Korean Circ J.
2009 Apr;39(4):168-170. 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.4.168.
Isolated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-Janus' Faces of Hyperthyroidism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Cardiovascular Center, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. princette@gmail.com
- 2Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiovascular Center, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2225693
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2009.39.4.168
Abstract
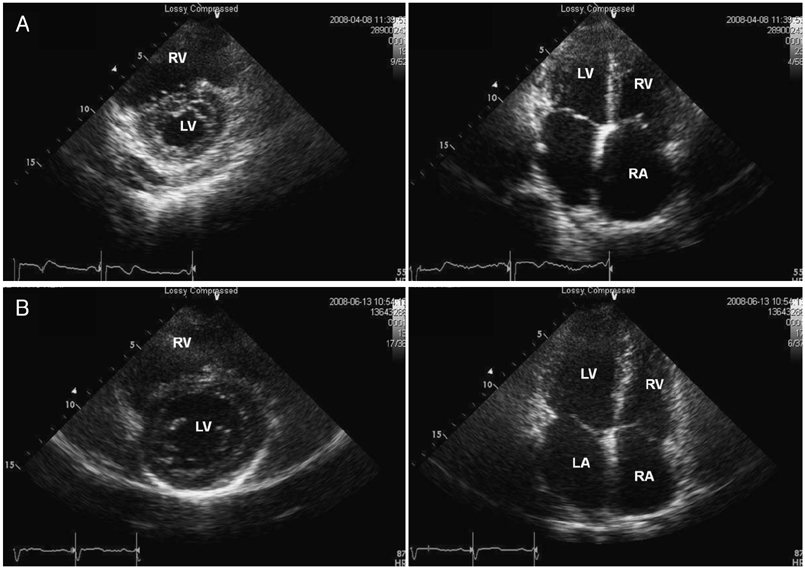
- We describe a 54-year-old woman with isolated pulmonary arterial hypertension accompanied by hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease. Her pulmonary artery hypertension resolved spontaneously after restoration of euthyroidism. This case suggests that hyperthyroidism should be considered a reversible cause of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kahaly GJ, Dillman WH. Thyroid hormone action in the heart. Endocr Rev. 2005. 26:704–728.2. Klein LI, Danzi S. Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. The cardiovascular system in thyrotoxicosis. Werner & Ingbar's The Thyroid: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 2005. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;559–568.3. Soroush-Yari A, Burstein S, Hoo GW, Santiago SM. Pulmonary hypertension in men with thyrotoxicosis. Respiration. 2005. 72:90–94.4. Lozano HF, Sharma CN. Reversible pulmonary hypertension, tricuspid regurgitation and right-sided heart failure associated with hyperthyroidism: case report and review of the literature. Cardiol Rev. 2004. 12:299–305.5. Ismail HM. Reversible pulmonary hypertension and isolated right-sided heart failure associated with hyperthyroidism. J Gen Intern Med. 2007. 22:148–150.6. Ojamaa K, Balkman C, Klein IL. Acute effects of triiodothyronine on arterial smooth muscle cells. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993. 56(1):Suppl. S61–S66.7. Siu CW, Zhang XH, Yung C, Kung AW, Lau CP, Tse HF. Hemodynamic changes in hyperthyroidism-related pulmonary hypertension: a prospective echocardiographic study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 92:1736–1742.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Ascites and Extensive Abdominal Distension Caused by Reversible Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Graves' Disease
- A Case of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated With Hyperthyroidism, Persistent After Euthyroidism Was Obtained
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension
- A Case of Isolated Pulmonary Takayasu's Arteritis Combined with Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Hyperthyroidism