J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Feb;53(2):132-135. 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.2.132.
Usefulness of Ultrasound for Detecting Suspected Peripheral Nerve Lesions in Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy : Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Sannae Wooridle Neurosurgical Clinic, Daejeon, Korea. brainspine@daum.net
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei Orthopedic Clinic, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Madi Neurosurgical Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Chungdam Madi Neurosurgical Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2190694
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.2.132
Abstract
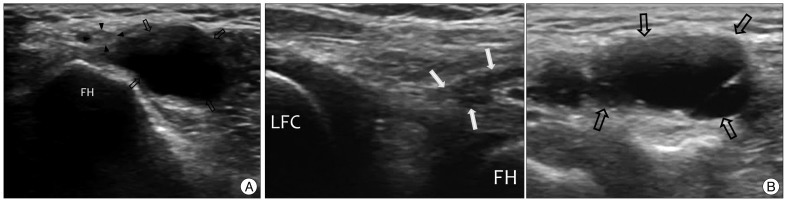
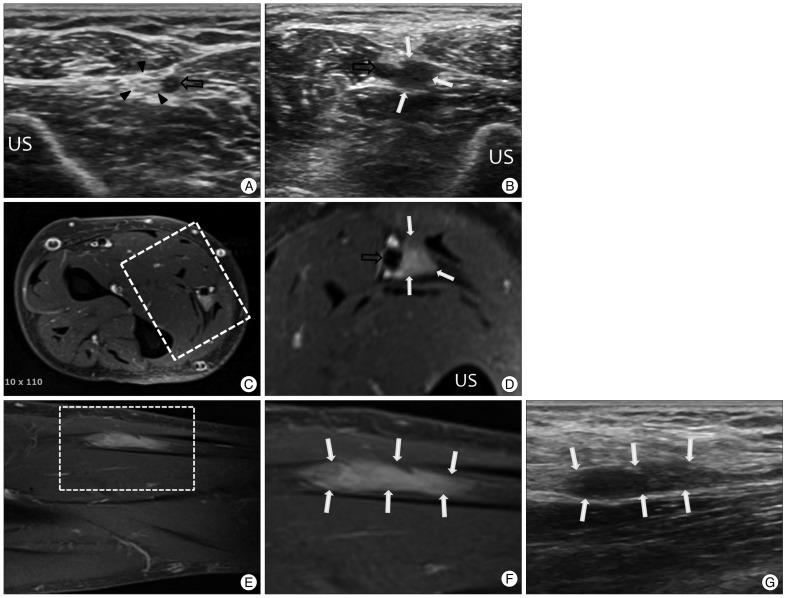
- Ultrasound scanning of a peripheral nerve along its expected course is a simple and useful method for determining the cause of peripheral neuropathy. We present 3 cases of peripheral neuropathy in which the pathology was detected by simple ultrasound scanning of the affected nerve. There were 2 cases of entrapment neuropathy due to mucoid cyst and 1 case of nerve sheath tumor. All lesions were visualized by simple ultrasound scanning of the involved peripheral nerve. Our results suggest that if a lesion affecting the peripheral nerve is suspected after history and physical examination or electrophysiologic studies, ultrasound scanning of the peripheral nerve of interest throughout its course is very helpful for identifying the causative lesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ultrasound Diagnosis of Double Crush Syndrome of the Ulnar Nerve by the Anconeus Epitrochlearis and a Ganglion
Sang-Uk Lee, Min-Wook Kim, Jae Min Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(1):75-77. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.1.75.
Reference
-
1. Beekman R, van den Berg LH, Franssen H, Visser LH, van Asseldonk JT, Wokke JH. Ultrasonography shows extensive nerve enlargements in multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurology. 2005; 65:305–307. PMID: 16043806.
Article2. Beekman R, Visser LH. High-resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system -- a review of the literature. Eur J Neurol. 2004; 11:305–314. PMID: 15142223.
Article3. Bianchi S, Martinoli C. Ultrasound of the Musculoskeletal System. 2007. Germany: Springer;p. 100–102.4. Cheng JW, Tang SF, Yu TY, Chou SW, Wong AM, Tsai WC. Sonographic features of soft tissue tumors in the hand and forearm. Chang Gung Med J. 2007; 30:547–554. PMID: 18350738.5. Du R, Auguste KI, Chin CT, Engstrom JW, Weinstein PR. Magnetic resonance neurography for the evaluation of peripheral nerve, brachial plexus, and nerve root disorders. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112:362–371. PMID: 19663545.
Article6. Fowler JR, Gaughan JP, Ilyas AM. The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome : a meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469:1089–1094. PMID: 20963527.
Article7. Iannicelli E, Almberger M, Chianta GA, Salvini V, Rossi G, Monacelli G, et al. High resolution ultrasonography in the diagnosis of the carpal tunnel syndrome. Radiol Med. 2005; 110:623–629. PMID: 16437047.8. Koenig RW, Pedro MT, Heinen CP, Schmidt T, Richter HP, Antoniadis G, et al. High-resolution ultrasonography in evaluating peripheral nerve entrapment and trauma. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 26:E13. PMID: 19435442.
Article9. Lee HY, Lee JC, Kim IM, Lee CY, Son EI, Kim DW, et al. The value of MRI in diagnosis of peripheral nerve disorders. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2001; 30:1120–1126.10. Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Gandolfo N, Valle M, Simonetti S, Derchi LE. US of nerve entrapments in osteofibrous tunnels of the upper and lower limbs. Radiographics. 2000; 20 Spec No:S199–S213. discussion S213-S217. PMID: 11046171.
Article11. Mhoon JT, Juel VC, Hobson-Webb LD. Median nerve ultrasound as a screening tool in carpal tunnel syndrome : correlation of cross-sectional area measures with electrodiagnostic abnormality. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:871–878. PMID: 23041984.12. Ng ES, Vijayan J, Therimadasamy AK, Tan TC, Chan YC, Lim A, et al. High resolution ultrasonography in the diagnosis of ulnar nerve lesions with particular reference to post-traumatic lesions and sites outside the elbow. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011; 122:188–189. PMID: 20541969.
Article13. Volpe A, Rossato G, Bottanelli M, Marchetta A, Caramaschi P, Bambara LM, et al. Ultrasound evaluation of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow : correlation with electrophysiological studies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:1098–1101. PMID: 19567661.
Article14. Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Neuromuscular ultrasound : emerging from the twilight. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 43:777–779. PMID: 21488061.
Article15. Wilder-Smith EP. Nerve Ultrasound : ready for clinical practice? Neurol Asia. 2012; 17:1–4.16. Wu S, Liu G, Tu R. Value of ultrasonography in neurilemmoma diagnosis : the role of round shape morphology. Med Ultrason. 2012; 14:192–196. PMID: 22957323.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to "Usefulness of Ultrasound for Detecting Suspected Peripheral Nerve Lesions in Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy : Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature" by Jung JH, et al. (J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 132-135, 2013)
- Diagnostic usefulness and limitations of the sural nerve biopsy
- Ultrasonographic Findings in Peripheral Neuropathy
- Diagnostic Usefulness of Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Anatomical Localization of Peripheral Nerve Injury: Detailed Lesion Localization Using Neuromuscular Ultrasound in a Patient with Traumatic Ulnar Nerve Injury at the Hand
- A beginner’s guide to peripheral nerve ultrasound