J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Jun;43(3):359-365. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.3.359.
Syndesmosis Injury Associated with the Weber Type B Lateral Malleolar Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea. soonlee@kumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2186453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.3.359
Abstract
-
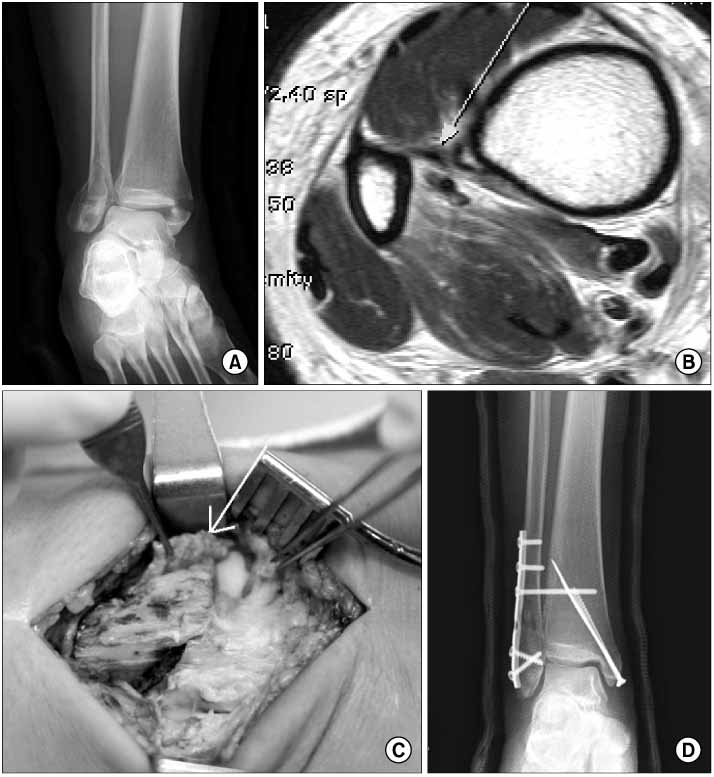
PURPOSE: We evaluated the syndesmosis instability associated with Weber type B lateral malleolar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighty one Weber type B lateral malleolar fractures were evaluated and classified according to the radiologic criteria. Syndesmosis instability was checked with a hook test during operation. The radiological and clinical results were assessed.
RESULTS
Twenty two cases were associated with a widening of the distal tibiofibular distance. Sixteen (73%) had syndesmosis instability confirmed with a hook test and were fixed with a syndesmotic screw. Eight (66%) out of 12 Wagstaffe fractures were fixed with a syndesmotic screw due to the instability. The distal tibiofibular distance was 7.4+/-2.4 mm, 4.6+/-1.9 mm and 4.9+/-1.9 mm preoperatively, postoperatively, and at the final follow up, respectively. All cases achieved union and good clinical results with more than 85 on the AOFAS score were obtained.
CONCLUSION
Weber type B lateral malleolar fractures can be associated with a syndesmosis injury. An intraoperative hook test should be carried out for accurate diagnosis. Considerable attention needs to be paid to Wagsteffe fractures, because of the high probability of combining syndesmosis instability.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amendola A. Controversies in diagnosis and management of syndesmosis injuries of the ankle. Foot Ankle. 1992. 13:44–50.
Article2. Boden SD, Labropoulos PA, McCowin P, Lestini WF, Hurwitz SR. Mechanical considerations for the syndesmosis screw. A cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:1548–1555.
Article3. Bonnin JG. Injury to the ligaments of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965. 47:609–611.
Article4. Cedell CA. Supination-outward rotation injuries of the ankle. A clinical and roentgenological study with special reference to the operative treatment. Acta Orthop Scand. 1967. Suppl 110. 3+.
Article5. Gardner MJ, Demetrakopoulos D, Briggs SM, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. The ability of the Lauge-Hansen classification to predict ligament injury and mechanism in ankle fractures: an MRI study. J Orthop Trauma. 2006. 20:267–272.
Article6. Jenkinson RJ, Sanders DW, Macleod MD, Domonkos A, Lydestadt J. Intraoperative diagnosis of syndesmosis injuries in external rotation ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:604–609.
Article7. Joy G, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP Jr. Precise evaluation of the reduction of severe ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974. 56:979–993.
Article8. Katznelson A, Lin E, Militiano J. Ruptures of the ligaments about the tibio-fibular syndesmosis. Injury. 1983. 15:170–172.
Article9. Kennedy JG, Soffe KE, Dalla Vedova P, et al. Evaluation of the syndesmotic screw in low Weber C ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:359–366.
Article10. Kerr R, Forrester DM, Kingston S. Magnetic resonance imaging of foot and ankle trauma. Orthop Clin North Am. 1990. 21:591–601.
Article11. Kim SK, Oh JK. One or two lag screws for fixation of Danis-Weber type B fractures of the ankle. J Trauma. 1999. 46:1039–1044.
Article12. Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994. 15:349–353.
Article13. Klossner O. Late results of operative and non-operative treatment of severe ankle fractures. A clinical study. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1962. Suppl 293. 1–93.14. Lee HS, Park SS, Kim JW, et al. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography for acute tear of tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2004. 8:1–6.15. Leeds HC, Ehrlich MG. Instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis after bimalleolar and trimalleolar ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:490–503.
Article16. Nielson JH, Sallis JG, Potter HG, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. Correlation of interosseous membrane tears to the level of the fibular fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:68–74.
Article17. Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Reed SC. Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: diagnosis and treatment by arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy. 1994. 10:561–568.
Article18. Ostrum RF, De Meo P, Subramanian R. A critical analysis of the anterior-posterior radiographic anatomy of the ankle syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 1995. 16:128–131.
Article19. Park JW, Kim SK, Hong JS, Park JH. Anterior tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture in weber type B lateral malleolar fracture. J Trauma. 2002. 52:655–659.
Article20. Pettrone FA, Gail M, Pee D, Fitzpatrick T, Van Herpe LB. Quantitative criteria for prediction of the results after displaced fracture of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983. 65:667–677.
Article21. Quigley TB. A simple aid to the reduction of abduction-external rotation fractures of the ankle. Am J Surg. 1959. 97:488–493.
Article22. Wagstaffe W. An unusual form of fracture of the fibula. St Thomas Hosp Rep. 1875. 6:43.23. Weening B, Bhandari M. Predictors of functional outcome following transsyndesmotic screw fixation of ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:102–108.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Ankle Lateral Malleolar Fractures Accompanying Osteoporosis using Lag Screw
- Comparison of Antiglide Plate Fixation and Lateral Plate Fixation for Danis-Weber Type B Isolated Lateral Malleolar Fractures
- Comparative Study for the Fixation Method in the Danis-Weber Type B Lateral Malleolar Fractures: An Antiglide Plate Fixation versus A Lateral Plate Fixation
- A Clinical Study of Fractures of Fibular with Diastasis
- Heterotopic Ossification of Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis after Ankle Fractures