J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Nov;58(5):476-478. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.476.
Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis with Long Cord Sign
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea. yschung@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2191415
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.476
Abstract
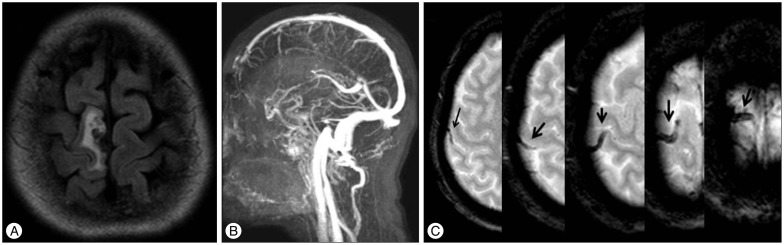
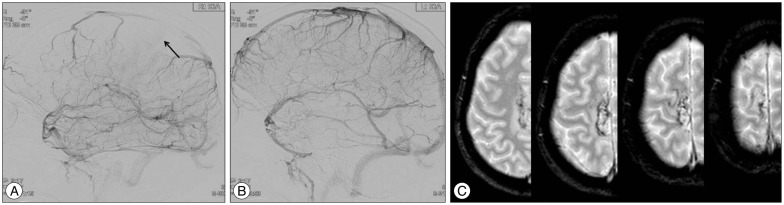
- Isolated cortical vein thrombosis (ICVT) is a rare disease, accounting for less than 1% of strokes. A 46-year-old woman presented with progressive left side weakness. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging with T2*-gradient echo (T2*-GE) sequence showed long cord sign at the right frontal cortex. The patient was treated with low molecular weight heparin, followed by oral warfarin for 6 months. The 3-month follow-up MR imaging showed recanalization of the previously thrombosed cortical vein. She was completely recovered without neurological deficits after 6 months. This provides that MR imaging with T2*-GE sequence can help to diagnosis the ICVT and outcomes of the ICVT are generally favorable.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn TB, Roh JK. A case of cortical vein thrombosis with the cord sign. Arch Neurol. 2003; 60:1314–1316. PMID: 12975301.
Article2. Boukobza M, Crassard I, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. MR imaging features of isolated cortical vein thrombosis : diagnosis and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:344–348. PMID: 19095790.
Article3. Coutinho JM, Gerritsma JJ, Zuurbier SM, Stam J. Isolated cortical vein thrombosis : systematic review of case reports and case series. Stroke. 2014; 45:1836–1838. PMID: 24743438.4. Derdeyn CP, Powers WJ. Isolated cortical venous thrombosis and ulcerative colitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988; 19:488–490. PMID: 9541304.5. Jacobs K, Moulin T, Bogousslavsky J, Woimant F, Dehaene I, Tatu L, et al. The stroke syndrome of cortical vein thrombosis. Neurology. 1996; 47:376–382. PMID: 8757007.
Article6. Kitamura Y, Hara K, Tsunematsu K. Isolated superficial sylvian vein thrombosis with long cord sign : case report and review of the literature. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014; 54:253–259. PMID: 24097090.
Article7. Mouraux A, Gille M, Dorban S, Peeters A. Cortical venous thrombosis after lumbar puncture. J Neurol. 2002; 249:1313–1315. PMID: 12242562.
Article8. Park DS, Moon CT, Chun YI, Koh YC, Kim HY, Roh HG. Clinical characteristics of cerebral venous thrombosis in a single center in Korea. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014; 56:289–294. PMID: 25371777.
Article9. Rathakrishnan R, Sharma VK, Luen TH, Chan BP. The clinico-radiological spectrum of isolated cortical vein thrombosis. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18:1408–1411. PMID: 21764320.
Article10. Sharma VK, Teoh HL. Isolated cortical vein thrombosis - the cord sign. J Radiol Case Rep. 2009; 3:21–24. PMID: 22470649.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concurrent Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolism as An Initial Presentation of Protein S Deficiency
- A Case of Cortical Vein Thrombosis in Wegener's Granulomatosis
- Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging for the Detection of Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Isolated Splenic Vein Thrombosis Associated with Acute Pancreatitis
- Deep Venous Thrombosis and Heterotopic Ossification in the Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury