Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2013 Jul;5(4):245-247. 10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.245.
A Case of Idiopathic Anaphylaxis Followed by Acute Liver Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. allergy@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 2260320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.245
Abstract
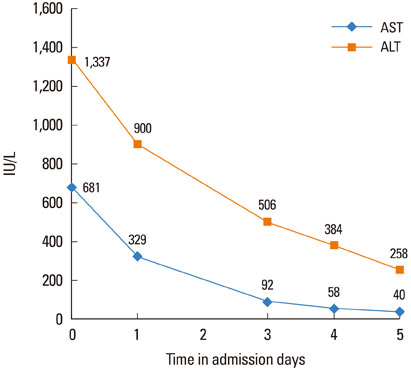
- Idiopathic anaphylaxis is characterized by recurrent anaphylaxis without a known trigger. The coexistence of acute liver injury with idiopathic anaphylaxis is rare, even in cases of severe anaphylaxis such as shock. An unusual case involving repeated episodes of anaphylactic shock accompanied by acute liver injury is described here. A 36-year-old woman who experienced anaphylaxis due to an unknown cause was referred to our hospital because of marked elevations in her liver enzyme levels. After a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of the acute liver injury, viral infection, drug use, and autoimmune hepatitis were excluded. The episodes were accompanied by elevated liver enzymes, which suggested that this was a case of anaphylaxis followed by acute liver injury. The patient will have to use self-injectable epinephrine to prevent future hepatic failure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Favorable outcome of omalizumab treatment in a patient with idiopathic anaphylaxis
Ga-Young Ban, Eun-Mi Yang, Ji-Hye Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Dong-Ho Nahm, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(5):380-383. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.5.380.
Reference
-
1. Greenberger PA. Idiopathic anaphylaxis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007; 27:273–293.2. Mazur N, Patterson R, Perlman D. A case of idiopathic anaphylaxis associated with respiratory infections. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:546–548.3. Lenchner K, Grammer LC. A current review of idiopathic anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 3:305–311.4. Okano A, Hajiro K, Takakuwa H, Nishio A. Acute liver injury that followed food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Intern Med. 1999; 38:650–654.5. Birrer R, Takuda Y, Takara T. Hypoxic hepatopathy: pathophysiology and prognosis. Intern Med. 2007; 46:1063–1070.6. Fuhrmann V, Jäger B, Zubkova A, Drolz A. Hypoxic hepatitis - epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical management. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2010; 122:129–139.7. Fuhrmann V, Kneidinger N, Herkner H, Heinz G, Nikfardjam M, Bojic A, Schellongowski P, Angermayr B, Kitzberger R, Warszawska J, Holzinger U, Schenk P, Madl C. Hypoxic hepatitis: underlying conditions and risk factors for mortality in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2009; 35:1397–1405.8. Li TK. Quantifying the risk for alcohol-use and alcohol-attributable health disorders: present findings and future research needs. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:Suppl 1. S2–S8.9. Zakhari S, Li TK. Determinants of alcohol use and abuse: impact of quantity and frequency patterns on liver disease. Hepatology. 2007; 46:2032–2039.10. Frazier TH, Stocker AM, Kershner NA, Marsano LS, McClain CJ. Treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011; 4:63–81.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of idiopathic anaphylaxis
- A Case of Rifampicin-induced Acute Renal Failure and Anaphylaxis
- A Case of Asymptomatic, Localized, and Idiopathic Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- Severe but reversible acute kidney injury resulting from Amanita punctata poisoning
- Case of Adult-onset Still's Disease with Anaphylatic Shock and Acute Kidney Failure