J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Jul;54(7):1097-1103. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.7.1097.
The Surgical Outcome of Intermittent Exotropia with Good Binocular Function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. mychoi@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2217422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.7.1097
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the success rate of surgery and binocular function after surgery in intermittent exotropia with good preoperative binocular function.
METHODS
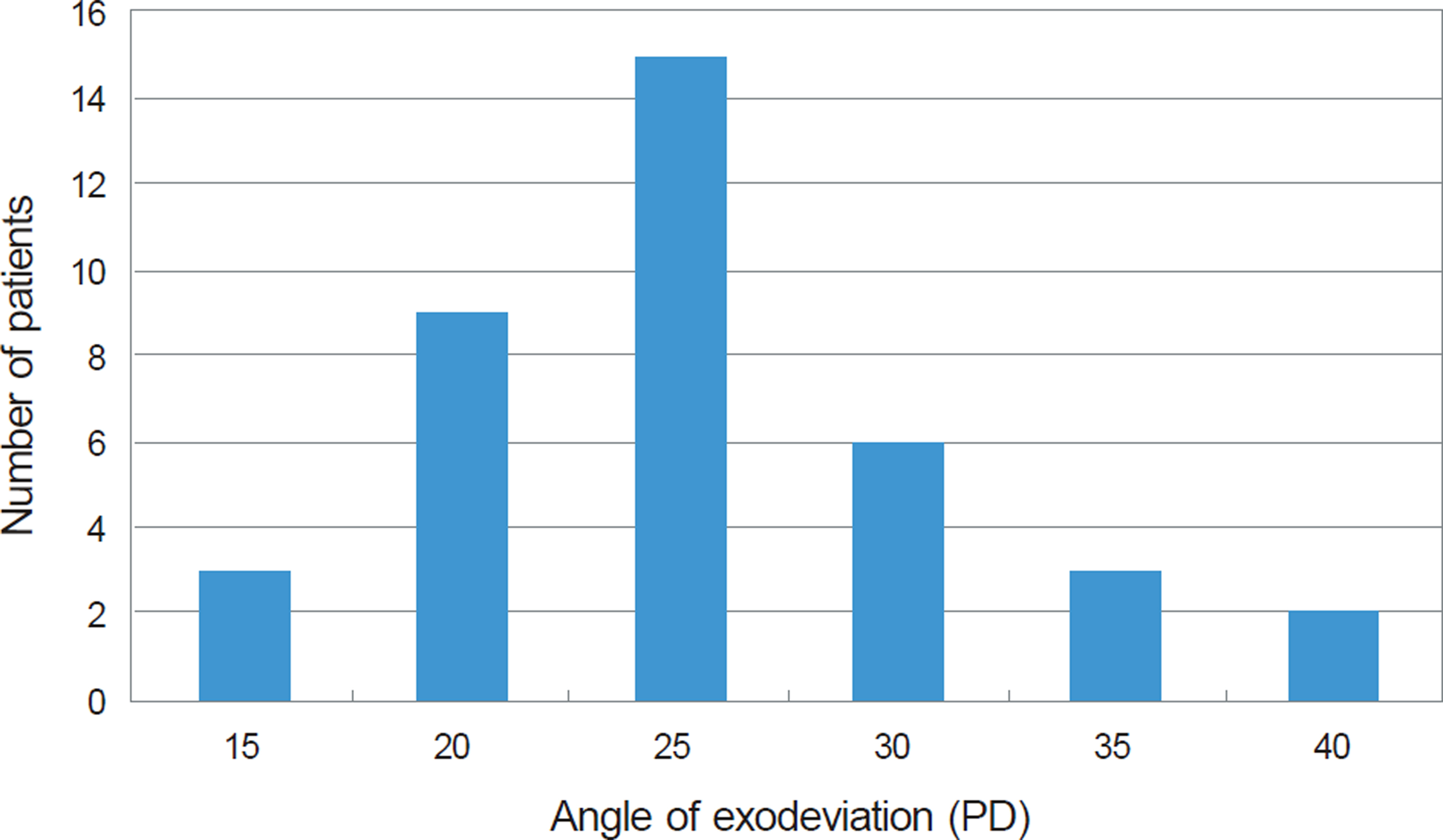
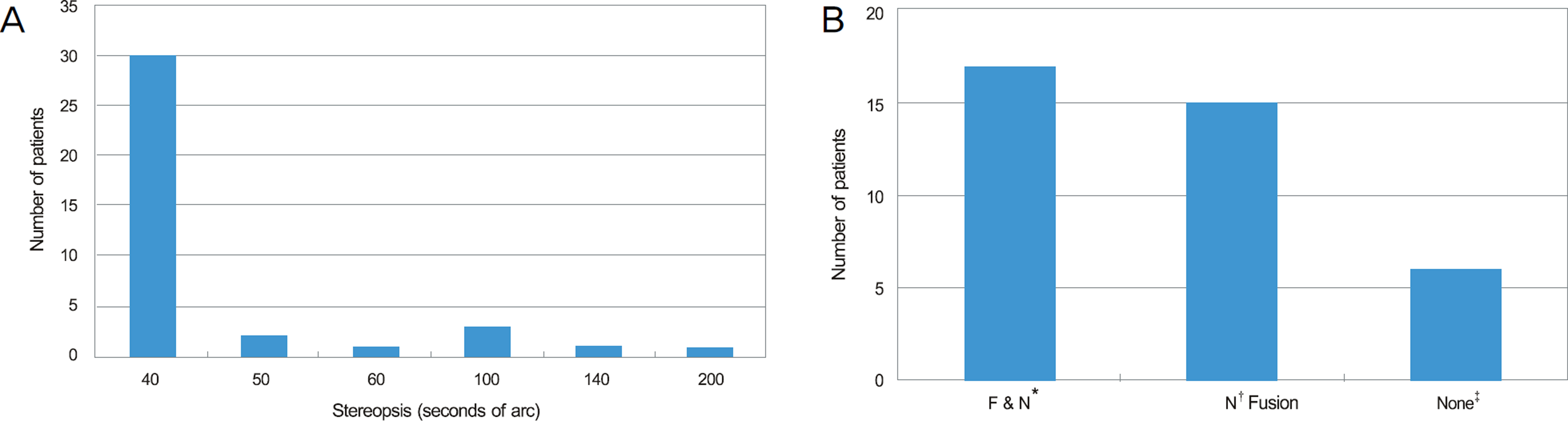
Thirty-eight intermittent exotropia patients who had good stereopsis of 40 seconds according to the Titmus test, showed fusion by Worth-4-dot test preoperatively, and had at least 1 year of postoperative follow-up were included in the present study. The age at operation, angle of exodeviation, visual acuity, stereopsis with Titmus test and fusional status with Worth-4-dot test after surgery were analyzed. A surgical success was defined as postoperative angle of deviation less than 10 prism diopter (PD).
RESULTS
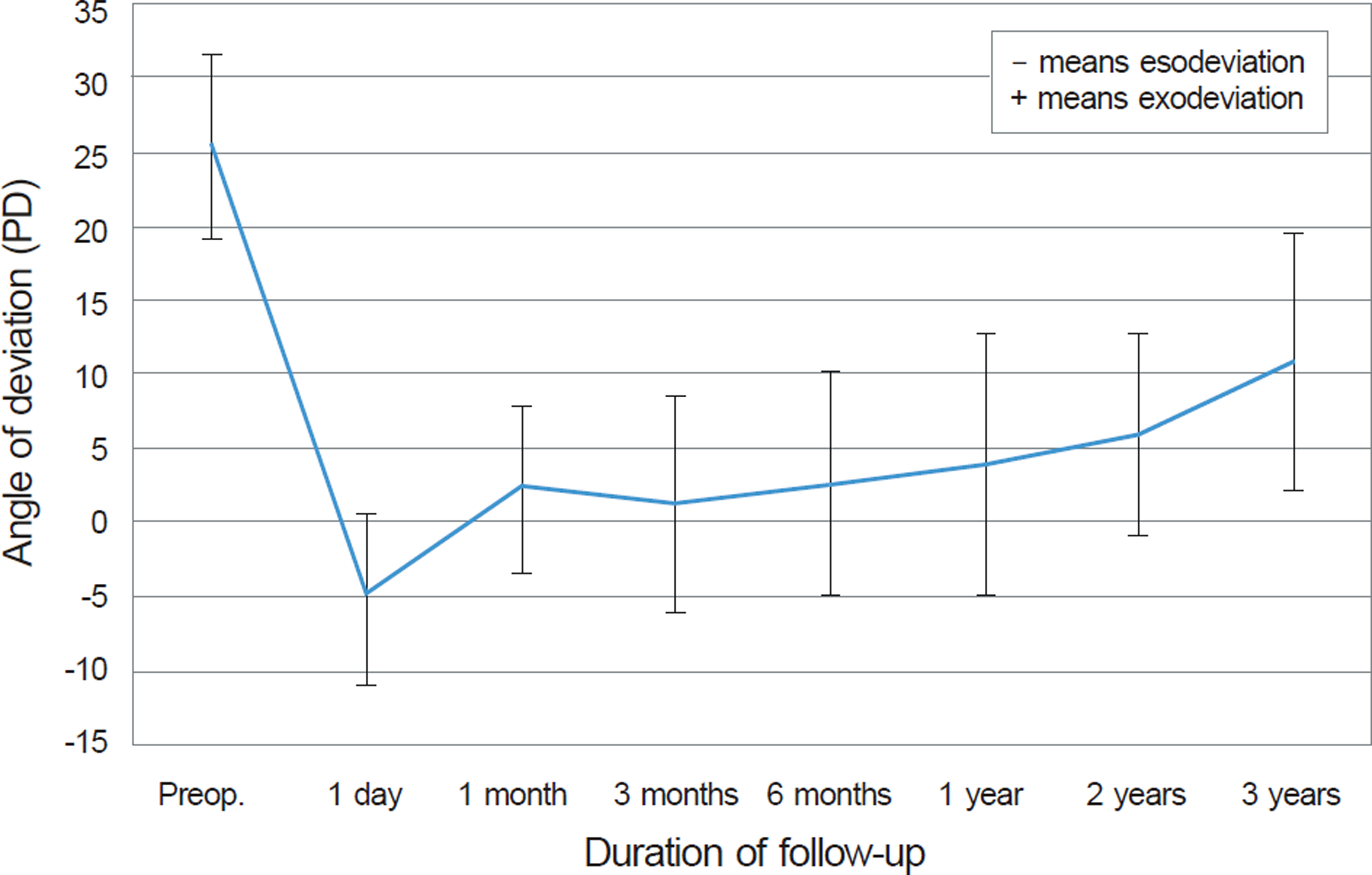
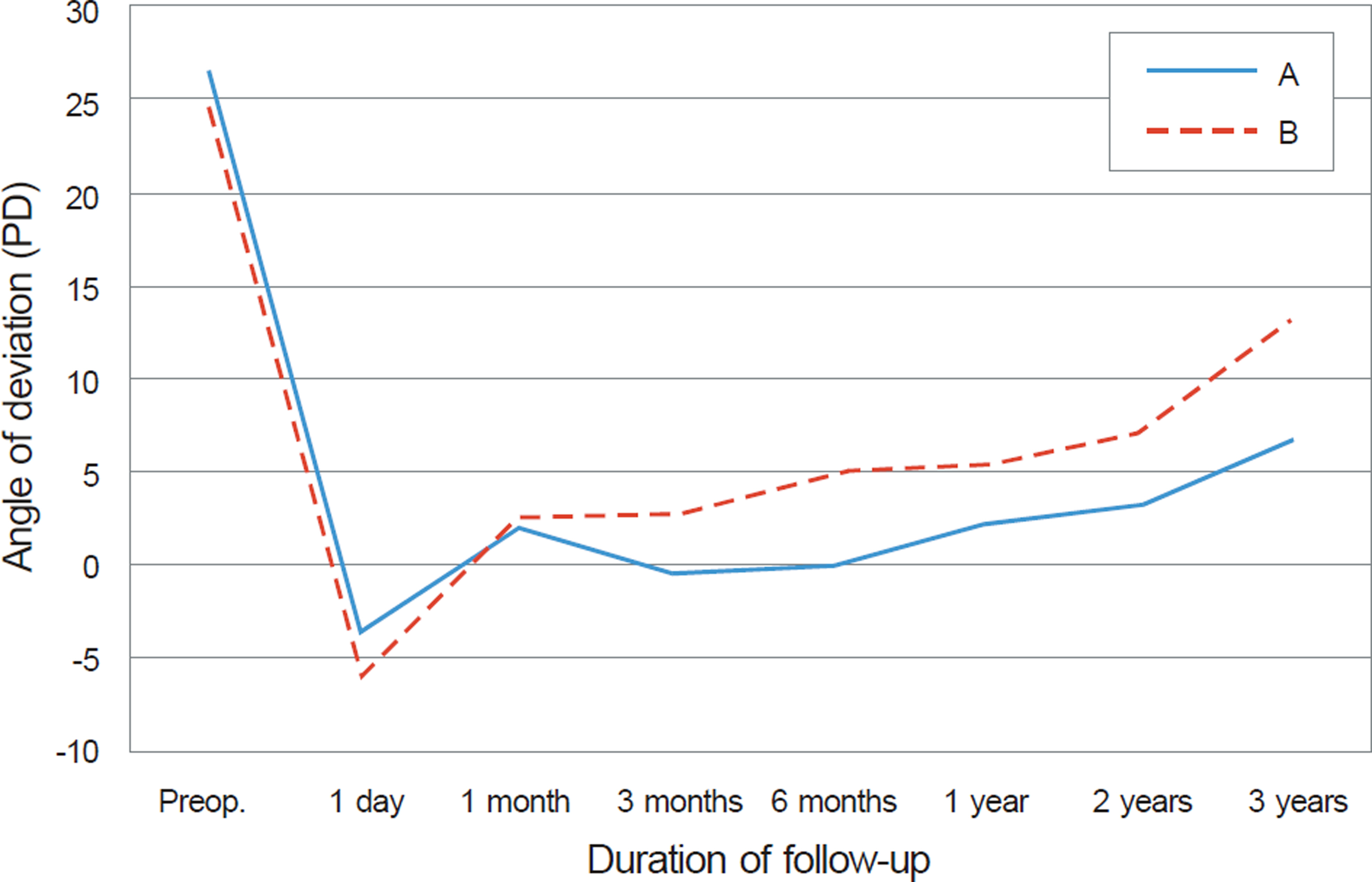
The patient mean age at the time of the operation was 7.9 years. The mean preoperative angle of exodeviation was 25.5 PD at far distance and 27.5 PD at near distance. The mean follow-up time was 22.9 months. The success rate of surgery was 81.6% at 6 months, 68.4% at 1 year and 60.5% on the last visit. Seventeen patients (44.7%) had stereopsis of 40 seconds and showed fusion at far and near distance after surgery. The stereopsis was worse than 100 seconds in 2 patients (5.3%), and fusion was maintained at only near distance in 15 patients (39.5%). In 7 patients (18.4%), the stereopsis decreased to 200 seconds or worse, or there was no fusion after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
The recurrence of exodeviation was a major cause of the surgical failure in the intermittent exotropia with good preoperative binocular function. Moreover, binocular function may decrease postoperatively in intermittent exotropia with good preoperative binocular function, so careful follow-up may be required to maintain this function.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jenkins R. Demographics: geographic variations in the prevalence and management of exotropia. Am Orthopt J. 1992; 42:82–7.
Article2. Figueira EC, Hing S. Intermittent exotropia: comparison of treatments. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:245–51.
Article3. von Noorden GK. Binocular vision and ocular motility: Theory and management of strabismus, 5th ed. St. Louis:: CV Mosby;1996. p. 341–59.4. Kushner BJ, Morton GV. Postoperative binocularity in adults with longstanding strabismus. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:316–9.
Article5. Heo NH, Paik HJ. The relationship between binocular function and the surgical outcome of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1588–93.6. Wright KW, Ryan SJ. Color atlas of ophthalmic surgery: stra-bismus. Philadelphia:: Lippincott;1991. p. 241–3.7. Burian HM. Exodeviation: their classification, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 62:1161–6.8. Burian HM, Franceschetti AT. Evaluation of diagnostic methods for the classification of exodeviations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971; 1:34–41.
Article9. Burian HM, Spivey BE. The surgical management of exodeviations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 59:603–20.10. Shin YJ, Chang BL. The clinical outcome of the consecutive eso-tropia after surgical correction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2085–90.11. Edelman PM, Brown MH, Murphree AL, Wright KW. Consecutive esodeviation··· then what? Am Orthopt J. 1988; 38:111–6.12. Campos EC, von Noorden GK. Binocular vision and ocular mo-tility; Theory and management of strabismus, 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. chap 13–17.13. Suh WJ, Lee UK, Kim MM. Change of postoperative distance ster-eoacuity in intermittent exotropic patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:758–63.14. Lee SY, Kim SJ, Ahn JH, et al. The effects of surgery on binocular function in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3180–6.15. Rutstein RP, Daum KM. Anomalies of binocular vision: Diagnosis and management. 1st ed. St. Louis:: Mosby;1997. p. 111–46.16. Lee SY. Comparison of distance and near stereoacuity in normal and intermittent exotropic children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:624–9.17. Beneish R, Flanders M. The role of stereopsis and early post-operative alignment in long-term surgical results of intermittent exotropia. Can J Ophthalmol. 1994; 29:119–24.18. Gill MK, Drummond GT. Indications and outcomes of strabismus repair in visually mature patients. Can J Ophthalmol. 1997; 32:436–40.19. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Clinical strabismus management: Principles and surgical techniques, 1st ed. Philadelphia:: Saunders;1999. p. 156–68.20. Baker JD, Davies GT. Monofixational intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979; 97:93–5.
Article21. Yildirim C, Mutlu FM, Chen Y, Altinsoy HI. Assessment of central and peripheral fusion and near and distance stereoacuity in inter-mittent exotropic patients before and after strabismus surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:222–30.
Article22. Pratt-Johnson JA, Barlow JM, Tillson G. Early surgery for inter-mittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1977; 84:689–94.23. Hardesty HH, Boynton JR, Keenan JP. Treatment of intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978; 96:268–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relationship between Binocular Function and the Surgical Outcome of Intermittent Exotropia
- Clinical effect of early surgery in infantile exotropia
- Consecutive Cyclic Esotropia Developing After Surgery for Intermittent Exotropia
- The Change of Sensory Binocularity according to the Surgical Results in Intermittent Exotropia
- The Relationship Between Bagolini Test and Other Sensory Tests and Surgical Outcome of Intermittent Exotropia