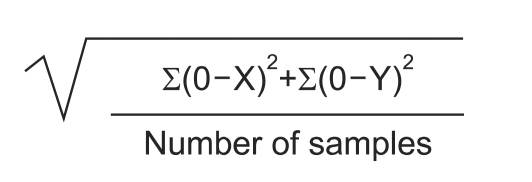Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Dec;35(6):873-879. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.873.
Comparison of Manual Balance and Balance Board Tests in Healthy Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan 330-721, Korea. yeop6lee@gmail.com
- KMID: 2266814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.873
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
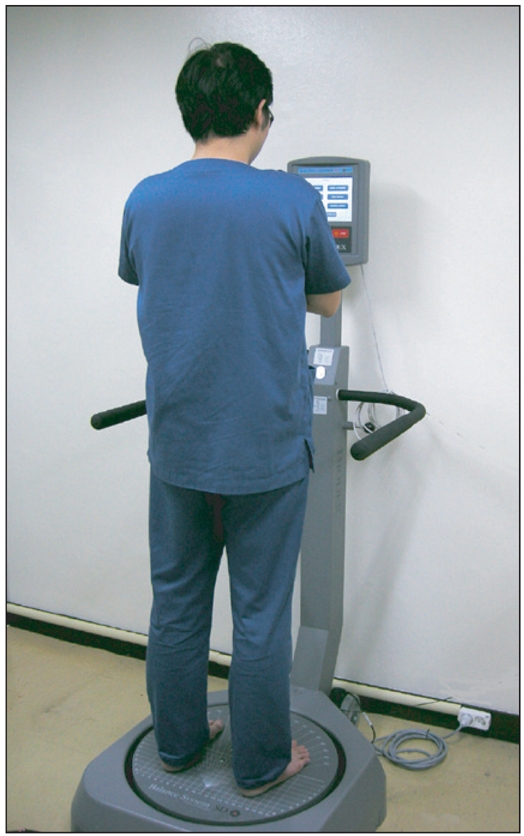
To investigate the correlations of scores on the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test and the Single Leg Stance (SLS) test with stability scores on the Biodex Balance System (BBS) in healthy adults. METHOD: The postural balance of 73 participants was measured on the TUG and SLS tests and with the Overall Stability Index (OSI) on the BBS. The participants were divided into groups by age and by times on the TUG and SLS. The correlations between TUG or SLS and OSI scores were analyzed by groups.
RESULTS
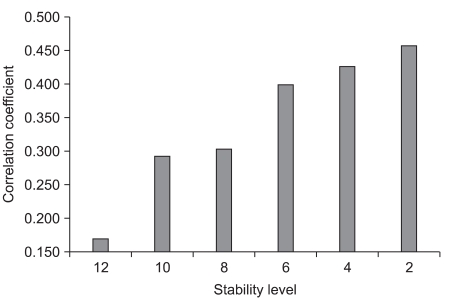
TUG scores were significantly correlated with OSI scores in age under 65 years, TUG over 10 seconds and SLS over 30 seconds groups (level 12). TUG scores were also correlated with OSI in total (level 10) and TUG under 10 seconds groups (level 2). However, there were no significant relationships between SLS and OSI scores.
CONCLUSION
OSI scores on the BBS are significantly correlated with TUG scores, especially at the easy levels. According to the findings of present study, relatively easy BBS levels are considered to assess the postural balance in healthy adults.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee WA. A control systems framework for understanding normal and abnormal posture. Am J Occup Ther. 1989; 43:291–301. PMID: 2655455.
Article2. Emery CA. Is there a clinical standing balance measurement appropriate for use in sports medicine? A review of the literature. J Sci Med Sport. 2003; 6:492–450. PMID: 14723398.
Article3. Yelnik A, Bonan I. Clinical toos for assessing balance disorders. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008; 38:439–445. PMID: 19026963.4. Yim-Chiplis PK, Talbot LA. Defining and measuring balance in adults. Biol Res Nurs. 2000; 1:321–331. PMID: 11232210.
Article5. Arnold BL, Schmitz RJ. Examination of balance measures produced by the biodex stability system. J Athl Train. 1998; 33:323–327. PMID: 16558529.6. Aydog E, Aydog ST, Cakci A, Doral MN. Dynamic postural stability in blind athletes using the Biodex Stability System. Int J Sports Med. 2006; 27:415–418. PMID: 16729385.
Article7. Aydog E, Bal A, Aydog ST, Cakci A. Evaluation of dynamic postural balance using the Biodex Stability System in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 25:462–467. PMID: 16247584.
Article8. Aydog E, Depedibi R, Bal A, Eksioglu E, Unlü E, Cakci A. Dynamic postural balance in ankylosing spondylitis patients. Rheumatology. 2006; 45:445–448. PMID: 16278280.9. Cakar E, Dincer U, Kiralp MZ, Cakar DB, Durmus O, Kilac H, Soydan FC, Sevinc S, Alper C. Junping combined exercise programs reduce fall risk and improve balance and life quality of elderly people who live in a long-term care facility. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2010; 46:59–67. PMID: 20332728.10. Alonso AC, Greve JM, Camanho GL. Evaluating the center of gravity of dislocations in soccer players with and without reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament using a balance platform. Clinics. 2009; 64:163–170. PMID: 19330239.
Article11. Podsiadlo D, Richardson S. The timed "Up&Go": a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991; 39:142–148. PMID: 1991946.12. Eggermont LH, Gavett BE, Volkers KM, Blankevoort CG, Scherder EJ, Jefferson AL, Steinberg E, Nair A, Green RC, Stern RA. Lower-extremity function in cognitively healthy aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:584–588. PMID: 20382291.
Article13. Sun SF, Hsu CW, Hwang CW, Hsu PT, Wang JL, Tsai SL, Chou YJ, Hsu YW, Huang CM, Wang YL. Hyaluronate improves pain, physical function and balance in the geriatric osteoarthritic knee: a 6-month follow-up study using clinical tests. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14:696–701. PMID: 16520067.
Article14. Vaillant J, Vuillerme N, Martigne P, Caillat-Miousse JL, Parisot J, Nougier V, Juvin R. Balance, aging, and osteoporosis: effects of cognitive exercises combined with physiotherapy. Joint Bone Spine. 2006; 73:414–418. PMID: 16488641.15. Vellas BJ, Wayne SJ, Romero L, Baumgartner RN, Rubenstein LZ, Garry PJ. One-leg balance is an important predictor of injurious falls in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997; 45:735–738. PMID: 9180669.
Article16. Bohannon RW, Larkin PA, Cook AC, Gear J, Singer J. Decrease in timed balance test scores with aging. Phys Ther. 1984; 64:1067–1070. PMID: 6739548.
Article17. Briggs RC, Gossman MR, Birch R, Drews JE, Shaddeau SA. Balance performance among noninstitutionalized elderly women. Phys Ther. 1989; 69:748–756. PMID: 2772037.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Action Observation Training Using Y-Balance on Balance Capability in Young Adults
- Effect of Balance Board Training with Tactile Stimulation on Affected Leg in Hemiplegic Patient
- Assessments of Static Balance Using Virtual Moving Surround
- Comparison of the Static Balance Ability according to the Subjective Visual Vertical in Healthy Adults
- Effect of Characteristics of Joint Motion of Lower Extremity according to Aging on Balance in Elderly