Korean J Crit Care Med.
2015 Aug;30(3):234-237. 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.234.
Acute Peripheral Arterial Tumorous Embolism after Lung Cancer Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjleedr@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2227657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.234
Abstract
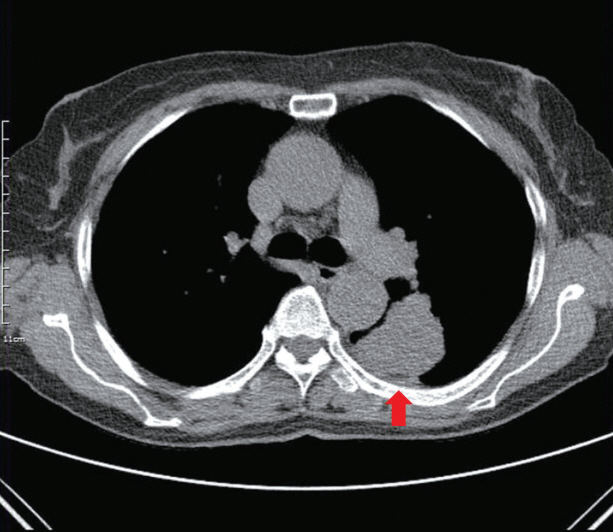
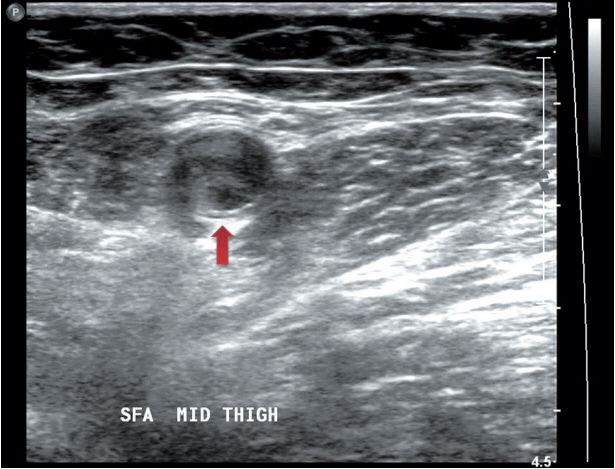
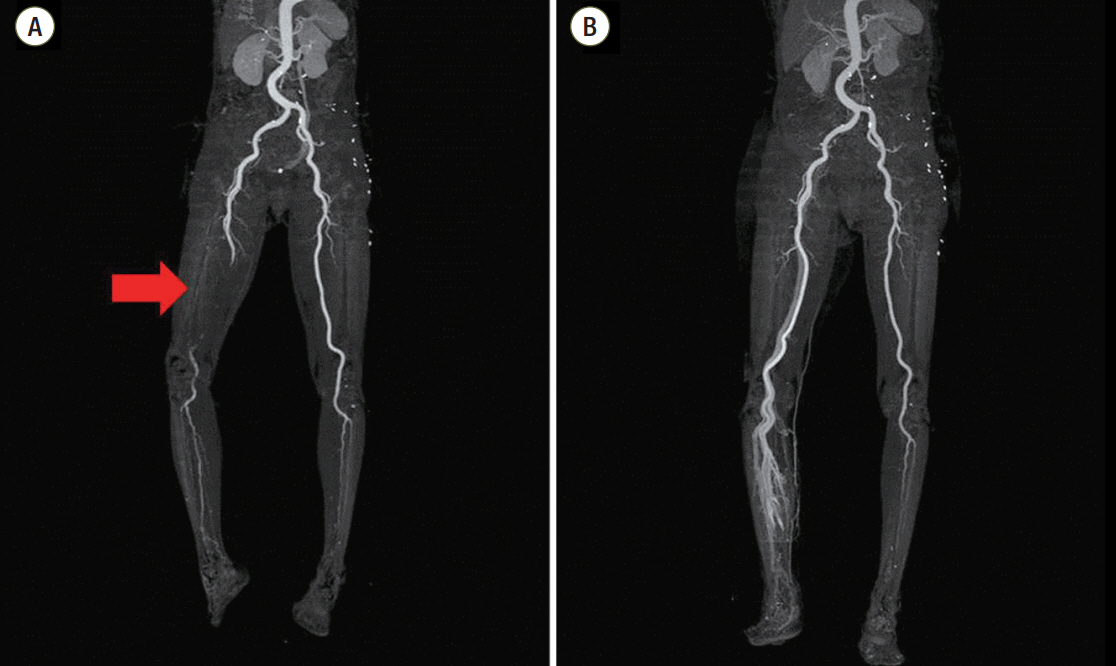
- Systemic tumor embolisms after pulmonary resections for malignancy are rare, but usually severe and sometimes fatal. Here, we report a case of a 70-year-old woman who underwent pulmonary resection for lung cancer and subsequently developed acute arterial occlusion of the lower extremities caused by a tumorous embolus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Morsey H, Aslam M, Standfield N. Tumor embolization causing acute ischemia with sometimes fatal results. Case report and review of literature. Int Angiol. 2004; 23:82–4.2. Whyte RI, Starkey TD, Orringer MB. Tumor emboli from lung neoplasms involving the pulmonary vein. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992; 104:421–5.
Article3. Ouriel K, Veith FJ, Sasahara AA. A comparison of recombinant urokinase with vascular surgery as initial treatment for acute arterial occlusion of the legs. Thrombolysis or Peripheral Arterial Surgery (TOPAS) Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1105–11.4. Tsao JH, Lo HC, How CK, Yen DH, Huang CI. Embolic occlusion of the aorta caused by cardiac myxoma. Resuscitation. 2010; 81:511.
Article5. Xiromeritis N, Klonaris C, Papas S, Valsamis M, Bastounis E. Recurrent peripheral arterial embolism from pulmonary cancer. Case report and review of the literature. Int Angiol. 2000; 19:79–83.6. Marinos T, Bitzikas G, Lymperiadis D, Galanos O. Peripheral tumor emboli to both lower extremity arteries after pneumonectomy for extensive pulmonary cancer. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2004; 45:592–3.7. Busse A. Ueber sarkomatose entartung der myone. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1904; 30:373.8. Groth KE. Tumor embolism of the common femoral artery, treated by embolectomy and heparin. Surgery. 1940; 8:617–32.9. Aylwin JA. Avoidable vascular spread in resection for bronchial carcinoma. Thorax. 1951; 6:250–67.
Article10. O’Connell JB, Quiñones-Baldrich WJ. Proper evaluation and management of acute embolic versus thrombotic limb ischemia. Semin Vasc Surg. 2009; 22:10–6.11. Rolston DM, Saul T, Wong T, Lewiss RE. Bedside ultrasound diagnosis of acute embolic femoral artery occlusion. J Emerg Med. 2013; 45:897–900.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Acute Cerebral Infarction and Peripheral Embolism in a Patient with Cardiac Myxoma
- A Case of Acute Lung Injury Complicated by Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Acute Aortic Thromboses Occurring in Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy
- A Case of Pulmonary Arterial Thrombosis in a Patient with Tuberculous-destroyed Lung and Pulmonary Hypertension
- Respiratory Effects of Acute Coronary Embolism