Ann Dermatol.
2014 Oct;26(5):592-597. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.592.
Usefulness of the Autologous Serum Test for the Diagnosis of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
- Affiliations
-
- 1M-ONEP Clinics, Istanbul, Turkey.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey. zekayikutlubay@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2265492
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.592
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The majority of chronic urticaria cases are chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) with no specific identifiable etiology. The role of autoantibodies in such cases remains controversial.
OBJECTIVE
This study determined the positivity rate of autologous serum tests in CIU patients.
METHODS
This study was performed on 30 patients with CIU and 30 individuals without any systemic or dermatologic disease. After the volar parts of right and left forearms were cleansed, 0.05 ml serum physiologic and 0.05 ml autologous serum were injected intradermally on the right forearm 5 cm apart from each other, resulting in the formation of small papules; meanwhile, 0.05 ml histamine alone was injected to the left forearm. The test results were evaluated after 30 minutes as positive in positive cases.
RESULTS
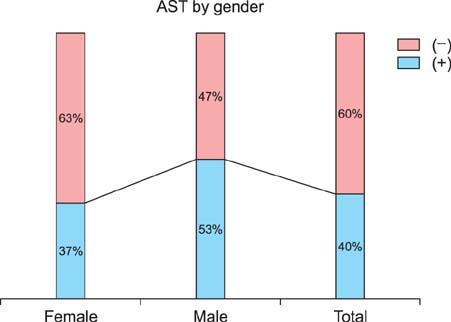
The autologous serum test produced significant and non-significant results in patients with CIU and controls, respectively. The positivity rates of the autologous serum test in the CIU and control groups were 53.3% and 26.6%, respectively. There was no relationship between autologous serum test positivity and sex in either group. In male patients with CIU, positive results ranged widely with age, while in female patients, positive results were mainly observed at younger ages with a narrow age range.
CONCLUSION
The autologous serum test is a useful test in the diagnosis and treatment of CIU as well as the selection of immunotherapy, especially in patients refractory to classic therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Levothyroxine Treatment on Clinical Symptoms in Hypothyroid Patients with Chronic Urticaria and Thyroid Autoimmunity
Do Hun Kim, Nam Hee Sung, Ai Young Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(2):199-204. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.2.199.
Reference
-
1. Sabroe RA, Greaves MW. Chronic idiopathic urticaria with functional autoantibodies: 12 years on. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 154:813–819.2. Wedi B. Urticaria. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2008; 6:306–317.
Article3. Ozdemir O. Idiopathic (autoimmune) chronic urticaria. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2006; 27:431–434.
Article4. Mete N, Gülbahar O, Sin A, Kokuludağ A, Sebik F. Kronik idiopatik ürtikerde otolog serum testi. Ege Tıp Dergisi. 2003; 42:25–29.5. George M, Balachandran C, Prabhu S. Chronic idiopathic urticaria: comparison of clinical features with positive autologous serum skin test. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008; 74:105–108.
Article6. Konstantinou GN, Asero R, Maurer M, Sabroe RA, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Grattan CE. EAACI/GA(2)LEN task force consensus report: the autologous serum skin test in urticaria. Allergy. 2009; 64:1256–1268.
Article7. Taskapan O, Kutlu A, Karabudak O. Evaluation of autologous serum skin test results in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria, allergic/non-allergic asthma or rhinitis and healthy people. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008; 33:754–758.
Article8. Guttman-Yassky E, Bergman R, Maor C, Mamorsky M, Pollack S, Shahar E. The autologous serum skin test in a cohort of chronic idiopathic urticaria patients compared to respiratory allergy patients and healthy individuals. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007; 21:35–39.
Article9. Philpott H, Kette F, Hissaria P, Gillis D, Smith W. Chronic urticaria: the autoimmune paradigm. Intern Med J. 2008; 38:852–857.
Article10. Najib U, Sheikh J. The spectrum of chronic urticaria. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009; 30:1–10.
Article11. Zuberbier T, Asero R, Bindslev-Jensen C, Walter Canonica G, Church MK, Giménez-Arnau A, et al. Dermatology Section of the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Global Allergy and Asthma European Network. European Dermatology Forum. World Allergy Organization. EAACI/GA(2)LEN/EDF/WAO guideline: definition, classification and diagnosis of urticaria. Allergy. 2009; 64:1417–1426.
Article12. Khan DA. Chronic urticaria: diagnosis and management. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008; 29:439–446.
Article13. Grattan CEH, Black AK. Urticaria and mastocytosis. In : Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Rook's textbook of dermatology. 7th ed. Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing Inc.;2004. p. 47.1–47.37.14. Al-Hamamy HR, Hameed AF, Abdulhadi AS. Autologous serum skin test as a diagnostic aid in chronic idiopathic urticaria. ISRN Dermatol. 2013; 2013:291524.
Article15. Krupashankar DS, Shashikala K, Madala R. Clinical and investigative assessment of patients with positive versus negative autologous serum skin test: a study of 80 South Indian patients. Indian J Dermatol. 2012; 57:434–438.
Article16. Kocatürk E, Kavala M, Kural E, Sarıgul S, Zındancı I. Autologous serum skin test vs autologous plasma skin test in patients with chronic urticaria: evaluation of reproducibility, sensitivity and specificity and relationship with disease activity, quality of life and anti-thyroid antibodies. Eur J Dermatol. 2011; 21:339–343.
Article17. Metz M, Giménez-Arnau A, Borzova E, Grattan CE, Magerl M, Maurer M. Frequency and clinical implications of skin autoreactivity to serum versus plasma in patients with chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:705–706.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Laboratory Findings and Medication Levels according to Antologous Serum Skin Test Reactivity in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- Autoantibody Against High Affinity IgE Receptor In Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
- A Study of an Autologous Serum Skin Test and Helicobacter pylori Infection in Patients with Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
- Reactivity to Autologous Serum Skin Test and Clinical Features in Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
- A Study on Clinical and Etiological Aspects of Chronic Urticaria by Questionnaire