J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2012 Aug;47(4):316-320. 10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.4.316.
Recurrent Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of the Median Nerve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. cusem9@daum.net
- KMID: 2185381
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.4.316
Abstract
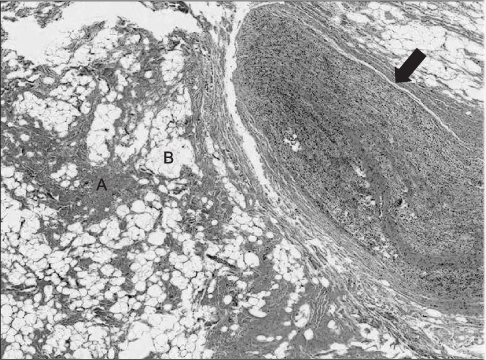
- Lipofibromatous hamartoma is a rare tumor of the peripheral nerves which is characterised by an excessive infiltration of the epineurium and perineurium by fibroadipose tissue and very few cases have been described and reported in the literature. Surgical treatments of lipofibromatous hamartoma include partial excision, debulking operation, nerve decompression and so on. We report a case of recurrent lipofibromatous hamartoma of the median nerve that partial excision was done previously but causing secondary carpal tunnel syndrome and a review of the literature regarding the etiology, pathogenesis and surgical management of lipofibromatous hamartoma.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Change of Preoperative and Postoperaive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of the Median Nerve
Sang Su Choi, Hong Je Kang, Jeong Woo Kim, Kwang Mi Kim
J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2013;18(4):161-166. doi: 10.12790/jkssh.2013.18.4.161.
Reference
-
1. Guthikonda M, Rengachary SS, Balko MG, van Loveren H. Lipofibromatous hamartoma of the median nerve: case report with magnetic resonance imaging correlation. Neurosurgery. 1994. 35:127–132.2. Al-Jabri T, Garg S, Mani GV. Lipofibromatous hamartoma of the median nerve. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010. 5:71.
Article3. Nilsson J, Sandberg K, Søe Nielsen N, Dahlin LB. Magnetic resonance imaging of peripheral nerve tumours in the up-per extremity. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2009. 43:153–159.
Article4. Johnson RJ, Bonfiglio M. Lipofibromatous hamartoma of the median nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51:984–990.
Article5. Houpt P, Storm van, Storm van Leeuwen JB. Intraneural lipofibroma of the median nerve. J Hand Surg Am. 1989. 14:706–709.
Article6. Marom EM, Helms CA. Fibrolipomatous hamartoma: pathognomonic on MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 1999. 28:260–264.
Article7. Warhold LG, Urban MA, Bora FW Jr, Brooks JS, Peters SB. Lipofibromatous hamartomas of the median nerve. J Hand Surg Am. 1993. 18:1032–1037.
Article8. Clavijo-Alvarez JA, Price M, Stofman GM. Preserved neurologic function following intraneural fascicular dissection and nerve graft for digital and median nerve lipofibromatous hamartoma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010. 125:120e–122e.
Article9. Louis DS, Hankin FM, Greene TL, Dick HM. Lipofibromas of the median nerve: long-term follow-up of four cases. . J Hand Surg Am. 1985. 10:403–408.
Article10. Paletta FX, Senay LC Jr. Lipofibromatous hamartoma of median nerve and ulnar nerve: surgical treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981. 68:915–921.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lipofibromatous Hamartoma on the Median nerve: A Case Report
- Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of Median Nerve with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Case Report
- The Change of Preoperative and Postoperaive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of the Median Nerve
- Symmetric Lipofibromatous Hamartoma Affecting Digital Nerves
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Caused by Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of the Median Nerve