Healthc Inform Res.
2014 Apr;20(2):135-144. 10.4258/hir.2014.20.2.135.
Impacts of Hospitals' Innovativeness on Information System Outsourcing Decisions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Care Administration, Kosin University, Busan, Korea. jpark@kosin.ac.kr
- KMID: 2284573
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2014.20.2.135
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
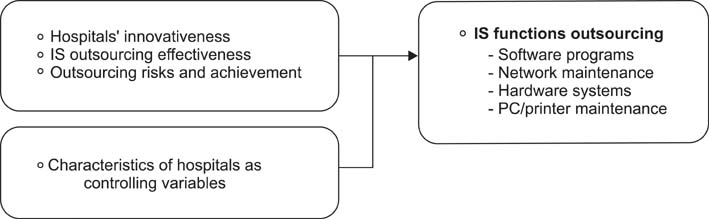
The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of hospitals' innovativeness on outsourcing decision-making regarding four information system (IS) functions, namely, software programs, network maintenance, hardware systems, and PC/printer maintenance.
METHODS
Using the 2011 roster of the Korean Hospital Association, this study selected 311 general hospitals as a study population. After identifying the managers who were in charge of outsourcing, this study administered questionnaires. A total of 103 hospitals responded.
RESULTS
Of the responding hospitals, 55.34% outsourced at least one IS function, whereas 88.35% outsourced at least one managerial function. IS outsourcing was motivated by the need for outside experts, but other managerial functions were outsourced for cost savings. Innovative and early adopter hospitals were 4.52 and 4.91 times more likely to outsource IS functions related with work processes (i.e., software and network maintenance) than early and late majority hospitals, respectively. IT outsourcing effectiveness significantly influenced the outsourcing decisions regarding four IS functions. Hospitals that had perceived more risks of outsourcing significantly preferred non-outsourcing on their hardware systems, but the risks of outsourcing were not significant for outsourcing decisions regarding the other IS functions. Hospitals' innovativeness also significantly explained the quantity of innovation adoptions. Innovative and early adopter hospitals did more outsourcing than early and late majority hospitals.
CONCLUSIONS
Hospitals' innovativeness influences decision-making regarding outsourcing. Innovative hospitals are more likely to outsource their work-process-related IS functions. Thus, organizational traits, especially hospitals' innovativeness, should be considered as a key success factor for IS management.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Quinn JB. Outsourcing innovation: the new engine of growth. Sloan Manag Rev. 2000; 41(4):13–28.2. Damanpour F. The adoption of technological, administrative, and ancillary innovations: impact of organizational factors. J Manag. 1987; 13(4):675–688.
Article3. Choy S, Shin HS, Choi I, Kim S. A study on facilitators and inhibitors to the introduction of outsourcing in the hospital information systems in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2007; 40(1):64–70.
Article4. Kim DS, Park HY. A study on information development status and strategies of large size Korean hospitals. Inform Policy. 2004; 11(3):13–19.5. Noh TH, Lee HJ, Park EJ, Kang HY. Outsourcing in hospital services: experience in Korean hospitals. Korean J Hosp Manage. 2003; 8(4):59–75.6. Grover V, Cheon MJ, Teng JTC. The effect of service quality and partnership on the outsourcing of information systems functions. J Manag Inf Syst. 1996; 12(4):89–116.
Article7. Klaas BS, McClendon JA, Gainey TW. Outsourcing HR: the impact of organizational characteristics. Hum Resour Manag. 2001; 40(2):125–138.
Article8. Loh L, Venkatraman N. An empirical study of information technology outsourcing: benefits, risks, and performance implications. In : Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Systems; 1995 Dec 10-13; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. p. 277–288.9. Earl MJ. The risks of outsourcing IT. Sloan Manag Rev. 1996; 37(3):26–32.10. Rogers EM. Diffusion of innovations. 4th ed. New York (NY): Free Press;1995.11. Rogers EM. Diffusion of innovations. 5th ed. New York (NY): Free Press;2003.12. Kessler EH, Chakrabarti AK. Innovation speed: a conceptual model of context, antecedents, and outcomes. Acad Manag Rev. 1996; 21(4):1143–1191.
Article13. Downs GW Jr, Mohr LB. Conceptual issues in the study of innovation. Adm Sci Q. 1980; 21(4):700–714.
Article14. Ryu JH, Sin GC, Hyeon CH. Utilization of outsourcing and the status of outsourcing industry in Korea. Hyundai Res Inst. 1998; 11(30):7.15. Park JS, Kim HS. Impacts of individual innovativeness on the acceptance of IT-based innovations in health care fields. Healthc Inform Res. 2010; 16(4):290–298.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Facilitators and Inhibitors to the Introduction of Outsourcing in the Hospital Information Systems in Korea
- Change Commitment and Learning Orientation as Factors Affecting the Innovativeness of Clinical Nurses
- Factors Affecting the Diffusion of Health Center Information System
- Consumer Innovativeness and Consumption Behavior of New Sauce Products for the Japanese Consumer
- A Survey Study of Nursing Information Systems Implementation in Korean Hospitals