J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Apr;84(4):256-260. 10.4174/jkss.2013.84.4.256.
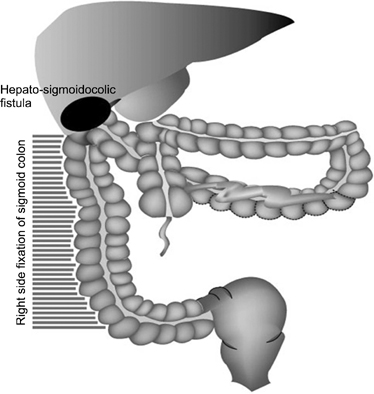
Right side fixation of sigmoid colon with a hepato-sigmoidocolic fistula in patient with hepatocellular carcinoma and midgut malrotation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. kjkim@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2212472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.84.4.256
Abstract
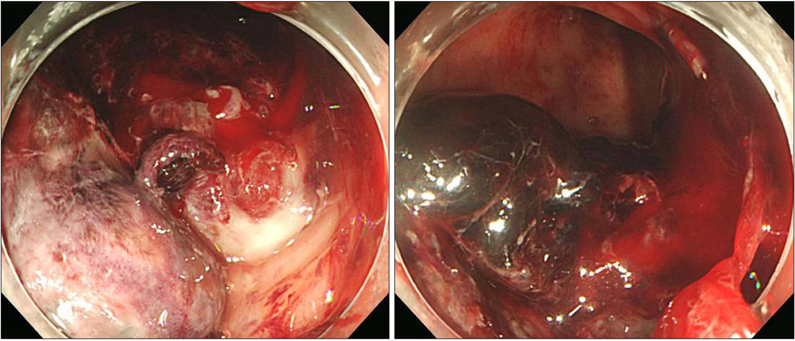
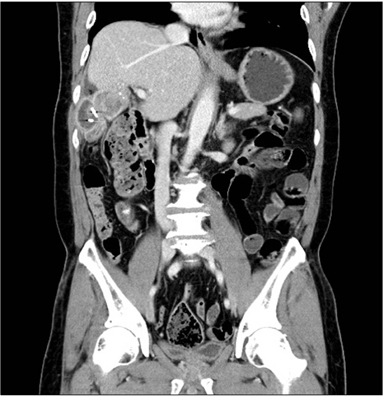
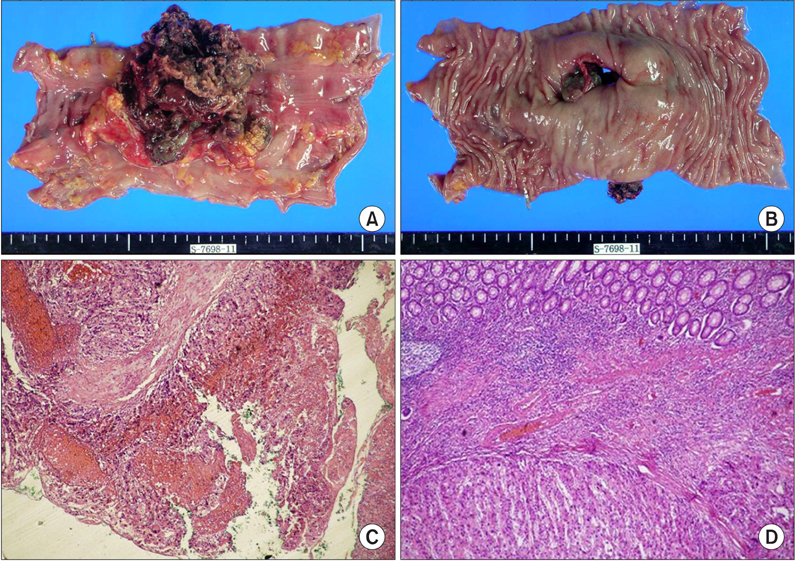
- The location of the sigmoid colon varies within the abdominal cavity, but its mesocolon is fixed to the left side. Right side fixation of the sigmoid colon is a very rare congenital positional anomaly. In addition, it has been reported that hepatocolic fistula is also a very rare disease that may present lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Here, the authors describe a case of a 71-year-old man who underwent surgery for hepato-sigmoidocolic fistula complicated by hepatocellular carcinoma and the right side fixation of the sigmoid colon.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Malas MA, Aslankoc R, Ungor B, Sulak O, Candir O. The development of large intestine during the fetal period. Early Hum Dev. 2004. 78:1–13.2. Fiorella DJ, Donnelly LF. Frequency of right lower quadrant position of the sigmoid colon in infants and young children. Radiology. 2001. 219:91–94.3. Berkelhammer C, Janarthan B, Bhagavan M, Schreiber S. Hepatocolic fistula and lower GI bleeding in hepatoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996. 91:2625–2626.4. Ortiz H, Carmona JA, Perez-Cabanas I. Colohepatic fistula due to hydatid disease. Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988. 31:546–547.5. Morris DL, Smith WD, Alexander-Williams J. Colohepatic fistula due to hydatid disease. World J Surg. 1983. 7:797–798.6. Bhattachayya B. Three cases of right-sided sigmoid colon. J Anat. 1926. 60(Pt 2):229–232.7. Wondrak E. Right-side fixation of the sigmoid colon. Rozhl Chir. 1957. 36:158–160.8. Schulz E, Bettenhaeuser K. On the roentgenologic differentiation of anomalies of the intestinal location (case of a fixed right location of an elongated sigmoid due to malrotation I). Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Nuklearmed. 1963. 99:801–804.9. Komiyama M, Shimada Y. A case of a right-sided sigmoid colon. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1991. 66:537–540.10. Singh Kalra TM, Mangla JC, Schwartz S, Lee JC. Hepatoma presenting as lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 1977. 67:485–488.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Left Side Appendicitis with Abscess Caused by Midgut Malrotation Mimicked by Complicated Diverticulitis of Sigmoid Colon: A Case Report
- A Case of Combined Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt, Midgut Malrotation, and Renal Rotational Anomaly in an Adult Patient
- Appendico-Sigmoid Fistula Due to Appendicitis
- Colouterine Fistula Caused by Diverticulitis of the Sigmoid Colon
- Malrotation complicating Midgut Volvulus: Ultrasonographic Finding