J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Dec;56(6):496-499. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.6.496.
Use of the Sundt Clip Graft in a Previously Coiled Internal Carotid Artery Blister-Like Aneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Cheju Halla Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Daegu Catholic University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. fhjhcho@gmail.com
- KMID: 2191142
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.6.496
Abstract
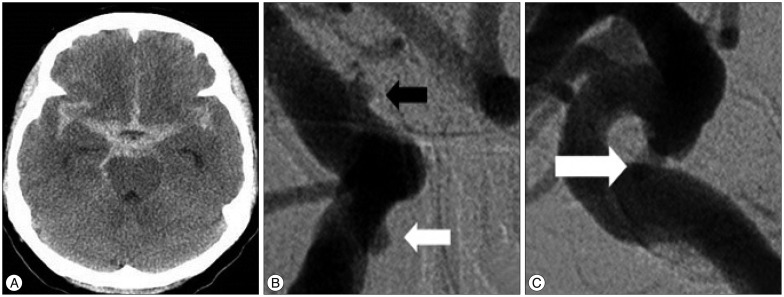
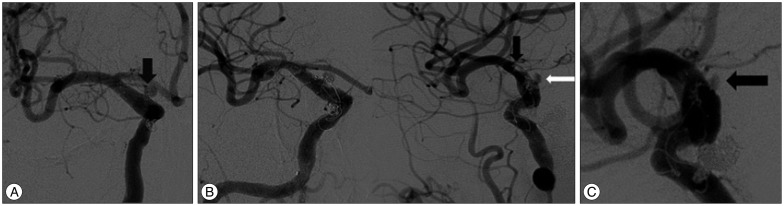
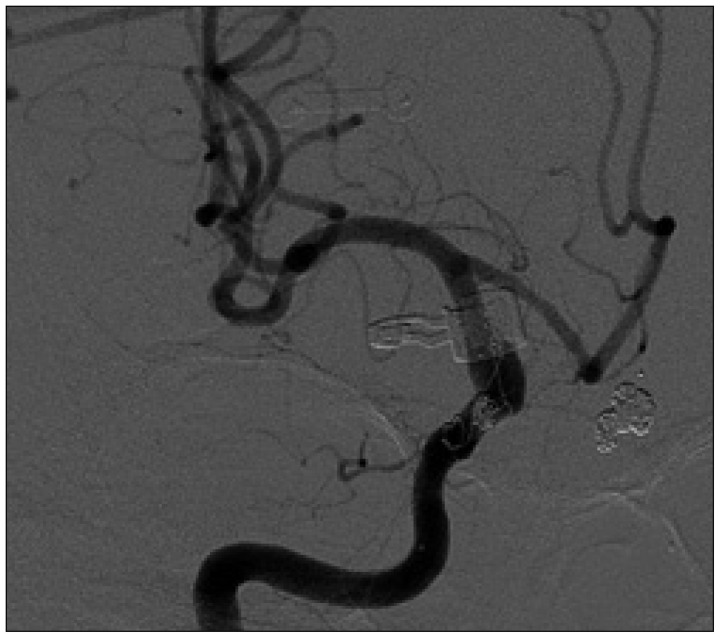
- Owing to the focal wall defect covered with thin fibrous tissues, an aneurysm arising from the dorsal wall of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is difficult to manage either surgically or endovascularly and is often associated with high morbidity and mortality. Unfortunately, the definitive treatment modality of such highly risky aneurysm has not yet been demonstrated. Upon encountering the complex intracranial pathophysiology of such a highly precarious aneurysm, a neurosurgeon would be faced with a challenge to decide on an optimal approach. This is a case of multiple paraclinoid aneurysms including the ICA dorsal wall aneurysm, presented with spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. With respect to treatment, direct clipping with a Sundt graft clip was performed after multiple endovascular interventions had failed. This surgical approach can be a treatment modality for a blood blister-like aneurysm after failed endovascular intervention(s).
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Blood Blister Like-aneurysm: Usefulness of Sundt Clip
Tae Joon Park, Ki Hong Kim, Jae Hoon Cho
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2017;19(3):171-183. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2017.19.3.171.
Reference
-
1. Abe M, Tabuchi K, Yokoyama H, Uchino A. Blood blisterlike aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 1998; 89:419–424. PMID: 9724116.
Article2. Başkaya MK, Ahmed AS, Ateş O, Niemann D. Surgical treatment of blood blister-like aneurysms of the supraclinoid internal carotid artery with extracranial-intracranial bypass and trapping. Neurosurg Focus. 2008; 24:E13. PMID: 18275289.
Article3. Cho TG, Hwang SN, Nam TK, Park SW. Salvage surgical treatment for failed endovascular procedure of a blood blister-like aneurysm. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2012; 14:99–103. PMID: 23210036.
Article4. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Deshmukh VR, Woo HH, Rasmussen PA, Masaryk TJ, et al. Endovascular reconstruction with the Neuroform stent as monotherapy for the treatment of uncoilable intradural pseudoaneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59:291–300. discussion 291-300. PMID: 16823325.
Article5. Garrett M, Spetzler RF. Surgical treatment of blister-like aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2012; 77:76–77. PMID: 22405389.
Article6. Gaughen JR Jr, Hasan D, Dumont AS, Jensen ME, McKenzie J, Evans AJ. The efficacy of endovascular stenting in the treatment of supraclinoid internal carotid artery blister aneurysms using a stent-in-stent technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:1132–1138. PMID: 20150303.
Article7. Joo SP, Kim TS, Moon KS, Kwak HJ, Lee JK, Kim JH, et al. Arterial suturing followed by clip reinforcement with circumferential wrapping for blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Surg Neurol. 2006; 66:424–428. discussion 428-429. PMID: 17015131.
Article8. Kawashima A, Okada Y, Kawamata T, Onda H, Kubo O, Hori T. Successful treatment of a blood blister-like aneurysm of the internal carotid artery by trapping with a high-flow bypass. J Clin Neurosci. 2008; 15:797–800. PMID: 18406147.
Article9. Kim BM, Chung EC, Park SI, Choi CS, Won YS. Treatment of blood blister-like aneurysm of the internal carotid artery with stent-assisted coil embolization followed by stent-within-a-stent technique. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2007; 107:1211–1213. PMID: 18077959.
Article10. Kim YG, Kim YD. Direct repair of a dorsal wall aneurysm on supraclinoid internal carotid artery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2005; 37:160–162.11. Lee CC, Hsieh TC, Wang YC, Lo YL, Lee ST, Yang TC. Ruptured symptomatic internal carotid artery dorsal wall aneurysm with rapid configurational change. Clinical experience and management outcome: an original article. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:1277–1284. PMID: 20831774.
Article12. Ogawa A, Suzuki M, Ogasawara K. Aneurysms at nonbranching sites in the surpaclinoid portion of the internal carotid artery : internal carotid artery trunk aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:578–583. discussion 583-586. PMID: 10981744.
Article13. Park JH, Park IS, Han DH, Kim SH, Oh CW, Kim JE, et al. Endovascular treatment of blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 2007; 106:812–819. PMID: 17542524.
Article14. Park PJ, Meyer FB. The Sundt clip graft. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66(6 Suppl Operative):300–305. discussion 305. PMID: 20489520.
Article15. Shigeta H, Kyoshima K, Nakagawa F, Kobayashi S. Dorsal internal carotid artery aneurysms with special reference to angiographic presentation and surgical management. Acta Neurochir(Wien). 1992; 119:42–48. PMID: 1481751.
Article16. Sim SY, Shin YS, Cho KG, Kim SY, Kim SH, Ahn YH, et al. Blood blister-like aneurysms at nonbranching sites of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:400–405. PMID: 16961134.
Article17. Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Matsumoto S, Yamashita M, Nagatomi H, Mori H. Ruptured "blisterlike" aneurysm with a pseudoaneurysm formation requiring delayed intervention with endovascular coil embolization. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101:159–162. PMID: 15255268.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Sundt Encircling Clip as a Vascular Rescue: A Case Report and a Review of Repair Methods for Arterial Tearing
- Direct Repair of a Dorsal Wall Aneurysm on Supraclinoid Internal Carotid Artery
- Salvage Surgical Treatment for Failed Endovascular Procedure of a Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm
- The Blood Blister Like-aneurysm: Usefulness of Sundt Clip
- Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm with Rupture Point Close to Origin of Anterior Choroidal Artery