Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Feb;38(1):52-56. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52.
Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial Radial Nerve and Cephalic Vein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ssoc0302@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2266540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
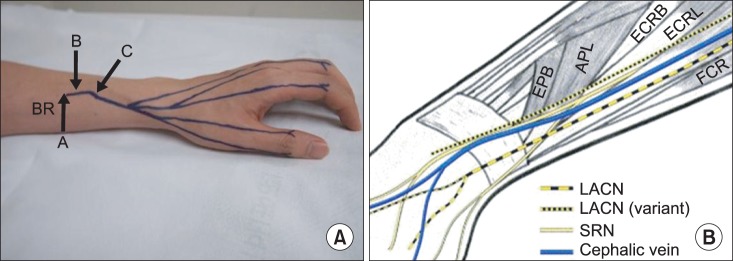
To investigate the anatomic relationship between the superficial radial nerve (SRN) and the cephalic vein (CV) through ultrasonography due to the possibility of SRN injury during cephalic venipuncture.
METHODS
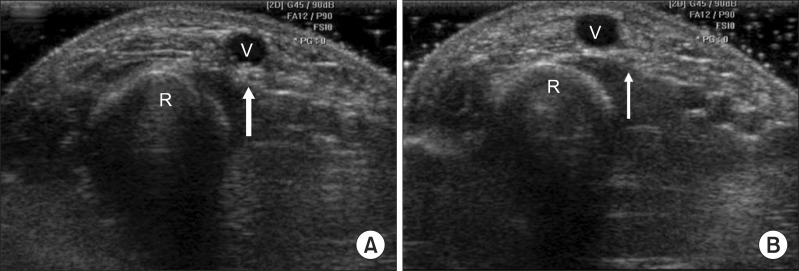
Both forearms of 51 healthy volunteers with no history of trauma or surgery were examined in proximal to distal direction using ultrasonography. We measured the distance between the radial styloid process (RSP) and the point where the SRN begins contact with the CV, and measured the distance between the RSP and the point where the SRN is separated from the CV. The point where the SRN penetrates the brachioradialis fascia was also evaluated.
RESULTS
The SRN came in contact with the CV at a mean of 9.35+/-1.05 cm from the RSP and separated from the CV at a mean of 6.29+/-1.17 cm from the RSP. The SRN pierced the brachioradialis fascia at a mean of 10.31+/-0.89 cm from the RSP and horizontally 1.35+/-0.36 cm medial to the radius margin. All parameters had no significant differences in gender or direction.
CONCLUSION
The SRN had close approximation to the CV in the distal second quarter of the forearm. We recommend for cephalic venipuncture to be avoided in this area, and, if needed, it should be carried out with care not to cause injury to the SRN.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jenkins DB. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. 9th ed. St. Louis, MO: Saunders;2009.2. Thrush DN, Belsole R. Radial nerve injury after routine peripheral vein cannulation. J Clin Anesth. 1995; 7:160–162. PMID: 7598927.
Article3. Dellon AL, Mackinnon SE. Treatment of the painful neuroma by neuroma resection and muscle implantation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 77:427–438. PMID: 2937074.
Article4. Kim JS, Yoo SH, Chung ME, Oh JS, Cho DW, Choi GH. Superficial radial nerve and cephalic vein: an anatomic study by cadaver dissection. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:394–396.5. Horowitz SH. Venipuncture-induced neuropathic pain: the clinical syndrome, with comparisons to experimental nerve injury models. Pain. 2001; 94:225–229. PMID: 11731059.
Article6. Kilic A, Kale A, Usta A, Bilgili F, Kabukcuoglu Y, Sokucu S. Anatomic course of the superficial branch of the radial nerve in the wrist and its location in relation to wrist arthroscopy portals: a cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25:1261–1264. PMID: 19896048.7. Ikiz ZA, Ucerler H. Anatomic characteristics and clinical importance of the superficial branch of the radial nerve. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004; 26:453–458. PMID: 15365770.
Article8. Yoon JS, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ulnar neuropathy with normal electrodiagnosis and abnormal nerve ultrasound. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:318–320. PMID: 20159139.
Article9. Won SJ, Kim BJ, Park KS, Yoon JS, Choi H. Reference values for nerve ultrasonography in the upper extremity. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:864–871. PMID: 23625758.
Article10. Steinberg BD, Plancher KD, Idler RS. Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation through the snuff box: an anatomic study. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20:57–62. PMID: 7722267.
Article11. Marx SC, Dhalapathy S, Marx CA, Babu MS, Pulakunta T, Vasanthakumar . Ultrasonographical and histological cross-sectional study of the human superficial branch of the radial nerve. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011; 52(3 Suppl):1081–1090. PMID: 22119829.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Superficial Radial Nerve and Cephalic Vein: An Anatomic Study by Cadaver Dissection
- Superficial Radial Neuropathy due to Anatomic Variation: A Case Report
- Pitfalls in Superficial Radial Sensory Nerve Conduction Study
- Cephalic Vein Supercharging to Prevent Venous Congestion for a Reverse Radial Forearm Flap Used in the Reconstruction of Dorsum of Hand: A Case Report
- Clinical, Electrophysiological, and Sonographic Findings in Patients With Nerve Injury After Vessel Puncture