, Drent M, Spaans F, Faber CG. Small fiber neuropathy: a common and important clinical disorder. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 227:119–130.
Article52. Tavee J, Culver D. Sarcoidosis and small-fiber neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2011; 15:201–206.
Article53. Finsterer J. Inherited mitochondrial neuropathies. J Neurol Sci. 2011; 304:9–16.
Article54. Mancuso M, Piazza S, Volpi L, Orsucci D, Calsolaro V, Caldarazzo Ienco E, et al. Nerve and muscle involvement in mitochondrial disorders: an electrophysiological study. Neurol Sci. 2012; 33:449–452.
Article55. Henning F, Oey PL, Oerlemans WG, Wokke JH. Small-fiber neuropathy and the 3243A>G mutation in mitochondrial DNA. J Neurol. 2007; 254:1281–1282.
Article56. Dyck PJ, Clark VM, Overland CJ, Davies JL, Pach JM, Dyck PJ, et al. Impaired glycemia and diabetic polyneuropathy: the OC IG Survey. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:584–591.57. Smith AG, Rose K, Singleton JR. Idiopathic neuropathy patients are at high risk for metabolic syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2008; 273:25–28.
Article58. Baptista MV, Ferreira S, Pinho-E-Melo T, Carvalho M, Cruz VT, Carmona C, et al. Mutations of the GLA gene in young patients with stroke: the PORTYSTROKE study--screening genetic conditions in Portuguese young stroke patients. Stroke. 2010; 41:431–436.
Article59. Morita H, Larson MG, Barr SC, Vasan RS, O'Donnell CJ, Hirschhorn JN, et al. Single-gene mutations and increased left ventricular wall thickness in the community: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2006; 113:2697–2705.
Article60. Lauria G, Cornblath DR, Johansson O, McArthur JC, Mellgren SI, Nolano M, et al. EFNS guidelines on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Eur J Neurol. 2005; 12:747–758.
Article61. Lauria G, Hsieh ST, Johansson O, Kennedy WR, Leger JM, Mellgren SI, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:903–912.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART) as a diagnostic tool of small fiber neuropathy
- Skin Biopsy: Emerging Method for Small Nerve Fiber Evaluation
- A Case of Autonomic Dysfunction and Painful Sensory Neuropathy in Sjogren's Syndrome
- Skin biopsy: an emerging method for small nerve fiber evaluation
- Fabry Disease in a Family: Four Patients and Five Carriers